mirror of
https://github.com/GerbilSoft/rom-properties.git
synced 2025-06-18 11:35:38 -04:00
[libfmt] Add an internal copy of libfmt-11.1.2.
Currently used as a header-only build. Will eventually be changed to build a DLL for Windows and Mac OS X. Other changes needed to get the Windows version to build with libfmt: Add #include <fmt/xchar.h> to some files for full wchar_t support in libfmt. Otherwise, errors like this appear: src\amiibo-data\amiiboc.cpp(175,8): error C2665: 'fmt::v11::print': no overloaded function could convert all the argument types extlib\libfmt\include\fmt\base.h(2925,17): message : could be 'void fmt::v11::print<TCHAR*&>(FILE *,fmt::v11::fstring<TCHAR *&>,TCHAR *&)' src\amiibo-data\amiiboc.cpp(175,8): message : 'void fmt::v11::print<TCHAR*&>(FILE *,fmt::v11::fstring<TCHAR *&>,TCHAR *&)': cannot convert argument 2 from 'wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING' to 'fmt::v11::fstring<TCHAR *&>' src\amiibo-data\amiiboc.cpp(175,22): message : No user-defined-conversion operator available that can perform this conversion, or the operator cannot be called extlib\libfmt\include\fmt\base.h(2908,17): message : or 'void fmt::v11::print<wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING,TCHAR*&>(fmt::v11::fstring<wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING,TCHAR *&>,wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING &&,TCHAR *&)' src\amiibo-data\amiiboc.cpp(175,8): message : 'void fmt::v11::print<wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING,TCHAR*&>(fmt::v11::fstring<wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING,TCHAR *&>,wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING &&,TCHAR *&)': cannot convert argument 1 from 'FILE *' to 'fmt::v11::fstring<wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING,TCHAR *&>' src\amiibo-data\amiiboc.cpp(175,14): message : No constructor could take the source type, or constructor overload resolution was ambiguous src\amiibo-data\amiiboc.cpp(175,8): message : while trying to match the argument list '(FILE *, wmain::<lambda_1>::()::FMT_COMPILE_STRING, TCHAR *)' [build.vc17_64\src\amiibo-data\amiiboc.vcxproj] Files modified for xchar.h: - amiibo-data/amiiboc.cpp - libromdata/stdafx.h (needed by WiiUPackage) - libromdata/tests/RomHeaderTest.cpp NOTE: Only included on Windows. xchar.h was added in libfmt-8.0.0, which was first added (in Ubuntu LTS releases) in Ubuntu 20.04. It's not needed on Linux, anyway. New option USE_INTERNAL_FMT to force the use of the internal copy of libfmt on Linux, for testing purposes. (...and also for Ubuntu 16.04) - TODO: Maybe use it on 18.04, etc. for improved performance?
This commit is contained in:
parent
3d5d77b634
commit
fa932de93f
@ -338,6 +338,9 @@ ENDIF(USE_INTERNAL_XML)
|
||||
IF(BUILD_TESTING)
|
||||
SET(EXTLIB_BUILD "${EXTLIB_BUILD}- Google Test\n")
|
||||
ENDIF(BUILD_TESTING)
|
||||
IF(USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
SET(EXTLIB_BUILD "${EXTLIB_BUILD}- libfmt\n")
|
||||
ENDIF(USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
|
||||
IF(BUILD_TRACKER_EXTRACTOR)
|
||||
SET(TRACKER_API_DISPLAY "${TRACKER_INSTALL_API_VERSION}")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Check for libfmt.
|
||||
# If libfmt isn't found, extlib/libfmt/ will be used instead.
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: Add internal libfmt.
|
||||
FIND_PACKAGE(Fmt REQUIRED)
|
||||
SET(Fmt_LIBRARY "fmt::fmt")
|
||||
|
||||
IF(0)
|
||||
IF(NOT USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
IF(Fmt_LIBRARY MATCHES "^fmt$" OR Fmt_LIBRARY MATCHES "^fmt")
|
||||
# Internal libfmt was previously in use.
|
||||
@ -20,6 +15,7 @@ IF(NOT USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
IF(Fmt_FOUND)
|
||||
# Found system libfmt.
|
||||
SET(HAVE_Fmt 1)
|
||||
SET(Fmt_LIBRARY "fmt::fmt")
|
||||
ELSE()
|
||||
# System libfmt was not found.
|
||||
MESSAGE(STATUS "Using the internal copy of libfmt since a system version was not found.")
|
||||
@ -33,16 +29,16 @@ IF(USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
# Using the internal libfmt library.
|
||||
SET(Fmt_FOUND 1)
|
||||
SET(HAVE_Fmt 1)
|
||||
SET(Fmt_VERSION 11.1.1 CACHE INTERNAL "libfmt version" FORCE)
|
||||
SET(Fmt_VERSION 11.1.2 CACHE INTERNAL "libfmt version" FORCE)
|
||||
# FIXME: When was it changed from LIBRARY to LIBRARIES?
|
||||
IF(WIN32 OR APPLE)
|
||||
IF(0 AND (WIN32 OR APPLE)) # TODO: Use DLLs on Windows and Mac OS X.
|
||||
# Using DLLs on Windows and Mac OS X.
|
||||
SET(USE_INTERNAL_FMT_DLL ON)
|
||||
SET(Fmt_LIBRARY fmt CACHE INTERNAL "libfmt library" FORCE)
|
||||
SET(Fmt_LIBRARY fmt::fmt CACHE INTERNAL "libfmt library" FORCE)
|
||||
ELSE()
|
||||
# Using static linking on other systems.
|
||||
SET(USE_INTERNAL_FMT_DLL OFF)
|
||||
SET(Fmt_LIBRARY fmt CACHE INTERNAL "libfmt library" FORCE)
|
||||
SET(Fmt_LIBRARY fmt::fmt-header-only CACHE INTERNAL "libfmt library" FORCE)
|
||||
ENDIF()
|
||||
SET(Fmt_LIBRARIES ${Fmt_LIBRARY} CACHE INTERNAL "libfmt libraries" FORCE)
|
||||
# FIXME: When was it changed from DIR to DIRS?
|
||||
@ -51,4 +47,4 @@ IF(USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
ELSE(USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
SET(USE_INTERNAL_FMT_DLL OFF)
|
||||
ENDIF(USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
ENDIF(0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ ENDIF()
|
||||
|
||||
OPTION(BUILD_CLI "Build the `rpcli` command line program." ON)
|
||||
|
||||
# ZLIB, libpng, XML, zstd
|
||||
# ZLIB, libpng, XML, zstd, libfmt
|
||||
# Internal versions are always used on Windows.
|
||||
OPTION(ENABLE_XML "Enable XML parsing for e.g. Windows manifests." ON)
|
||||
OPTION(ENABLE_ZSTD "Enable ZSTD decompression. (Required for some unit tests.)" ON)
|
||||
@ -52,6 +52,7 @@ IF(WIN32)
|
||||
SET(USE_INTERNAL_ZSTD ${ENABLE_ZSTD})
|
||||
SET(USE_INTERNAL_LZ4 ${ENABLE_LZ4})
|
||||
SET(USE_INTERNAL_LZO ${ENABLE_LZO})
|
||||
SET(USE_INTERNAL_FMT ON)
|
||||
ELSE(WIN32)
|
||||
OPTION(USE_INTERNAL_ZLIB "Use the internal copy of zlib." OFF)
|
||||
OPTION(USE_INTERNAL_PNG "Use the internal copy of libpng." OFF)
|
||||
@ -59,6 +60,7 @@ ELSE(WIN32)
|
||||
OPTION(USE_INTERNAL_ZSTD "Use the internal copy of zstd." OFF)
|
||||
OPTION(USE_INTERNAL_LZ4 "Use the internal copy of LZ4." OFF)
|
||||
OPTION(USE_INTERNAL_LZO "Use the internal copy of LZO." OFF)
|
||||
OPTION(USE_INTERNAL_FMT "Use the internal copy of libfmt." OFF)
|
||||
ENDIF()
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: If APNG export is added, verify that system libpng
|
||||
|
||||
26
extlib/CMakeLists.txt
vendored
26
extlib/CMakeLists.txt
vendored
@ -413,3 +413,29 @@ ENDIF(NOT HAVE_WCWIDTH)
|
||||
# MicroTAR (for libromdata tests)
|
||||
ADD_SUBDIRECTORY(microtar)
|
||||
SET_EXTLIB_PROPERTIES(microtar)
|
||||
|
||||
IF(USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
# Use the internal copy of libfmt.
|
||||
# TODO: Build DLLs on Windows and Mac OS X.
|
||||
# For now, a header-only build will be used.
|
||||
SET(SKIP_INSTALL_LIBRARIES ON)
|
||||
SET(SKIP_INSTALL_ALL ON)
|
||||
SET(BUILD_SHARED_LIBS OFF)
|
||||
SET(BUILD_STATIC_LIBS ON)
|
||||
|
||||
SET(FMT_PEDANTIC OFF)
|
||||
SET(FMT_WERROR OFF)
|
||||
|
||||
SET(FMT_DOC OFF)
|
||||
SET(FMT_INSTALL OFF) # TODO: Enable for DLL builds?
|
||||
SET(FMT_TEST OFF)
|
||||
SET(FMT_CUDA_TEST OFF)
|
||||
SET(FMT_OS ON)
|
||||
SET(FMT_MODULE OFF)
|
||||
SET(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS OFF)
|
||||
SET(FMT_UNICODE ON)
|
||||
|
||||
ADD_SUBDIRECTORY(libfmt)
|
||||
SET_EXTLIB_PROPERTIES(fmt)
|
||||
SET_EXTLIB_PROPERTIES(fmt-header-only)
|
||||
ENDIF(USE_INTERNAL_FMT)
|
||||
|
||||
14
extlib/libfmt/.clang-format
vendored
Normal file
14
extlib/libfmt/.clang-format
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
# Run manually to reformat a file:
|
||||
# clang-format -i --style=file <file>
|
||||
Language: Cpp
|
||||
BasedOnStyle: Google
|
||||
IndentPPDirectives: AfterHash
|
||||
IndentCaseLabels: false
|
||||
AlwaysBreakTemplateDeclarations: false
|
||||
DerivePointerAlignment: false
|
||||
AllowShortCaseLabelsOnASingleLine: true
|
||||
AlignConsecutiveShortCaseStatements:
|
||||
Enabled: true
|
||||
AcrossEmptyLines: true
|
||||
AcrossComments: true
|
||||
AlignCaseColons: false
|
||||
531
extlib/libfmt/CMakeLists.txt
vendored
Normal file
531
extlib/libfmt/CMakeLists.txt
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,531 @@
|
||||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8...3.28)
|
||||
|
||||
# Fallback for using newer policies on CMake <3.12.
|
||||
if (${CMAKE_VERSION} VERSION_LESS 3.12)
|
||||
cmake_policy(VERSION ${CMAKE_MAJOR_VERSION}.${CMAKE_MINOR_VERSION})
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Determine if fmt is built as a subproject (using add_subdirectory)
|
||||
# or if it is the master project.
|
||||
if (NOT DEFINED FMT_MASTER_PROJECT)
|
||||
set(FMT_MASTER_PROJECT OFF)
|
||||
if (CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR STREQUAL CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR)
|
||||
set(FMT_MASTER_PROJECT ON)
|
||||
message(STATUS "CMake version: ${CMAKE_VERSION}")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Joins arguments and places the results in ${result_var}.
|
||||
function(join result_var)
|
||||
set(result "")
|
||||
foreach (arg ${ARGN})
|
||||
set(result "${result}${arg}")
|
||||
endforeach ()
|
||||
set(${result_var} "${result}" PARENT_SCOPE)
|
||||
endfunction()
|
||||
|
||||
# DEPRECATED! Should be merged into add_module_library.
|
||||
function(enable_module target)
|
||||
if (MSVC)
|
||||
set(BMI ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${target}.ifc)
|
||||
target_compile_options(${target}
|
||||
PRIVATE /interface /ifcOutput ${BMI}
|
||||
INTERFACE /reference fmt=${BMI})
|
||||
set_target_properties(${target} PROPERTIES ADDITIONAL_CLEAN_FILES ${BMI})
|
||||
set_source_files_properties(${BMI} PROPERTIES GENERATED ON)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
endfunction()
|
||||
|
||||
set(FMT_USE_CMAKE_MODULES FALSE)
|
||||
if (CMAKE_VERSION VERSION_GREATER_EQUAL 3.28 AND
|
||||
CMAKE_GENERATOR STREQUAL "Ninja")
|
||||
set(FMT_USE_CMAKE_MODULES TRUE)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Adds a library compiled with C++20 module support.
|
||||
# `enabled` is a CMake variables that specifies if modules are enabled.
|
||||
# If modules are disabled `add_module_library` falls back to creating a
|
||||
# non-modular library.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Usage:
|
||||
# add_module_library(<name> [sources...] FALLBACK [sources...] [IF enabled])
|
||||
function(add_module_library name)
|
||||
cmake_parse_arguments(AML "" "IF" "FALLBACK" ${ARGN})
|
||||
set(sources ${AML_UNPARSED_ARGUMENTS})
|
||||
|
||||
add_library(${name})
|
||||
set_target_properties(${name} PROPERTIES LINKER_LANGUAGE CXX)
|
||||
|
||||
if (NOT ${${AML_IF}})
|
||||
# Create a non-modular library.
|
||||
target_sources(${name} PRIVATE ${AML_FALLBACK})
|
||||
set_target_properties(${name} PROPERTIES CXX_SCAN_FOR_MODULES OFF)
|
||||
return()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Modules require C++20.
|
||||
target_compile_features(${name} PUBLIC cxx_std_20)
|
||||
if (CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX)
|
||||
target_compile_options(${name} PUBLIC -fmodules-ts)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(${name} PRIVATE FMT_MODULE)
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_USE_CMAKE_MODULES)
|
||||
target_sources(${name} PUBLIC FILE_SET fmt TYPE CXX_MODULES
|
||||
FILES ${sources})
|
||||
else()
|
||||
# `std` is affected by CMake options and may be higher than C++20.
|
||||
get_target_property(std ${name} CXX_STANDARD)
|
||||
|
||||
if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
|
||||
set(pcms)
|
||||
foreach (src ${sources})
|
||||
get_filename_component(pcm ${src} NAME_WE)
|
||||
set(pcm ${pcm}.pcm)
|
||||
|
||||
# Propagate -fmodule-file=*.pcm to targets that link with this library.
|
||||
target_compile_options(
|
||||
${name} PUBLIC -fmodule-file=${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${pcm})
|
||||
|
||||
# Use an absolute path to prevent target_link_libraries prepending -l
|
||||
# to it.
|
||||
set(pcms ${pcms} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${pcm})
|
||||
add_custom_command(
|
||||
OUTPUT ${pcm}
|
||||
COMMAND ${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER}
|
||||
-std=c++${std} -x c++-module --precompile -c
|
||||
-o ${pcm} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/${src}
|
||||
"-I$<JOIN:$<TARGET_PROPERTY:${name},INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES>,;-I>"
|
||||
# Required by the -I generator expression above.
|
||||
COMMAND_EXPAND_LISTS
|
||||
DEPENDS ${src})
|
||||
endforeach ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Add .pcm files as sources to make sure they are built before the library.
|
||||
set(sources)
|
||||
foreach (pcm ${pcms})
|
||||
get_filename_component(pcm_we ${pcm} NAME_WE)
|
||||
set(obj ${pcm_we}.o)
|
||||
# Use an absolute path to prevent target_link_libraries prepending -l.
|
||||
set(sources ${sources} ${pcm} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/${obj})
|
||||
add_custom_command(
|
||||
OUTPUT ${obj}
|
||||
COMMAND ${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER} $<TARGET_PROPERTY:${name},COMPILE_OPTIONS>
|
||||
-c -o ${obj} ${pcm}
|
||||
DEPENDS ${pcm})
|
||||
endforeach ()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
target_sources(${name} PRIVATE ${sources})
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endfunction()
|
||||
|
||||
include(CMakeParseArguments)
|
||||
|
||||
# Sets a cache variable with a docstring joined from multiple arguments:
|
||||
# set(<variable> <value>... CACHE <type> <docstring>...)
|
||||
# This allows splitting a long docstring for readability.
|
||||
function(set_verbose)
|
||||
# cmake_parse_arguments is broken in CMake 3.4 (cannot parse CACHE) so use
|
||||
# list instead.
|
||||
list(GET ARGN 0 var)
|
||||
list(REMOVE_AT ARGN 0)
|
||||
list(GET ARGN 0 val)
|
||||
list(REMOVE_AT ARGN 0)
|
||||
list(REMOVE_AT ARGN 0)
|
||||
list(GET ARGN 0 type)
|
||||
list(REMOVE_AT ARGN 0)
|
||||
join(doc ${ARGN})
|
||||
set(${var} ${val} CACHE ${type} ${doc})
|
||||
endfunction()
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the default CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE to Release.
|
||||
# This should be done before the project command since the latter can set
|
||||
# CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE itself (it does so for nmake).
|
||||
if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE)
|
||||
set_verbose(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release CACHE STRING
|
||||
"Choose the type of build, options are: None(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS or "
|
||||
"CMAKE_C_FLAGS used) Debug Release RelWithDebInfo MinSizeRel.")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
project(FMT CXX)
|
||||
include(GNUInstallDirs)
|
||||
set_verbose(FMT_INC_DIR ${CMAKE_INSTALL_INCLUDEDIR} CACHE STRING
|
||||
"Installation directory for include files, a relative path that "
|
||||
"will be joined with ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX} or an absolute path.")
|
||||
|
||||
option(FMT_PEDANTIC "Enable extra warnings and expensive tests." OFF)
|
||||
option(FMT_WERROR "Halt the compilation with an error on compiler warnings."
|
||||
OFF)
|
||||
|
||||
# Options that control generation of various targets.
|
||||
option(FMT_DOC "Generate the doc target." ${FMT_MASTER_PROJECT})
|
||||
option(FMT_INSTALL "Generate the install target." ON)
|
||||
option(FMT_TEST "Generate the test target." ${FMT_MASTER_PROJECT})
|
||||
option(FMT_FUZZ "Generate the fuzz target." OFF)
|
||||
option(FMT_CUDA_TEST "Generate the cuda-test target." OFF)
|
||||
option(FMT_OS "Include OS-specific APIs." ON)
|
||||
option(FMT_MODULE "Build a module instead of a traditional library." OFF)
|
||||
option(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS "Expose headers with marking them as system." OFF)
|
||||
option(FMT_UNICODE "Enable Unicode support." ON)
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_TEST AND FMT_MODULE)
|
||||
# The tests require {fmt} to be compiled as traditional library
|
||||
message(STATUS "Testing is incompatible with build mode 'module'.")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
set(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE "")
|
||||
if (FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS)
|
||||
set(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE SYSTEM)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
if (CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME STREQUAL "MSDOS")
|
||||
set(FMT_TEST OFF)
|
||||
message(STATUS "MSDOS is incompatible with gtest")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get version from base.h
|
||||
file(READ include/fmt/base.h base_h)
|
||||
if (NOT base_h MATCHES "FMT_VERSION ([0-9]+)([0-9][0-9])([0-9][0-9])")
|
||||
message(FATAL_ERROR "Cannot get FMT_VERSION from base.h.")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
# Use math to skip leading zeros if any.
|
||||
math(EXPR CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MAJOR ${CMAKE_MATCH_1})
|
||||
math(EXPR CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MINOR ${CMAKE_MATCH_2})
|
||||
math(EXPR CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_PATCH ${CMAKE_MATCH_3})
|
||||
join(FMT_VERSION ${CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MAJOR}.${CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MINOR}.
|
||||
${CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_PATCH})
|
||||
message(STATUS "{fmt} version: ${FMT_VERSION}")
|
||||
|
||||
message(STATUS "Build type: ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}")
|
||||
|
||||
if (NOT CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY)
|
||||
set(CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/bin)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
set(CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${CMAKE_MODULE_PATH}
|
||||
"${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/support/cmake")
|
||||
|
||||
include(CheckCXXCompilerFlag)
|
||||
include(JoinPaths)
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND NOT DEFINED CMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET)
|
||||
set_verbose(CMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET hidden CACHE STRING
|
||||
"Preset for the export of private symbols")
|
||||
set_property(CACHE CMAKE_CXX_VISIBILITY_PRESET PROPERTY STRINGS
|
||||
hidden default)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND NOT DEFINED CMAKE_VISIBILITY_INLINES_HIDDEN)
|
||||
set_verbose(CMAKE_VISIBILITY_INLINES_HIDDEN ON CACHE BOOL
|
||||
"Whether to add a compile flag to hide symbols of inline functions")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "GNU")
|
||||
set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS -pedantic-errors -Wall -Wextra -pedantic
|
||||
-Wold-style-cast -Wundef
|
||||
-Wredundant-decls -Wwrite-strings -Wpointer-arith
|
||||
-Wcast-qual -Wformat=2 -Wmissing-include-dirs
|
||||
-Wcast-align
|
||||
-Wctor-dtor-privacy -Wdisabled-optimization
|
||||
-Winvalid-pch -Woverloaded-virtual
|
||||
-Wconversion -Wundef
|
||||
-Wno-ctor-dtor-privacy -Wno-format-nonliteral)
|
||||
if (NOT CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 4.6)
|
||||
set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}
|
||||
-Wno-dangling-else -Wno-unused-local-typedefs)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
if (NOT CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 5.0)
|
||||
set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} -Wdouble-promotion
|
||||
-Wtrampolines -Wzero-as-null-pointer-constant -Wuseless-cast
|
||||
-Wvector-operation-performance -Wsized-deallocation -Wshadow)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
if (NOT CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 6.0)
|
||||
set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} -Wshift-overflow=2
|
||||
-Wduplicated-cond)
|
||||
# Workaround for GCC regression
|
||||
# [12/13/14/15 regression] New (since gcc 12) false positive null-dereference in vector.resize
|
||||
# https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=108860
|
||||
if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 12.0)
|
||||
set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS} -Wnull-dereference)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
set(WERROR_FLAG -Werror)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
|
||||
set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS -Wall -Wextra -pedantic -Wconversion -Wundef
|
||||
-Wdeprecated -Wweak-vtables -Wshadow
|
||||
-Wno-gnu-zero-variadic-macro-arguments)
|
||||
check_cxx_compiler_flag(-Wzero-as-null-pointer-constant HAS_NULLPTR_WARNING)
|
||||
if (HAS_NULLPTR_WARNING)
|
||||
set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS}
|
||||
-Wzero-as-null-pointer-constant)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
set(WERROR_FLAG -Werror)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (MSVC)
|
||||
set(PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS /W3)
|
||||
set(WERROR_FLAG /WX)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND CMAKE_GENERATOR MATCHES "Visual Studio")
|
||||
# If Microsoft SDK is installed create script run-msbuild.bat that
|
||||
# calls SetEnv.cmd to set up build environment and runs msbuild.
|
||||
# It is useful when building Visual Studio projects with the SDK
|
||||
# toolchain rather than Visual Studio.
|
||||
include(FindSetEnv)
|
||||
if (WINSDK_SETENV)
|
||||
set(MSBUILD_SETUP "call \"${WINSDK_SETENV}\"")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
# Set FrameworkPathOverride to get rid of MSB3644 warnings.
|
||||
join(netfxpath
|
||||
"C:\\Program Files\\Reference Assemblies\\Microsoft\\Framework\\"
|
||||
".NETFramework\\v4.0")
|
||||
file(WRITE run-msbuild.bat "
|
||||
${MSBUILD_SETUP}
|
||||
${CMAKE_MAKE_PROGRAM} -p:FrameworkPathOverride=\"${netfxpath}\" %*")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
function(add_headers VAR)
|
||||
set(headers ${${VAR}})
|
||||
foreach (header ${ARGN})
|
||||
set(headers ${headers} include/fmt/${header})
|
||||
endforeach()
|
||||
set(${VAR} ${headers} PARENT_SCOPE)
|
||||
endfunction()
|
||||
|
||||
# Define the fmt library, its includes and the needed defines.
|
||||
add_headers(FMT_HEADERS args.h base.h chrono.h color.h compile.h core.h format.h
|
||||
format-inl.h os.h ostream.h printf.h ranges.h std.h
|
||||
xchar.h)
|
||||
set(FMT_SOURCES src/format.cc)
|
||||
|
||||
add_module_library(fmt src/fmt.cc FALLBACK
|
||||
${FMT_SOURCES} ${FMT_HEADERS} README.md ChangeLog.md
|
||||
IF FMT_MODULE)
|
||||
add_library(fmt::fmt ALIAS fmt)
|
||||
if (FMT_MODULE)
|
||||
enable_module(fmt)
|
||||
elseif (FMT_OS)
|
||||
target_sources(fmt PRIVATE src/os.cc)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(fmt PRIVATE FMT_OS=0)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_WERROR)
|
||||
target_compile_options(fmt PRIVATE ${WERROR_FLAG})
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
if (FMT_PEDANTIC)
|
||||
target_compile_options(fmt PRIVATE ${PEDANTIC_COMPILE_FLAGS})
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (cxx_std_11 IN_LIST CMAKE_CXX_COMPILE_FEATURES)
|
||||
target_compile_features(fmt PUBLIC cxx_std_11)
|
||||
else ()
|
||||
message(WARNING "Feature cxx_std_11 is unknown for the CXX compiler")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
target_include_directories(fmt ${FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE} BEFORE PUBLIC
|
||||
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
|
||||
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:${FMT_INC_DIR}>)
|
||||
|
||||
set(FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX d CACHE STRING "Debug library postfix.")
|
||||
|
||||
set_target_properties(fmt PROPERTIES
|
||||
VERSION ${FMT_VERSION} SOVERSION ${CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MAJOR}
|
||||
PUBLIC_HEADER "${FMT_HEADERS}"
|
||||
DEBUG_POSTFIX "${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX}"
|
||||
|
||||
# Workaround for Visual Studio 2017:
|
||||
# Ensure the .pdb is created with the same name and in the same directory
|
||||
# as the .lib. Newer VS versions already do this by default, but there is no
|
||||
# harm in setting it for those too. Ignored by other generators.
|
||||
COMPILE_PDB_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY "${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}"
|
||||
COMPILE_PDB_NAME "fmt"
|
||||
COMPILE_PDB_NAME_DEBUG "fmt${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Set FMT_LIB_NAME for pkg-config fmt.pc. We cannot use the OUTPUT_NAME target
|
||||
# property because it's not set by default.
|
||||
set(FMT_LIB_NAME fmt)
|
||||
if (CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE STREQUAL "Debug")
|
||||
set(FMT_LIB_NAME ${FMT_LIB_NAME}${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX})
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (BUILD_SHARED_LIBS)
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(fmt PRIVATE FMT_LIB_EXPORT INTERFACE FMT_SHARED)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
if (FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST)
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(fmt PUBLIC FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
add_library(fmt-header-only INTERFACE)
|
||||
add_library(fmt::fmt-header-only ALIAS fmt-header-only)
|
||||
|
||||
if (NOT MSVC)
|
||||
# Unicode is always supported on compilers other than MSVC.
|
||||
elseif (FMT_UNICODE)
|
||||
# Unicode support requires compiling with /utf-8.
|
||||
target_compile_options(fmt PUBLIC $<$<AND:$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>,$<CXX_COMPILER_ID:MSVC>>:/utf-8>)
|
||||
target_compile_options(fmt-header-only INTERFACE $<$<AND:$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>,$<CXX_COMPILER_ID:MSVC>>:/utf-8>)
|
||||
else ()
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(fmt PUBLIC FMT_UNICODE=0)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(fmt-header-only INTERFACE FMT_HEADER_ONLY=1)
|
||||
target_compile_features(fmt-header-only INTERFACE cxx_std_11)
|
||||
|
||||
target_include_directories(fmt-header-only
|
||||
${FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE} BEFORE INTERFACE
|
||||
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
|
||||
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:${FMT_INC_DIR}>)
|
||||
|
||||
# Install targets.
|
||||
if (FMT_INSTALL)
|
||||
include(CMakePackageConfigHelpers)
|
||||
set_verbose(FMT_CMAKE_DIR ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}/cmake/fmt CACHE STRING
|
||||
"Installation directory for cmake files, a relative path that "
|
||||
"will be joined with ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX} or an absolute "
|
||||
"path.")
|
||||
set(version_config ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/fmt-config-version.cmake)
|
||||
set(project_config ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/fmt-config.cmake)
|
||||
set(pkgconfig ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/fmt.pc)
|
||||
set(targets_export_name fmt-targets)
|
||||
|
||||
set_verbose(FMT_LIB_DIR ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR} CACHE STRING
|
||||
"Installation directory for libraries, a relative path that "
|
||||
"will be joined to ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX} or an absolute path.")
|
||||
|
||||
set_verbose(FMT_PKGCONFIG_DIR ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}/pkgconfig CACHE STRING
|
||||
"Installation directory for pkgconfig (.pc) files, a relative "
|
||||
"path that will be joined with ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX} or an "
|
||||
"absolute path.")
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate the version, config and target files into the build directory.
|
||||
write_basic_package_version_file(
|
||||
${version_config}
|
||||
VERSION ${FMT_VERSION}
|
||||
COMPATIBILITY AnyNewerVersion)
|
||||
|
||||
join_paths(libdir_for_pc_file "\${exec_prefix}" "${FMT_LIB_DIR}")
|
||||
join_paths(includedir_for_pc_file "\${prefix}" "${FMT_INC_DIR}")
|
||||
|
||||
configure_file(
|
||||
"${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/support/cmake/fmt.pc.in"
|
||||
"${pkgconfig}"
|
||||
@ONLY)
|
||||
configure_package_config_file(
|
||||
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/support/cmake/fmt-config.cmake.in
|
||||
${project_config}
|
||||
INSTALL_DESTINATION ${FMT_CMAKE_DIR})
|
||||
|
||||
set(INSTALL_TARGETS fmt fmt-header-only)
|
||||
|
||||
set(INSTALL_FILE_SET)
|
||||
if (FMT_USE_CMAKE_MODULES)
|
||||
set(INSTALL_FILE_SET FILE_SET fmt DESTINATION "${FMT_INC_DIR}/fmt")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
# Install the library and headers.
|
||||
install(TARGETS ${INSTALL_TARGETS}
|
||||
COMPONENT fmt-core
|
||||
EXPORT ${targets_export_name}
|
||||
LIBRARY DESTINATION ${FMT_LIB_DIR}
|
||||
ARCHIVE DESTINATION ${FMT_LIB_DIR}
|
||||
PUBLIC_HEADER DESTINATION "${FMT_INC_DIR}/fmt"
|
||||
RUNTIME DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_BINDIR}
|
||||
${INSTALL_FILE_SET})
|
||||
|
||||
# Use a namespace because CMake provides better diagnostics for namespaced
|
||||
# imported targets.
|
||||
export(TARGETS ${INSTALL_TARGETS} NAMESPACE fmt::
|
||||
FILE ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/${targets_export_name}.cmake)
|
||||
|
||||
# Install version, config and target files.
|
||||
install(FILES ${project_config} ${version_config}
|
||||
DESTINATION ${FMT_CMAKE_DIR}
|
||||
COMPONENT fmt-core)
|
||||
install(EXPORT ${targets_export_name} DESTINATION ${FMT_CMAKE_DIR}
|
||||
NAMESPACE fmt::
|
||||
COMPONENT fmt-core)
|
||||
|
||||
install(FILES "${pkgconfig}" DESTINATION "${FMT_PKGCONFIG_DIR}"
|
||||
COMPONENT fmt-core)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
function(add_doc_target)
|
||||
find_program(DOXYGEN doxygen
|
||||
PATHS "$ENV{ProgramFiles}/doxygen/bin"
|
||||
"$ENV{ProgramFiles\(x86\)}/doxygen/bin")
|
||||
if (NOT DOXYGEN)
|
||||
message(STATUS "Target 'doc' disabled because doxygen not found")
|
||||
return ()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
find_program(MKDOCS mkdocs)
|
||||
if (NOT MKDOCS)
|
||||
message(STATUS "Target 'doc' disabled because mkdocs not found")
|
||||
return ()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
set(sources )
|
||||
foreach (source api.md index.md syntax.md get-started.md fmt.css fmt.js)
|
||||
set(sources ${sources} doc/${source})
|
||||
endforeach()
|
||||
|
||||
add_custom_target(
|
||||
doc
|
||||
COMMAND
|
||||
${CMAKE_COMMAND}
|
||||
-E env PYTHONPATH=${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/support/python
|
||||
${MKDOCS} build -f ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/support/mkdocs.yml
|
||||
# MkDocs requires the site dir to be outside of the doc dir.
|
||||
--site-dir ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/doc-html
|
||||
--no-directory-urls
|
||||
SOURCES ${sources})
|
||||
|
||||
include(GNUInstallDirs)
|
||||
install(DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/doc-html/
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_DATAROOTDIR}/doc/fmt
|
||||
COMPONENT fmt-doc OPTIONAL)
|
||||
endfunction()
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_DOC)
|
||||
add_doc_target()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_TEST)
|
||||
enable_testing()
|
||||
add_subdirectory(test)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Control fuzzing independent of the unit tests.
|
||||
if (FMT_FUZZ)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(test/fuzzing)
|
||||
|
||||
# The FMT_FUZZ macro is used to prevent resource exhaustion in fuzzing
|
||||
# mode and make fuzzing practically possible. It is similar to
|
||||
# FUZZING_BUILD_MODE_UNSAFE_FOR_PRODUCTION but uses a different name to
|
||||
# avoid interfering with fuzzing of projects that use {fmt}.
|
||||
# See also https://llvm.org/docs/LibFuzzer.html#fuzzer-friendly-build-mode.
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(fmt PUBLIC FMT_FUZZ)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
set(gitignore ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/.gitignore)
|
||||
if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND EXISTS ${gitignore})
|
||||
# Get the list of ignored files from .gitignore.
|
||||
file (STRINGS ${gitignore} lines)
|
||||
list(REMOVE_ITEM lines /doc/html)
|
||||
foreach (line ${lines})
|
||||
string(REPLACE "." "[.]" line "${line}")
|
||||
string(REPLACE "*" ".*" line "${line}")
|
||||
set(ignored_files ${ignored_files} "${line}$" "${line}/")
|
||||
endforeach ()
|
||||
set(ignored_files ${ignored_files} /.git /build/doxyxml .vagrant)
|
||||
|
||||
set(CPACK_SOURCE_GENERATOR ZIP)
|
||||
set(CPACK_SOURCE_IGNORE_FILES ${ignored_files})
|
||||
set(CPACK_SOURCE_PACKAGE_FILE_NAME fmt-${FMT_VERSION})
|
||||
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_NAME fmt)
|
||||
set(CPACK_RESOURCE_FILE_README ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/README.md)
|
||||
include(CPack)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
20
extlib/libfmt/CONTRIBUTING.md
vendored
Normal file
20
extlib/libfmt/CONTRIBUTING.md
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
Contributing to {fmt}
|
||||
=====================
|
||||
|
||||
By submitting a pull request or a patch, you represent that you have the right
|
||||
to license your contribution to the {fmt} project owners and the community,
|
||||
agree that your contributions are licensed under the {fmt} license, and agree
|
||||
to future changes to the licensing.
|
||||
|
||||
All C++ code must adhere to [Google C++ Style Guide](
|
||||
https://google.github.io/styleguide/cppguide.html) with the following
|
||||
exceptions:
|
||||
|
||||
* Exceptions are permitted
|
||||
* snake_case should be used instead of UpperCamelCase for function and type
|
||||
names
|
||||
|
||||
All documentation must adhere to the [Google Developer Documentation Style
|
||||
Guide](https://developers.google.com/style).
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks for contributing!
|
||||
2891
extlib/libfmt/ChangeLog.md
vendored
Normal file
2891
extlib/libfmt/ChangeLog.md
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
27
extlib/libfmt/LICENSE
vendored
Normal file
27
extlib/libfmt/LICENSE
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich and {fmt} contributors
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining
|
||||
a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the
|
||||
"Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
|
||||
without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,
|
||||
distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to
|
||||
permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to
|
||||
the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be
|
||||
included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
|
||||
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF
|
||||
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
|
||||
NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE
|
||||
LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION
|
||||
OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION
|
||||
WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
|
||||
|
||||
--- Optional exception to the license ---
|
||||
|
||||
As an exception, if, as a result of your compiling your source code, portions
|
||||
of this Software are embedded into a machine-executable object form of such
|
||||
source code, you may redistribute such embedded portions in such object form
|
||||
without including the above copyright and permission notices.
|
||||
485
extlib/libfmt/README.md
vendored
Normal file
485
extlib/libfmt/README.md
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,485 @@
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/156254208-f5b743a9-88cf-439d-b0c0-923d53e8d551.png" alt="{fmt}" width="25%"/>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows)
|
||||
[](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?\%0Acolspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20\%0ASummary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
|
||||
[](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt)
|
||||
[](https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt)
|
||||
|
||||
**{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe
|
||||
alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams.
|
||||
|
||||
If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds
|
||||
that help victims of the war in Ukraine: <https://www.stopputin.net/>.
|
||||
|
||||
[Documentation](https://fmt.dev)
|
||||
|
||||
[Cheat Sheets](https://hackingcpp.com/cpp/libs/fmt.html)
|
||||
|
||||
Q&A: ask questions on [StackOverflow with the tag
|
||||
fmt](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt).
|
||||
|
||||
Try {fmt} in [Compiler Explorer](https://godbolt.org/z/8Mx1EW73v).
|
||||
|
||||
# Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Simple [format API](https://fmt.dev/latest/api/) with positional
|
||||
arguments for localization
|
||||
- Implementation of [C++20
|
||||
std::format](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format) and
|
||||
[C++23 std::print](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/io/print)
|
||||
- [Format string syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax/) similar
|
||||
to Python\'s
|
||||
[format](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format)
|
||||
- Fast IEEE 754 floating-point formatter with correct rounding,
|
||||
shortness and round-trip guarantees using the
|
||||
[Dragonbox](https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox) algorithm
|
||||
- Portable Unicode support
|
||||
- Safe [printf
|
||||
implementation](https://fmt.dev/latest/api/#printf-formatting)
|
||||
including the POSIX extension for positional arguments
|
||||
- Extensibility: [support for user-defined
|
||||
types](https://fmt.dev/latest/api/#formatting-user-defined-types)
|
||||
- High performance: faster than common standard library
|
||||
implementations of `(s)printf`, iostreams, `to_string` and
|
||||
`to_chars`, see [Speed tests](#speed-tests) and [Converting a
|
||||
hundred million integers to strings per
|
||||
second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html)
|
||||
- Small code size both in terms of source code with the minimum
|
||||
configuration consisting of just three files, `core.h`, `format.h`
|
||||
and `format-inl.h`, and compiled code; see [Compile time and code
|
||||
bloat](#compile-time-and-code-bloat)
|
||||
- Reliability: the library has an extensive set of
|
||||
[tests](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/tree/master/test) and is
|
||||
[continuously fuzzed](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?colspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20Summary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
|
||||
- Safety: the library is fully type-safe, errors in format strings can
|
||||
be reported at compile time, automatic memory management prevents
|
||||
buffer overflow errors
|
||||
- Ease of use: small self-contained code base, no external
|
||||
dependencies, permissive MIT
|
||||
[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE)
|
||||
- [Portability](https://fmt.dev/latest/#portability) with
|
||||
consistent output across platforms and support for older compilers
|
||||
- Clean warning-free codebase even on high warning levels such as
|
||||
`-Wall -Wextra -pedantic`
|
||||
- Locale independence by default
|
||||
- Optional header-only configuration enabled with the
|
||||
`FMT_HEADER_ONLY` macro
|
||||
|
||||
See the [documentation](https://fmt.dev) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
# Examples
|
||||
|
||||
**Print to stdout** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Tevcjh))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/core.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print("Hello, world!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Format a string** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/oK8h33))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42);
|
||||
// s == "The answer is 42."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Format a string using positional arguments**
|
||||
([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Yn7Txe))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("I'd rather be {1} than {0}.", "right", "happy");
|
||||
// s == "I'd rather be happy than right."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Print dates and times** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/c31ExdY3W))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/chrono.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
|
||||
fmt::print("Date and time: {}\n", now);
|
||||
fmt::print("Time: {:%H:%M}\n", now);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
Date and time: 2023-12-26 19:10:31.557195597
|
||||
Time: 19:10
|
||||
|
||||
**Print a container** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/MxM1YqjE7))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <fmt/ranges.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
std::vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3};
|
||||
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
[1, 2, 3]
|
||||
|
||||
**Check a format string at compile time**
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("{:d}", "I am not a number");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This gives a compile-time error in C++20 because `d` is an invalid
|
||||
format specifier for a string.
|
||||
|
||||
**Write a file from a single thread**
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/os.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
auto out = fmt::output_file("guide.txt");
|
||||
out.print("Don't {}", "Panic");
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This can be [5 to 9 times faster than
|
||||
fprintf](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/08/04/optimal-file-buffer-size.html).
|
||||
|
||||
**Print with colors and text styles**
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/color.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold,
|
||||
"Hello, {}!\n", "world");
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) |
|
||||
fmt::emphasis::underline, "Olá, {}!\n", "Mundo");
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic,
|
||||
"你好{}!\n", "世界");
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output on a modern terminal with Unicode support:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
## Speed tests
|
||||
|
||||
| Library | Method | Run Time, s |
|
||||
|-------------------|---------------|-------------|
|
||||
| libc | printf | 0.91 |
|
||||
| libc++ | std::ostream | 2.49 |
|
||||
| {fmt} 9.1 | fmt::print | 0.74 |
|
||||
| Boost Format 1.80 | boost::format | 6.26 |
|
||||
| Folly Format | folly::format | 1.87 |
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is the fastest of the benchmarked methods, \~20% faster than
|
||||
`printf`.
|
||||
|
||||
The above results were generated by building `tinyformat_test.cpp` on
|
||||
macOS 12.6.1 with `clang++ -O3 -DNDEBUG -DSPEED_TEST -DHAVE_FORMAT`, and
|
||||
taking the best of three runs. In the test, the format string
|
||||
`"%0.10f:%04d:%+g:%s:%p:%c:%%\n"` or equivalent is filled 2,000,000
|
||||
times with output sent to `/dev/null`; for further details refer to the
|
||||
[source](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/src/tinyformat-test.cc).
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is up to 20-30x faster than `std::ostringstream` and `sprintf` on
|
||||
IEEE754 `float` and `double` formatting
|
||||
([dtoa-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark)) and faster
|
||||
than [double-conversion](https://github.com/google/double-conversion)
|
||||
and [ryu](https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu):
|
||||
|
||||
[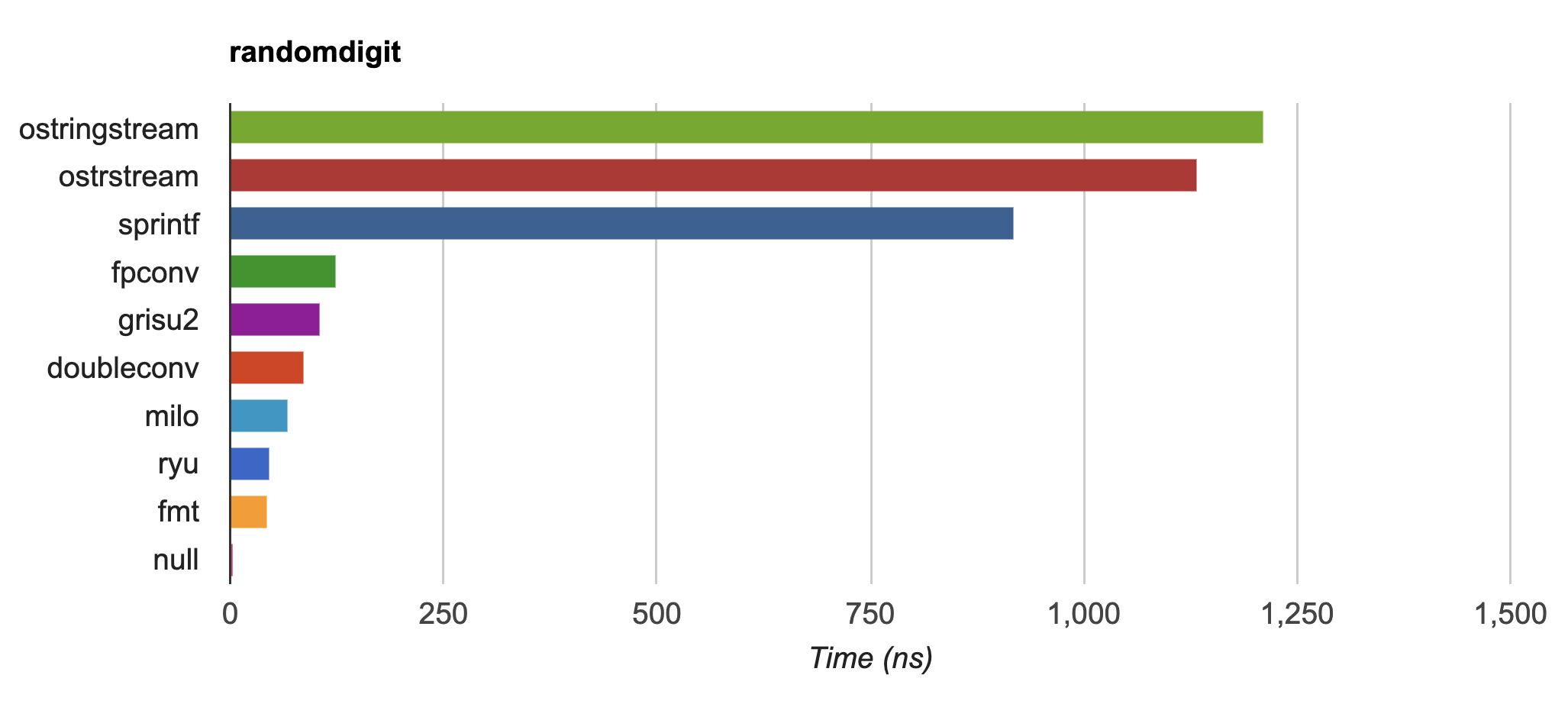](https://fmt.dev/unknown_mac64_clang12.0.html)
|
||||
|
||||
## Compile time and code bloat
|
||||
|
||||
The script [bloat-test.py][test] from [format-benchmark][bench] tests compile
|
||||
time and code bloat for nontrivial projects. It generates 100 translation units
|
||||
and uses `printf()` or its alternative five times in each to simulate a
|
||||
medium-sized project. The resulting executable size and compile time (Apple
|
||||
clang version 15.0.0 (clang-1500.1.0.2.5), macOS Sonoma, best of three) is shown
|
||||
in the following tables.
|
||||
|
||||
[test]: https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/bloat-test.py
|
||||
[bench]: https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
**Optimized build (-O3)**
|
||||
|
||||
| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
|
||||
|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
|
||||
| printf | 1.6 | 54 | 50 |
|
||||
| IOStreams | 25.9 | 98 | 84 |
|
||||
| fmt 83652df | 4.8 | 54 | 50 |
|
||||
| tinyformat | 29.1 | 161 | 136 |
|
||||
| Boost Format | 55.0 | 530 | 317 |
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is fast to compile and is comparable to `printf` in terms of per-call
|
||||
binary size (within a rounding error on this system).
|
||||
|
||||
**Non-optimized build**
|
||||
|
||||
| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
|
||||
|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
|
||||
| printf | 1.4 | 54 | 50 |
|
||||
| IOStreams | 23.4 | 92 | 68 |
|
||||
| {fmt} 83652df | 4.4 | 89 | 85 |
|
||||
| tinyformat | 24.5 | 204 | 161 |
|
||||
| Boost Format | 36.4 | 831 | 462 |
|
||||
|
||||
`libc`, `lib(std)c++`, and `libfmt` are all linked as shared libraries
|
||||
to compare formatting function overhead only. Boost Format is a
|
||||
header-only library so it doesn\'t provide any linkage options.
|
||||
|
||||
## Running the tests
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to [Building the
|
||||
library](https://fmt.dev/latest/get-started/#building-from-source) for
|
||||
instructions on how to build the library and run the unit tests.
|
||||
|
||||
Benchmarks reside in a separate repository,
|
||||
[format-benchmarks](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark), so to
|
||||
run the benchmarks you first need to clone this repository and generate
|
||||
Makefiles with CMake:
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark.git
|
||||
$ cd format-benchmark
|
||||
$ cmake .
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can run the speed test:
|
||||
|
||||
$ make speed-test
|
||||
|
||||
or the bloat test:
|
||||
|
||||
$ make bloat-test
|
||||
|
||||
# Migrating code
|
||||
|
||||
[clang-tidy](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/) v18 provides the
|
||||
[modernize-use-std-print](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/checks/modernize/use-std-print.html)
|
||||
check that is capable of converting occurrences of `printf` and
|
||||
`fprintf` to `fmt::print` if configured to do so. (By default it
|
||||
converts to `std::print`.)
|
||||
|
||||
# Notable projects using this library
|
||||
|
||||
- [0 A.D.](https://play0ad.com/): a free, open-source, cross-platform
|
||||
real-time strategy game
|
||||
- [AMPL/MP](https://github.com/ampl/mp): an open-source library for
|
||||
mathematical programming
|
||||
- [Apple's FoundationDB](https://github.com/apple/foundationdb): an open-source,
|
||||
distributed, transactional key-value store
|
||||
- [Aseprite](https://github.com/aseprite/aseprite): animated sprite
|
||||
editor & pixel art tool
|
||||
- [AvioBook](https://www.aviobook.aero/en): a comprehensive aircraft
|
||||
operations suite
|
||||
- [Blizzard Battle.net](https://battle.net/): an online gaming
|
||||
platform
|
||||
- [Celestia](https://celestia.space/): real-time 3D visualization of
|
||||
space
|
||||
- [Ceph](https://ceph.com/): a scalable distributed storage system
|
||||
- [ccache](https://ccache.dev/): a compiler cache
|
||||
- [ClickHouse](https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse): an
|
||||
analytical database management system
|
||||
- [ContextVision](https://www.contextvision.com/): medical imaging software
|
||||
- [Contour](https://github.com/contour-terminal/contour/): a modern
|
||||
terminal emulator
|
||||
- [CUAUV](https://cuauv.org/): Cornell University\'s autonomous
|
||||
underwater vehicle
|
||||
- [Drake](https://drake.mit.edu/): a planning, control, and analysis
|
||||
toolbox for nonlinear dynamical systems (MIT)
|
||||
- [Envoy](https://github.com/envoyproxy/envoy): C++ L7 proxy and
|
||||
communication bus (Lyft)
|
||||
- [FiveM](https://fivem.net/): a modification framework for GTA V
|
||||
- [fmtlog](https://github.com/MengRao/fmtlog): a performant
|
||||
fmtlib-style logging library with latency in nanoseconds
|
||||
- [Folly](https://github.com/facebook/folly): Facebook open-source
|
||||
library
|
||||
- [GemRB](https://gemrb.org/): a portable open-source implementation
|
||||
of Bioware's Infinity Engine
|
||||
- [Grand Mountain
|
||||
Adventure](https://store.steampowered.com/app/1247360/Grand_Mountain_Adventure/):
|
||||
a beautiful open-world ski & snowboarding game
|
||||
- [HarpyWar/pvpgn](https://github.com/pvpgn/pvpgn-server): Player vs
|
||||
Player Gaming Network with tweaks
|
||||
- [KBEngine](https://github.com/kbengine/kbengine): an open-source
|
||||
MMOG server engine
|
||||
- [Keypirinha](https://keypirinha.com/): a semantic launcher for
|
||||
Windows
|
||||
- [Kodi](https://kodi.tv/) (formerly xbmc): home theater software
|
||||
- [Knuth](https://kth.cash/): high-performance Bitcoin full-node
|
||||
- [libunicode](https://github.com/contour-terminal/libunicode/): a
|
||||
modern C++17 Unicode library
|
||||
- [MariaDB](https://mariadb.org/): relational database management
|
||||
system
|
||||
- [Microsoft Verona](https://github.com/microsoft/verona): research
|
||||
programming language for concurrent ownership
|
||||
- [MongoDB](https://mongodb.com/): distributed document database
|
||||
- [MongoDB Smasher](https://github.com/duckie/mongo_smasher): a small
|
||||
tool to generate randomized datasets
|
||||
- [OpenSpace](https://openspaceproject.com/): an open-source
|
||||
astrovisualization framework
|
||||
- [PenUltima Online (POL)](https://www.polserver.com/): an MMO server,
|
||||
compatible with most Ultima Online clients
|
||||
- [PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch): an open-source
|
||||
machine learning library
|
||||
- [quasardb](https://www.quasardb.net/): a distributed,
|
||||
high-performance, associative database
|
||||
- [Quill](https://github.com/odygrd/quill): asynchronous low-latency
|
||||
logging library
|
||||
- [QKW](https://github.com/ravijanjam/qkw): generalizing aliasing to
|
||||
simplify navigation, and execute complex multi-line terminal
|
||||
command sequences
|
||||
- [redis-cerberus](https://github.com/HunanTV/redis-cerberus): a Redis
|
||||
cluster proxy
|
||||
- [redpanda](https://vectorized.io/redpanda): a 10x faster Kafka®
|
||||
replacement for mission-critical systems written in C++
|
||||
- [rpclib](http://rpclib.net/): a modern C++ msgpack-RPC server and
|
||||
client library
|
||||
- [Salesforce Analytics
|
||||
Cloud](https://www.salesforce.com/analytics-cloud/overview/):
|
||||
business intelligence software
|
||||
- [Scylla](https://www.scylladb.com/): a Cassandra-compatible NoSQL
|
||||
data store that can handle 1 million transactions per second on a
|
||||
single server
|
||||
- [Seastar](http://www.seastar-project.org/): an advanced, open-source
|
||||
C++ framework for high-performance server applications on modern
|
||||
hardware
|
||||
- [spdlog](https://github.com/gabime/spdlog): super fast C++ logging
|
||||
library
|
||||
- [Stellar](https://www.stellar.org/): financial platform
|
||||
- [Touch Surgery](https://www.touchsurgery.com/): surgery simulator
|
||||
- [TrinityCore](https://github.com/TrinityCore/TrinityCore):
|
||||
open-source MMORPG framework
|
||||
- [🐙 userver framework](https://userver.tech/): open-source
|
||||
asynchronous framework with a rich set of abstractions and database
|
||||
drivers
|
||||
- [Windows Terminal](https://github.com/microsoft/terminal): the new
|
||||
Windows terminal
|
||||
|
||||
[More\...](https://github.com/search?q=fmtlib&type=Code)
|
||||
|
||||
If you are aware of other projects using this library, please let me
|
||||
know by [email](mailto:victor.zverovich@gmail.com) or by submitting an
|
||||
[issue](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
# Motivation
|
||||
|
||||
So why yet another formatting library?
|
||||
|
||||
There are plenty of methods for doing this task, from standard ones like
|
||||
the printf family of function and iostreams to Boost Format and
|
||||
FastFormat libraries. The reason for creating a new library is that
|
||||
every existing solution that I found either had serious issues or
|
||||
didn\'t provide all the features I needed.
|
||||
|
||||
## printf
|
||||
|
||||
The good thing about `printf` is that it is pretty fast and readily
|
||||
available being a part of the C standard library. The main drawback is
|
||||
that it doesn\'t support user-defined types. `printf` also has safety
|
||||
issues although they are somewhat mitigated with [\_\_attribute\_\_
|
||||
((format (printf,
|
||||
\...))](https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Function-Attributes.html) in
|
||||
GCC. There is a POSIX extension that adds positional arguments required
|
||||
for
|
||||
[i18n](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internationalization_and_localization)
|
||||
to `printf` but it is not a part of C99 and may not be available on some
|
||||
platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
## iostreams
|
||||
|
||||
The main issue with iostreams is best illustrated with an example:
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
std::cout << std::setprecision(2) << std::fixed << 1.23456 << "\n";
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is a lot of typing compared to printf:
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
printf("%.2f\n", 1.23456);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Matthew Wilson, the author of FastFormat, called this \"chevron hell\".
|
||||
iostreams don\'t support positional arguments by design.
|
||||
|
||||
The good part is that iostreams support user-defined types and are safe
|
||||
although error handling is awkward.
|
||||
|
||||
## Boost Format
|
||||
|
||||
This is a very powerful library that supports both `printf`-like format
|
||||
strings and positional arguments. Its main drawback is performance.
|
||||
According to various benchmarks, it is much slower than other methods
|
||||
considered here. Boost Format also has excessive build times and severe
|
||||
code bloat issues (see [Benchmarks](#benchmarks)).
|
||||
|
||||
## FastFormat
|
||||
|
||||
This is an interesting library that is fast, safe and has positional
|
||||
arguments. However, it has significant limitations, citing its author:
|
||||
|
||||
> Three features that have no hope of being accommodated within the
|
||||
> current design are:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> - Leading zeros (or any other non-space padding)
|
||||
> - Octal/hexadecimal encoding
|
||||
> - Runtime width/alignment specification
|
||||
|
||||
It is also quite big and has a heavy dependency, on STLSoft, which might be
|
||||
too restrictive for use in some projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## Boost Spirit.Karma
|
||||
|
||||
This is not a formatting library but I decided to include it here for
|
||||
completeness. As iostreams, it suffers from the problem of mixing
|
||||
verbatim text with arguments. The library is pretty fast, but slower on
|
||||
integer formatting than `fmt::format_to` with format string compilation
|
||||
on Karma\'s own benchmark, see [Converting a hundred million integers to
|
||||
strings per
|
||||
second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html).
|
||||
|
||||
# License
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is distributed under the MIT
|
||||
[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE).
|
||||
|
||||
# Documentation License
|
||||
|
||||
The [Format String Syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax/) section
|
||||
in the documentation is based on the one from Python [string module
|
||||
documentation](https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html#module-string).
|
||||
For this reason, the documentation is distributed under the Python
|
||||
Software Foundation license available in
|
||||
[doc/python-license.txt](https://raw.github.com/fmtlib/fmt/master/doc/python-license.txt).
|
||||
It only applies if you distribute the documentation of {fmt}.
|
||||
|
||||
# Maintainers
|
||||
|
||||
The {fmt} library is maintained by Victor Zverovich
|
||||
([vitaut](https://github.com/vitaut)) with contributions from many other
|
||||
people. See
|
||||
[Contributors](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/graphs/contributors) and
|
||||
[Releases](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases) for some of the
|
||||
names. Let us know if your contribution is not listed or mentioned
|
||||
incorrectly and we\'ll make it right.
|
||||
|
||||
# Security Policy
|
||||
|
||||
To report a security issue, please disclose it at [security
|
||||
advisory](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/security/advisories/new).
|
||||
|
||||
This project is maintained by a team of volunteers on a
|
||||
reasonable-effort basis. As such, please give us at least *90* days to
|
||||
work on a fix before public exposure.
|
||||
13
extlib/libfmt/_MODIFIED_LIBFMT.txt
vendored
Normal file
13
extlib/libfmt/_MODIFIED_LIBFMT.txt
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
This copy of libfmt 11.1.2 is a modified version of the original.
|
||||
|
||||
commit 8303d140a1a11f19b982a9f664bbe59a1ccda3f4
|
||||
Update version
|
||||
|
||||
Tag: 11.1.2
|
||||
|
||||
The following changes have been made to the original:
|
||||
|
||||
- Removed documentation and test suites.
|
||||
|
||||
To obtain the original libfmt-11.1.2, visit:
|
||||
https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt
|
||||
3290
extlib/libfmt/doc/ChangeLog-old.md
vendored
Normal file
3290
extlib/libfmt/doc/ChangeLog-old.md
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
673
extlib/libfmt/doc/api.md
vendored
Normal file
673
extlib/libfmt/doc/api.md
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,673 @@
|
||||
# API Reference
|
||||
|
||||
The {fmt} library API consists of the following components:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`fmt/base.h`](#base-api): the base API providing main formatting functions
|
||||
for `char`/UTF-8 with C++20 compile-time checks and minimal dependencies
|
||||
- [`fmt/format.h`](#format-api): `fmt::format` and other formatting functions
|
||||
as well as locale support
|
||||
- [`fmt/ranges.h`](#ranges-api): formatting of ranges and tuples
|
||||
- [`fmt/chrono.h`](#chrono-api): date and time formatting
|
||||
- [`fmt/std.h`](#std-api): formatters for standard library types
|
||||
- [`fmt/compile.h`](#compile-api): format string compilation
|
||||
- [`fmt/color.h`](#color-api): terminal colors and text styles
|
||||
- [`fmt/os.h`](#os-api): system APIs
|
||||
- [`fmt/ostream.h`](#ostream-api): `std::ostream` support
|
||||
- [`fmt/args.h`](#args-api): dynamic argument lists
|
||||
- [`fmt/printf.h`](#printf-api): safe `printf`
|
||||
- [`fmt/xchar.h`](#xchar-api): optional `wchar_t` support
|
||||
|
||||
All functions and types provided by the library reside in namespace `fmt`
|
||||
and macros have prefix `FMT_`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Base API
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/base.h` defines the base API which provides main formatting functions
|
||||
for `char`/UTF-8 with C++20 compile-time checks. It has minimal include
|
||||
dependencies for better compile times. This header is only beneficial when
|
||||
using {fmt} as a library (the default) and not in the header-only mode.
|
||||
It also provides `formatter` specializations for the following types:
|
||||
|
||||
- `int`, `long long`,
|
||||
- `unsigned`, `unsigned long long`
|
||||
- `float`, `double`, `long double`
|
||||
- `bool`
|
||||
- `char`
|
||||
- `const char*`, [`fmt::string_view`](#basic_string_view)
|
||||
- `const void*`
|
||||
|
||||
The following functions use [format string syntax](syntax.md) similar to that
|
||||
of [str.format](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format)
|
||||
in Python. They take *fmt* and *args* as arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
*fmt* is a format string that contains literal text and replacement fields
|
||||
surrounded by braces `{}`. The fields are replaced with formatted arguments
|
||||
in the resulting string. [`fmt::format_string`](#format_string) is a format
|
||||
string which can be implicitly constructed from a string literal or a
|
||||
`constexpr` string and is checked at compile time in C++20. To pass a runtime
|
||||
format string wrap it in [`fmt::runtime`](#runtime).
|
||||
|
||||
*args* is an argument list representing objects to be formatted.
|
||||
|
||||
I/O errors are reported as [`std::system_error`](
|
||||
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/error/system_error) exceptions unless
|
||||
specified otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
::: print(format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: print(FILE*, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: println(format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: println(FILE*, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: format_to(OutputIt&&, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: format_to_n(OutputIt, size_t, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: format_to_n_result
|
||||
|
||||
::: formatted_size(format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="udt"></a>
|
||||
### Formatting User-Defined Types
|
||||
|
||||
The {fmt} library provides formatters for many standard C++ types.
|
||||
See [`fmt/ranges.h`](#ranges-api) for ranges and tuples including standard
|
||||
containers such as `std::vector`, [`fmt/chrono.h`](#chrono-api) for date and
|
||||
time formatting and [`fmt/std.h`](#std-api) for other standard library types.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways to make a user-defined type formattable: providing a
|
||||
`format_as` function or specializing the `formatter` struct template.
|
||||
|
||||
Use `format_as` if you want to make your type formattable as some other
|
||||
type with the same format specifiers. The `format_as` function should
|
||||
take an object of your type and return an object of a formattable type.
|
||||
It should be defined in the same namespace as your type.
|
||||
|
||||
Example ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/nvME4arz8)):
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
|
||||
namespace kevin_namespacy {
|
||||
|
||||
enum class film {
|
||||
house_of_cards, american_beauty, se7en = 7
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
auto format_as(film f) { return fmt::underlying(f); }
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print("{}\n", kevin_namespacy::film::se7en); // Output: 7
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Using specialization is more complex but gives you full control over
|
||||
parsing and formatting. To use this method specialize the `formatter`
|
||||
struct template for your type and implement `parse` and `format`
|
||||
methods.
|
||||
|
||||
The recommended way of defining a formatter is by reusing an existing
|
||||
one via inheritance or composition. This way you can support standard
|
||||
format specifiers without implementing them yourself. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
// color.h:
|
||||
#include <fmt/base.h>
|
||||
|
||||
enum class color {red, green, blue};
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct fmt::formatter<color>: formatter<string_view> {
|
||||
// parse is inherited from formatter<string_view>.
|
||||
|
||||
auto format(color c, format_context& ctx) const
|
||||
-> format_context::iterator;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
// color.cc:
|
||||
#include "color.h"
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
|
||||
auto fmt::formatter<color>::format(color c, format_context& ctx) const
|
||||
-> format_context::iterator {
|
||||
string_view name = "unknown";
|
||||
switch (c) {
|
||||
case color::red: name = "red"; break;
|
||||
case color::green: name = "green"; break;
|
||||
case color::blue: name = "blue"; break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return formatter<string_view>::format(name, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that `formatter<string_view>::format` is defined in `fmt/format.h`
|
||||
so it has to be included in the source file. Since `parse` is inherited
|
||||
from `formatter<string_view>` it will recognize all string format
|
||||
specifications, for example
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::format("{:>10}", color::blue)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
will return `" blue"`.
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- The experimental `nested_formatter` provides an easy way of applying a
|
||||
formatter to one or more subobjects.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
|
||||
struct point {
|
||||
double x, y;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
struct fmt::formatter<point> : nested_formatter<double> {
|
||||
auto format(point p, format_context& ctx) const {
|
||||
return write_padded(ctx, [=](auto out) {
|
||||
return format_to(out, "({}, {})", this->nested(p.x),
|
||||
this->nested(p.y));
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print("[{:>20.2f}]", point{1, 2});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
prints:
|
||||
|
||||
[ (1.00, 2.00)]
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that fill, align and width are applied to the whole object which
|
||||
is the recommended behavior while the remaining specifiers apply to
|
||||
elements. -->
|
||||
|
||||
In general the formatter has the following form:
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct fmt::formatter<T> {
|
||||
// Parses format specifiers and stores them in the formatter.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// [ctx.begin(), ctx.end()) is a, possibly empty, character range that
|
||||
// contains a part of the format string starting from the format
|
||||
// specifications to be parsed, e.g. in
|
||||
//
|
||||
// fmt::format("{:f} continued", ...);
|
||||
//
|
||||
// the range will contain "f} continued". The formatter should parse
|
||||
// specifiers until '}' or the end of the range. In this example the
|
||||
// formatter should parse the 'f' specifier and return an iterator
|
||||
// pointing to '}'.
|
||||
constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx)
|
||||
-> format_parse_context::iterator;
|
||||
|
||||
// Formats value using the parsed format specification stored in this
|
||||
// formatter and writes the output to ctx.out().
|
||||
auto format(const T& value, format_context& ctx) const
|
||||
-> format_context::iterator;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to at least support fill, align and width that apply
|
||||
to the whole object and have the same semantics as in standard
|
||||
formatters.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also write a formatter for a hierarchy of classes:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
// demo.h:
|
||||
#include <type_traits>
|
||||
#include <fmt/core.h>
|
||||
|
||||
struct A {
|
||||
virtual ~A() {}
|
||||
virtual std::string name() const { return "A"; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct B : A {
|
||||
virtual std::string name() const { return "B"; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct fmt::formatter<T, std::enable_if_t<std::is_base_of_v<A, T>, char>> :
|
||||
fmt::formatter<std::string> {
|
||||
auto format(const A& a, format_context& ctx) const {
|
||||
return formatter<std::string>::format(a.name(), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
// demo.cc:
|
||||
#include "demo.h"
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
B b;
|
||||
A& a = b;
|
||||
fmt::print("{}", a); // Output: B
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Providing both a `formatter` specialization and a `format_as` overload is
|
||||
disallowed.
|
||||
|
||||
::: basic_format_parse_context
|
||||
|
||||
::: context
|
||||
|
||||
::: format_context
|
||||
|
||||
### Compile-Time Checks
|
||||
|
||||
Compile-time format string checks are enabled by default on compilers
|
||||
that support C++20 `consteval`. On older compilers you can use the
|
||||
[FMT_STRING](#legacy-checks) macro defined in `fmt/format.h` instead.
|
||||
|
||||
Unused arguments are allowed as in Python's `str.format` and ordinary functions.
|
||||
|
||||
See [Type Erasure](#type-erasure) for an example of how to enable compile-time
|
||||
checks in your own functions with `fmt::format_string` while avoiding template
|
||||
bloat.
|
||||
|
||||
::: fstring
|
||||
|
||||
::: format_string
|
||||
|
||||
::: runtime(string_view)
|
||||
|
||||
### Type Erasure
|
||||
|
||||
You can create your own formatting function with compile-time checks and
|
||||
small binary footprint, for example ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/b9Pbasvzc)):
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
|
||||
void vlog(const char* file, int line,
|
||||
fmt::string_view fmt, fmt::format_args args) {
|
||||
fmt::print("{}: {}: {}", file, line, fmt::vformat(fmt, args));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
void log(const char* file, int line,
|
||||
fmt::format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
vlog(file, line, fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#define MY_LOG(fmt, ...) log(__FILE__, __LINE__, fmt, __VA_ARGS__)
|
||||
|
||||
MY_LOG("invalid squishiness: {}", 42);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that `vlog` is not parameterized on argument types which improves
|
||||
compile times and reduces binary code size compared to a fully
|
||||
parameterized version.
|
||||
|
||||
::: make_format_args(T&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: basic_format_args
|
||||
|
||||
::: format_args
|
||||
|
||||
::: basic_format_arg
|
||||
|
||||
### Named Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
::: arg(const Char*, const T&)
|
||||
|
||||
Named arguments are not supported in compile-time checks at the moment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Compatibility
|
||||
|
||||
::: basic_string_view
|
||||
|
||||
::: string_view
|
||||
|
||||
## Format API
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/format.h` defines the full format API providing additional
|
||||
formatting functions and locale support.
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="format"></a>
|
||||
::: format(format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: vformat(string_view, format_args)
|
||||
|
||||
::: operator""_a()
|
||||
|
||||
### Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
::: ptr(T)
|
||||
|
||||
::: underlying(Enum)
|
||||
|
||||
::: to_string(const T&)
|
||||
|
||||
::: group_digits(T)
|
||||
|
||||
::: detail::buffer
|
||||
|
||||
::: basic_memory_buffer
|
||||
|
||||
### System Errors
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} does not use `errno` to communicate errors to the user, but it may
|
||||
call system functions which set `errno`. Users should not make any
|
||||
assumptions about the value of `errno` being preserved by library
|
||||
functions.
|
||||
|
||||
::: system_error
|
||||
|
||||
::: format_system_error
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Allocators
|
||||
|
||||
The {fmt} library supports custom dynamic memory allocators. A custom
|
||||
allocator class can be specified as a template argument to
|
||||
[`fmt::basic_memory_buffer`](#basic_memory_buffer):
|
||||
|
||||
using custom_memory_buffer =
|
||||
fmt::basic_memory_buffer<char, fmt::inline_buffer_size, custom_allocator>;
|
||||
|
||||
It is also possible to write a formatting function that uses a custom
|
||||
allocator:
|
||||
|
||||
using custom_string =
|
||||
std::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, custom_allocator>;
|
||||
|
||||
auto vformat(custom_allocator alloc, fmt::string_view fmt,
|
||||
fmt::format_args args) -> custom_string {
|
||||
auto buf = custom_memory_buffer(alloc);
|
||||
fmt::vformat_to(std::back_inserter(buf), fmt, args);
|
||||
return custom_string(buf.data(), buf.size(), alloc);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename ...Args>
|
||||
auto format(custom_allocator alloc, fmt::string_view fmt,
|
||||
const Args& ... args) -> custom_string {
|
||||
return vformat(alloc, fmt, fmt::make_format_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
The allocator will be used for the output container only. Formatting
|
||||
functions normally don't do any allocations for built-in and string
|
||||
types except for non-default floating-point formatting that occasionally
|
||||
falls back on `sprintf`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Locale
|
||||
|
||||
All formatting is locale-independent by default. Use the `'L'` format
|
||||
specifier to insert the appropriate number separator characters from the
|
||||
locale:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/core.h>
|
||||
#include <locale>
|
||||
|
||||
std::locale::global(std::locale("en_US.UTF-8"));
|
||||
auto s = fmt::format("{:L}", 1000000); // s == "1,000,000"
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/format.h` provides the following overloads of formatting functions
|
||||
that take `std::locale` as a parameter. The locale type is a template
|
||||
parameter to avoid the expensive `<locale>` include.
|
||||
|
||||
::: format(const Locale&, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: format_to(OutputIt, const Locale&, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: formatted_size(const Locale&, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="legacy-checks"></a>
|
||||
### Legacy Compile-Time Checks
|
||||
|
||||
`FMT_STRING` enables compile-time checks on older compilers. It requires
|
||||
C++14 or later and is a no-op in C++11.
|
||||
|
||||
::: FMT_STRING
|
||||
|
||||
To force the use of legacy compile-time checks, define the preprocessor
|
||||
variable `FMT_ENFORCE_COMPILE_STRING`. When set, functions accepting
|
||||
`FMT_STRING` will fail to compile with regular strings.
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="ranges-api"></a>
|
||||
## Range and Tuple Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/ranges.h` provides formatting support for ranges and tuples:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/ranges.h>
|
||||
|
||||
fmt::print("{}", std::tuple<char, int>{'a', 42});
|
||||
// Output: ('a', 42)
|
||||
|
||||
Using `fmt::join`, you can separate tuple elements with a custom separator:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/ranges.h>
|
||||
|
||||
auto t = std::tuple<int, char>{1, 'a'};
|
||||
fmt::print("{}", fmt::join(t, ", "));
|
||||
// Output: 1, a
|
||||
|
||||
::: join(Range&&, string_view)
|
||||
|
||||
::: join(It, Sentinel, string_view)
|
||||
|
||||
::: join(std::initializer_list<T>, string_view)
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="chrono-api"></a>
|
||||
## Date and Time Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/chrono.h` provides formatters for
|
||||
|
||||
- [`std::chrono::duration`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/duration)
|
||||
- [`std::chrono::time_point`](
|
||||
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/time_point)
|
||||
- [`std::tm`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/chrono/c/tm)
|
||||
|
||||
The format syntax is described in [Chrono Format Specifications](syntax.md#
|
||||
chrono-format-specifications).
|
||||
|
||||
**Example**:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/chrono.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr);
|
||||
|
||||
fmt::print("The date is {:%Y-%m-%d}.", fmt::localtime(t));
|
||||
// Output: The date is 2020-11-07.
|
||||
// (with 2020-11-07 replaced by the current date)
|
||||
|
||||
using namespace std::literals::chrono_literals;
|
||||
|
||||
fmt::print("Default format: {} {}\n", 42s, 100ms);
|
||||
// Output: Default format: 42s 100ms
|
||||
|
||||
fmt::print("strftime-like format: {:%H:%M:%S}\n", 3h + 15min + 30s);
|
||||
// Output: strftime-like format: 03:15:30
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
::: localtime(std::time_t)
|
||||
|
||||
::: gmtime(std::time_t)
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="std-api"></a>
|
||||
## Standard Library Types Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/std.h` provides formatters for:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`std::atomic`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/atomic/atomic)
|
||||
- [`std::atomic_flag`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/atomic/atomic_flag)
|
||||
- [`std::bitset`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/bitset)
|
||||
- [`std::error_code`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/error/error_code)
|
||||
- [`std::exception`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/error/exception)
|
||||
- [`std::filesystem::path`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/filesystem/path)
|
||||
- [`std::monostate`](
|
||||
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/variant/monostate)
|
||||
- [`std::optional`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/optional)
|
||||
- [`std::source_location`](
|
||||
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/source_location)
|
||||
- [`std::thread::id`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/thread/id)
|
||||
- [`std::variant`](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/variant/variant)
|
||||
|
||||
::: ptr(const std::unique_ptr<T, Deleter>&)
|
||||
|
||||
::: ptr(const std::shared_ptr<T>&)
|
||||
|
||||
### Variants
|
||||
|
||||
A `std::variant` is only formattable if every variant alternative is
|
||||
formattable, and requires the `__cpp_lib_variant` [library
|
||||
feature](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/feature_test).
|
||||
|
||||
**Example**:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/std.h>
|
||||
|
||||
fmt::print("{}", std::variant<char, float>('x'));
|
||||
// Output: variant('x')
|
||||
|
||||
fmt::print("{}", std::variant<std::monostate, char>());
|
||||
// Output: variant(monostate)
|
||||
|
||||
## Bit-Fields and Packed Structs
|
||||
|
||||
To format a bit-field or a field of a struct with `__attribute__((packed))`
|
||||
applied to it, you need to convert it to the underlying or compatible type via
|
||||
a cast or a unary `+` ([godbolt](https://www.godbolt.org/z/3qKKs6T5Y)):
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
struct smol {
|
||||
int bit : 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
auto s = smol();
|
||||
fmt::print("{}", +s.bit);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is a known limitation of "perfect" forwarding in C++.
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="compile-api"></a>
|
||||
## Format String Compilation
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/compile.h` provides format string compilation and compile-time
|
||||
(`constexpr`) formatting enabled via the `FMT_COMPILE` macro or the `_cf`
|
||||
user-defined literal defined in namespace `fmt::literals`. Format strings
|
||||
marked with `FMT_COMPILE` or `_cf` are parsed, checked and converted into
|
||||
efficient formatting code at compile-time. This supports arguments of built-in
|
||||
and string types as well as user-defined types with `format` functions taking
|
||||
the format context type as a template parameter in their `formatter`
|
||||
specializations. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct fmt::formatter<point> {
|
||||
constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const point& p, FormatContext& ctx) const;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Format string compilation can generate more binary code compared to the
|
||||
default API and is only recommended in places where formatting is a
|
||||
performance bottleneck.
|
||||
|
||||
::: FMT_COMPILE
|
||||
|
||||
::: operator""_cf
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="color-api"></a>
|
||||
## Terminal Colors and Text Styles
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/color.h` provides support for terminal color and text style output.
|
||||
|
||||
::: print(const text_style&, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: fg(detail::color_type)
|
||||
|
||||
::: bg(detail::color_type)
|
||||
|
||||
::: styled(const T&, text_style)
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="os-api"></a>
|
||||
## System APIs
|
||||
|
||||
::: ostream
|
||||
|
||||
::: windows_error
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="ostream-api"></a>
|
||||
## `std::ostream` Support
|
||||
|
||||
`fmt/ostream.h` provides `std::ostream` support including formatting of
|
||||
user-defined types that have an overloaded insertion operator
|
||||
(`operator<<`). In order to make a type formattable via `std::ostream`
|
||||
you should provide a `formatter` specialization inherited from
|
||||
`ostream_formatter`:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/ostream.h>
|
||||
|
||||
struct date {
|
||||
int year, month, day;
|
||||
|
||||
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const date& d) {
|
||||
return os << d.year << '-' << d.month << '-' << d.day;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct fmt::formatter<date> : ostream_formatter {};
|
||||
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("The date is {}", date{2012, 12, 9});
|
||||
// s == "The date is 2012-12-9"
|
||||
|
||||
::: streamed(const T&)
|
||||
|
||||
::: print(std::ostream&, format_string<T...>, T&&...)
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="args-api"></a>
|
||||
## Dynamic Argument Lists
|
||||
|
||||
The header `fmt/args.h` provides `dynamic_format_arg_store`, a builder-like API
|
||||
that can be used to construct format argument lists dynamically.
|
||||
|
||||
::: dynamic_format_arg_store
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="printf-api"></a>
|
||||
## Safe `printf`
|
||||
|
||||
The header `fmt/printf.h` provides `printf`-like formatting
|
||||
functionality. The following functions use [printf format string
|
||||
syntax](https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/009695399/functions/fprintf.html)
|
||||
with the POSIX extension for positional arguments. Unlike their standard
|
||||
counterparts, the `fmt` functions are type-safe and throw an exception
|
||||
if an argument type doesn't match its format specification.
|
||||
|
||||
::: printf(string_view, const T&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: fprintf(std::FILE*, const S&, const T&...)
|
||||
|
||||
::: sprintf(const S&, const T&...)
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="xchar-api"></a>
|
||||
## Wide Strings
|
||||
|
||||
The optional header `fmt/xchar.h` provides support for `wchar_t` and
|
||||
exotic character types.
|
||||
|
||||
::: is_char
|
||||
|
||||
::: wstring_view
|
||||
|
||||
::: wformat_context
|
||||
|
||||
::: to_wstring(const T&)
|
||||
|
||||
## Compatibility with C++20 `std::format`
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} implements nearly all of the [C++20 formatting
|
||||
library](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format) with the
|
||||
following differences:
|
||||
|
||||
- Names are defined in the `fmt` namespace instead of `std` to avoid
|
||||
collisions with standard library implementations.
|
||||
- Width calculation doesn't use grapheme clusterization. The latter has
|
||||
been implemented in a separate branch but hasn't been integrated yet.
|
||||
61
extlib/libfmt/doc/fmt.css
vendored
Normal file
61
extlib/libfmt/doc/fmt.css
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
:root {
|
||||
--md-primary-fg-color: #0050D0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.md-grid {
|
||||
max-width: 960px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@media (min-width: 400px) {
|
||||
.md-tabs {
|
||||
display: block;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.docblock {
|
||||
border-left: .05rem solid var(--md-primary-fg-color);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.docblock-desc {
|
||||
margin-left: 1em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pre > code.decl {
|
||||
white-space: pre-wrap;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
code.decl > div {
|
||||
text-indent: -2ch; /* Negative indent to counteract the indent on the first line */
|
||||
padding-left: 2ch; /* Add padding to the left to create an indent */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.features-container {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
flex-wrap: wrap;
|
||||
gap: 20px;
|
||||
justify-content: center; /* Center the items horizontally */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.feature {
|
||||
flex: 1 1 calc(50% - 20px); /* Two columns with space between */
|
||||
max-width: 600px; /* Set the maximum width for the feature boxes */
|
||||
box-sizing: border-box;
|
||||
padding: 10px;
|
||||
overflow: hidden; /* Hide overflow content */
|
||||
text-overflow: ellipsis; /* Handle text overflow */
|
||||
white-space: normal; /* Allow text wrapping */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.feature h2 {
|
||||
margin-top: 0px;
|
||||
font-weight: bold;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@media (max-width: 768px) {
|
||||
.feature {
|
||||
flex: 1 1 100%; /* Stack columns on smaller screens */
|
||||
max-width: 100%; /* Allow full width on smaller screens */
|
||||
white-space: normal; /* Allow text wrapping on smaller screens */
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
4
extlib/libfmt/doc/fmt.js
vendored
Normal file
4
extlib/libfmt/doc/fmt.js
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
document$.subscribe(() => {
|
||||
hljs.highlightAll(),
|
||||
{ language: 'c++' }
|
||||
})
|
||||
222
extlib/libfmt/doc/get-started.md
vendored
Normal file
222
extlib/libfmt/doc/get-started.md
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,222 @@
|
||||
# Get Started
|
||||
|
||||
Compile and run {fmt} examples online with [Compiler Explorer](
|
||||
https://godbolt.org/z/P7h6cd6o3).
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is compatible with any build system. The next section describes its usage
|
||||
with CMake, while the [Build Systems](#build-systems) section covers the rest.
|
||||
|
||||
## CMake
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} provides two CMake targets: `fmt::fmt` for the compiled library and
|
||||
`fmt::fmt-header-only` for the header-only library. It is recommended to use
|
||||
the compiled library for improved build times.
|
||||
|
||||
There are three primary ways to use {fmt} with CMake:
|
||||
|
||||
* **FetchContent**: Starting from CMake 3.11, you can use [`FetchContent`](
|
||||
https://cmake.org/cmake/help/v3.30/module/FetchContent.html) to automatically
|
||||
download {fmt} as a dependency at configure time:
|
||||
|
||||
include(FetchContent)
|
||||
|
||||
FetchContent_Declare(
|
||||
fmt
|
||||
GIT_REPOSITORY https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt
|
||||
GIT_TAG e69e5f977d458f2650bb346dadf2ad30c5320281) # 10.2.1
|
||||
FetchContent_MakeAvailable(fmt)
|
||||
|
||||
target_link_libraries(<your-target> fmt::fmt)
|
||||
|
||||
* **Installed**: You can find and use an [installed](#installation) version of
|
||||
{fmt} in your `CMakeLists.txt` file as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
find_package(fmt)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(<your-target> fmt::fmt)
|
||||
|
||||
* **Embedded**: You can add the {fmt} source tree to your project and include it
|
||||
in your `CMakeLists.txt` file:
|
||||
|
||||
add_subdirectory(fmt)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(<your-target> fmt::fmt)
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
### Debian/Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
To install {fmt} on Debian, Ubuntu, or any other Debian-based Linux
|
||||
distribution, use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
apt install libfmt-dev
|
||||
|
||||
### Homebrew
|
||||
|
||||
Install {fmt} on macOS using [Homebrew](https://brew.sh/):
|
||||
|
||||
brew install fmt
|
||||
|
||||
### Conda
|
||||
|
||||
Install {fmt} on Linux, macOS, and Windows with [Conda](
|
||||
https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/), using its [conda-forge package](
|
||||
https://github.com/conda-forge/fmt-feedstock):
|
||||
|
||||
conda install -c conda-forge fmt
|
||||
|
||||
### vcpkg
|
||||
|
||||
Download and install {fmt} using the vcpkg package manager:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg.git
|
||||
cd vcpkg
|
||||
./bootstrap-vcpkg.sh
|
||||
./vcpkg integrate install
|
||||
./vcpkg install fmt
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- The fmt package in vcpkg is kept up to date by Microsoft team members and
|
||||
community contributors. If the version is out of date, please [create an
|
||||
issue or pull request](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) on the vcpkg
|
||||
repository. -->
|
||||
|
||||
## Building from Source
|
||||
|
||||
CMake works by generating native makefiles or project files that can be
|
||||
used in the compiler environment of your choice. The typical workflow
|
||||
starts with:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir build # Create a directory to hold the build output.
|
||||
cd build
|
||||
cmake .. # Generate native build scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
run in the `fmt` repository.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are on a Unix-like system, you should now see a Makefile in the
|
||||
current directory. Now you can build the library by running `make`.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the library has been built you can invoke `make test` to run the tests.
|
||||
|
||||
You can control generation of the make `test` target with the `FMT_TEST`
|
||||
CMake option. This can be useful if you include fmt as a subdirectory in
|
||||
your project but don't want to add fmt's tests to your `test` target.
|
||||
|
||||
To build a shared library set the `BUILD_SHARED_LIBS` CMake variable to `TRUE`:
|
||||
|
||||
cmake -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=TRUE ..
|
||||
|
||||
To build a static library with position-independent code (e.g. for
|
||||
linking it into another shared library such as a Python extension), set the
|
||||
`CMAKE_POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE` CMake variable to `TRUE`:
|
||||
|
||||
cmake -DCMAKE_POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE=TRUE ..
|
||||
|
||||
After building the library you can install it on a Unix-like system by
|
||||
running `sudo make install`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Building the Docs
|
||||
|
||||
To build the documentation you need the following software installed on
|
||||
your system:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Python](https://www.python.org/)
|
||||
- [Doxygen](http://www.stack.nl/~dimitri/doxygen/)
|
||||
- [MkDocs](https://www.mkdocs.org/) with `mkdocs-material`, `mkdocstrings`,
|
||||
`pymdown-extensions` and `mike`
|
||||
|
||||
First generate makefiles or project files using CMake as described in
|
||||
the previous section. Then compile the `doc` target/project, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
make doc
|
||||
|
||||
This will generate the HTML documentation in `doc/html`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Build Systems
|
||||
|
||||
### build2
|
||||
|
||||
You can use [build2](https://build2.org), a dependency manager and a build
|
||||
system, to use {fmt}.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently this package is available in these package repositories:
|
||||
|
||||
- <https://cppget.org/fmt/> for released and published versions.
|
||||
- <https://github.com/build2-packaging/fmt> for unreleased or custom versions.
|
||||
|
||||
**Usage:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `build2` package name: `fmt`
|
||||
- Library target name: `lib{fmt}`
|
||||
|
||||
To make your `build2` project depend on `fmt`:
|
||||
|
||||
- Add one of the repositories to your configurations, or in your
|
||||
`repositories.manifest`, if not already there:
|
||||
|
||||
:
|
||||
role: prerequisite
|
||||
location: https://pkg.cppget.org/1/stable
|
||||
|
||||
- Add this package as a dependency to your `manifest` file (example
|
||||
for version 10):
|
||||
|
||||
depends: fmt ~10.0.0
|
||||
|
||||
- Import the target and use it as a prerequisite to your own target
|
||||
using `fmt` in the appropriate `buildfile`:
|
||||
|
||||
import fmt = fmt%lib{fmt}
|
||||
lib{mylib} : cxx{**} ... $fmt
|
||||
|
||||
Then build your project as usual with `b` or `bdep update`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Meson
|
||||
|
||||
[Meson WrapDB](https://mesonbuild.com/Wrapdb-projects.html) includes an `fmt`
|
||||
package.
|
||||
|
||||
**Usage:**
|
||||
|
||||
- Install the `fmt` subproject from the WrapDB by running:
|
||||
|
||||
meson wrap install fmt
|
||||
|
||||
from the root of your project.
|
||||
|
||||
- In your project's `meson.build` file, add an entry for the new subproject:
|
||||
|
||||
fmt = subproject('fmt')
|
||||
fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_dep')
|
||||
|
||||
- Include the new dependency object to link with fmt:
|
||||
|
||||
my_build_target = executable(
|
||||
'name', 'src/main.cc', dependencies: [fmt_dep])
|
||||
|
||||
**Options:**
|
||||
|
||||
If desired, {fmt} can be built as a static library, or as a header-only library.
|
||||
|
||||
For a static build, use the following subproject definition:
|
||||
|
||||
fmt = subproject('fmt', default_options: 'default_library=static')
|
||||
fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_dep')
|
||||
|
||||
For the header-only version, use:
|
||||
|
||||
fmt = subproject('fmt', default_options: ['header-only=true'])
|
||||
fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_header_only_dep')
|
||||
|
||||
### Android NDK
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} provides [Android.mk file](
|
||||
https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/support/Android.mk) that can be used
|
||||
to build the library with [Android NDK](
|
||||
https://developer.android.com/tools/sdk/ndk/index.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### Other
|
||||
|
||||
To use the {fmt} library with any other build system, add
|
||||
`include/fmt/base.h`, `include/fmt/format.h`, `include/fmt/format-inl.h`,
|
||||
`src/format.cc` and optionally other headers from a [release archive](
|
||||
https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases) or the [git repository](
|
||||
https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt) to your project, add `include` to include
|
||||
directories and make sure `src/format.cc` is compiled and linked with your code.
|
||||
151
extlib/libfmt/doc/index.md
vendored
Normal file
151
extlib/libfmt/doc/index.md
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
hide:
|
||||
- navigation
|
||||
- toc
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# A modern formatting library
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="features-container">
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="feature">
|
||||
<h2>Safety</h2>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Inspired by Python's formatting facility, {fmt} provides a safe replacement
|
||||
for the <code>printf</code> family of functions. Errors in format strings,
|
||||
which are a common source of vulnerabilities in C, are <b>reported at
|
||||
compile time</b>. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><code class="language-cpp"
|
||||
>fmt::format("{:d}", "I am not a number");</code></pre>
|
||||
|
||||
will give a compile-time error because <code>d</code> is not a valid
|
||||
format specifier for strings. APIs like <a href="api/#format">
|
||||
<code>fmt::format</code></a> <b>prevent buffer overflow errors</b> via
|
||||
automatic memory management.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<a href="api#compile-time-checks">→ Learn more</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="feature">
|
||||
<h2>Extensibility</h2>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Formatting of most <b>standard types</b>, including all containers, dates,
|
||||
and times is <b>supported out-of-the-box</b>. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><code class="language-cpp"
|
||||
>fmt::print("{}", std::vector{1, 2, 3});</code></pre>
|
||||
|
||||
prints the vector in a JSON-like format:
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><code>[1, 2, 3]</code></pre>
|
||||
|
||||
You can <b>make your own types formattable</b> and even make compile-time
|
||||
checks work for them.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<a href="api#udt">→ Learn more</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="feature">
|
||||
<h2>Performance</h2>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
{fmt} can be anywhere from <b>tens of percent to 20-30 times faster</b> than
|
||||
iostreams and <code>sprintf</code>, especially for numeric formatting.
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt?tab=readme-ov-file#benchmarks">
|
||||
<img src="perf.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
The library <b>minimizes dynamic memory allocations</b> and can optionally
|
||||
<a href="api#compile-api">compile format strings</a> to optimal code.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="feature">
|
||||
<h2>Unicode support</h2>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
{fmt} provides <b>portable Unicode support</b> on major operating systems
|
||||
with UTF-8 and <code>char</code> strings. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><code class="language-cpp"
|
||||
>fmt::print("Слава Україні!");</code></pre>
|
||||
|
||||
will be printed correctly on Linux, macOS, and even Windows console,
|
||||
irrespective of the codepages.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
The default is <b>locale-independent</b>, but you can opt into localized
|
||||
formatting and {fmt} makes it work with Unicode, addressing issues in the
|
||||
standard libary.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="feature">
|
||||
<h2>Fast compilation</h2>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
The library makes extensive use of <b>type erasure</b> to achieve fast
|
||||
compilation. <code>fmt/base.h</code> provides a subset of the API with
|
||||
<b>minimal include dependencies</b> and enough functionality to replace
|
||||
all uses of <code>*printf</code>.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Code using {fmt} is usually several times faster to compile than the
|
||||
equivalent iostreams code, and while <code>printf</code> compiles faster
|
||||
still, the gap is narrowing.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<a href=
|
||||
"https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt?tab=readme-ov-file#compile-time-and-code-bloat">
|
||||
→ Learn more</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="feature">
|
||||
<h2>Small binary footprint</h2>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Type erasure is also used to prevent template bloat, resulting in <b>compact
|
||||
per-call binary code</b>. For example, a call to <code>fmt::print</code> with
|
||||
a single argument is just <a href="https://godbolt.org/g/TZU4KF">a few
|
||||
instructions</a>, comparable to <code>printf</code> despite adding
|
||||
runtime safety, and much smaller than the equivalent iostreams code.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
The library itself has small binary footprint and some components such as
|
||||
floating-point formatting can be disabled to make it even smaller for
|
||||
resource-constrained devices.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="feature">
|
||||
<h2>Portability</h2>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
{fmt} has a <b>small self-contained codebase</b> with the core consisting of
|
||||
just three headers and no external dependencies.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
The library is highly portable and requires only a minimal <b>subset of
|
||||
C++11</b> features which are available in GCC 4.9, Clang 3.4, MSVC 19.10
|
||||
(2017) and later. Newer compiler and standard library features are used
|
||||
if available, and enable additional functionality.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Where possible, the output of formatting functions is <b>consistent across
|
||||
platforms</b>.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="feature">
|
||||
<h2>Open source</h2>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
{fmt} is in the top hundred open-source C++ libraries on GitHub and has
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/graphs/contributors">hundreds of
|
||||
all-time contributors</a>.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
The library is distributed under a permissive MIT
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt#license">license</a> and is
|
||||
<b>relied upon by many open-source projects</b>, including Blender, PyTorch,
|
||||
Apple's FoundationDB, Windows Terminal, MongoDB, and others.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
1
extlib/libfmt/doc/perf.svg
vendored
Normal file
1
extlib/libfmt/doc/perf.svg
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1" viewBox="20 0 550 300" aria-label="A chart." style="overflow: hidden;"><defs id="_ABSTRACT_RENDERER_ID_0"><clipPath id="_ABSTRACT_RENDERER_ID_1"><rect x="120" y="45" width="560" height="210"></rect></clipPath></defs><rect x="0" y="0" width="800" height="300" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#ffffff"></rect><g><text text-anchor="start" x="120" y="27.05" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" font-weight="bold" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#000000">double to string</text><rect x="120" y="16" width="560" height="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill-opacity="0" fill="#ffffff"></rect></g><g><rect x="120" y="45" width="560" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill-opacity="0" fill="#ffffff"></rect><g clip-path="url(#_ABSTRACT_RENDERER_ID_1)"><g><rect x="120" y="45" width="1" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#cccccc"></rect><rect x="213" y="45" width="1" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#cccccc"></rect><rect x="306" y="45" width="1" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#cccccc"></rect><rect x="400" y="45" width="1" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#cccccc"></rect><rect x="493" y="45" width="1" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#cccccc"></rect><rect x="586" y="45" width="1" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#cccccc"></rect><rect x="679" y="45" width="1" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#cccccc"></rect></g><g><rect x="121" y="53" width="450" height="26" stroke="#ff9900" stroke-width="1" fill="#ff9900"></rect><rect x="121" y="95" width="421" height="26" stroke="#109618" stroke-width="1" fill="#109618"></rect><rect x="121" y="137" width="341" height="26" stroke="#990099" stroke-width="1" fill="#990099"></rect><rect x="121" y="179" width="31" height="26" stroke="#3366cc" stroke-width="1" fill="#3366cc"></rect><rect x="121" y="221" width="15" height="26" stroke="#dc3912" stroke-width="1" fill="#dc3912"></rect></g><g><rect x="120" y="45" width="1" height="210" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#333333"></rect></g></g><g></g><g><g><text text-anchor="middle" x="120.5" y="272.3833333333333" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#444444">0</text></g><g><text text-anchor="middle" x="213.6667" y="272.3833333333333" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#444444">250</text></g><g><text text-anchor="middle" x="306.8333" y="272.3833333333333" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#444444">500</text></g><g><text text-anchor="middle" x="400" y="272.3833333333333" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#444444">750</text></g><g><text text-anchor="middle" x="493.1667" y="272.3833333333333" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#444444">1,000</text></g><g><text text-anchor="middle" x="586.3333" y="272.3833333333333" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#444444">1,250</text></g><g><text text-anchor="middle" x="679.5" y="272.3833333333333" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#444444">1,500</text></g><g><text text-anchor="end" x="107" y="70.95" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#222222">ostringstream</text></g><g><text text-anchor="end" x="107" y="112.74999999999999" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#222222">ostrstream</text></g><g><text text-anchor="end" x="107" y="154.55" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#222222">sprintf</text></g><g><text text-anchor="end" x="107" y="196.35" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#222222">doubleconv</text></g><g><text text-anchor="end" x="107" y="238.15" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#222222">fmt</text></g></g></g><g><g><text text-anchor="middle" x="300" y="291.71666666666664" font-family="Arial" font-size="13" font-style="italic" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill="#222222">Time (ns), smaller is better</text><rect x="120" y="280.66666666666663" width="560" height="13" stroke="none" stroke-width="0" fill-opacity="0" fill="#ffffff"></rect></g></g><g></g></svg>
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.3 KiB |
290
extlib/libfmt/doc/python-license.txt
vendored
Normal file
290
extlib/libfmt/doc/python-license.txt
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
|
||||
A. HISTORY OF THE SOFTWARE
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
|
||||
Python was created in the early 1990s by Guido van Rossum at Stichting
|
||||
Mathematisch Centrum (CWI, see http://www.cwi.nl) in the Netherlands
|
||||
as a successor of a language called ABC. Guido remains Python's
|
||||
principal author, although it includes many contributions from others.
|
||||
|
||||
In 1995, Guido continued his work on Python at the Corporation for
|
||||
National Research Initiatives (CNRI, see http://www.cnri.reston.va.us)
|
||||
in Reston, Virginia where he released several versions of the
|
||||
software.
|
||||
|
||||
In May 2000, Guido and the Python core development team moved to
|
||||
BeOpen.com to form the BeOpen PythonLabs team. In October of the same
|
||||
year, the PythonLabs team moved to Digital Creations (now Zope
|
||||
Corporation, see http://www.zope.com). In 2001, the Python Software
|
||||
Foundation (PSF, see http://www.python.org/psf/) was formed, a
|
||||
non-profit organization created specifically to own Python-related
|
||||
Intellectual Property. Zope Corporation is a sponsoring member of
|
||||
the PSF.
|
||||
|
||||
All Python releases are Open Source (see http://www.opensource.org for
|
||||
the Open Source Definition). Historically, most, but not all, Python
|
||||
releases have also been GPL-compatible; the table below summarizes
|
||||
the various releases.
|
||||
|
||||
Release Derived Year Owner GPL-
|
||||
from compatible? (1)
|
||||
|
||||
0.9.0 thru 1.2 1991-1995 CWI yes
|
||||
1.3 thru 1.5.2 1.2 1995-1999 CNRI yes
|
||||
1.6 1.5.2 2000 CNRI no
|
||||
2.0 1.6 2000 BeOpen.com no
|
||||
1.6.1 1.6 2001 CNRI yes (2)
|
||||
2.1 2.0+1.6.1 2001 PSF no
|
||||
2.0.1 2.0+1.6.1 2001 PSF yes
|
||||
2.1.1 2.1+2.0.1 2001 PSF yes
|
||||
2.2 2.1.1 2001 PSF yes
|
||||
2.1.2 2.1.1 2002 PSF yes
|
||||
2.1.3 2.1.2 2002 PSF yes
|
||||
2.2.1 2.2 2002 PSF yes
|
||||
2.2.2 2.2.1 2002 PSF yes
|
||||
2.2.3 2.2.2 2003 PSF yes
|
||||
2.3 2.2.2 2002-2003 PSF yes
|
||||
2.3.1 2.3 2002-2003 PSF yes
|
||||
2.3.2 2.3.1 2002-2003 PSF yes
|
||||
2.3.3 2.3.2 2002-2003 PSF yes
|
||||
2.3.4 2.3.3 2004 PSF yes
|
||||
2.3.5 2.3.4 2005 PSF yes
|
||||
2.4 2.3 2004 PSF yes
|
||||
2.4.1 2.4 2005 PSF yes
|
||||
2.4.2 2.4.1 2005 PSF yes
|
||||
2.4.3 2.4.2 2006 PSF yes
|
||||
2.4.4 2.4.3 2006 PSF yes
|
||||
2.5 2.4 2006 PSF yes
|
||||
2.5.1 2.5 2007 PSF yes
|
||||
2.5.2 2.5.1 2008 PSF yes
|
||||
2.5.3 2.5.2 2008 PSF yes
|
||||
2.6 2.5 2008 PSF yes
|
||||
2.6.1 2.6 2008 PSF yes
|
||||
2.6.2 2.6.1 2009 PSF yes
|
||||
2.6.3 2.6.2 2009 PSF yes
|
||||
2.6.4 2.6.3 2009 PSF yes
|
||||
2.6.5 2.6.4 2010 PSF yes
|
||||
3.0 2.6 2008 PSF yes
|
||||
3.0.1 3.0 2009 PSF yes
|
||||
3.1 3.0.1 2009 PSF yes
|
||||
3.1.1 3.1 2009 PSF yes
|
||||
3.1.2 3.1.1 2010 PSF yes
|
||||
3.1.3 3.1.2 2010 PSF yes
|
||||
3.1.4 3.1.3 2011 PSF yes
|
||||
3.2 3.1 2011 PSF yes
|
||||
3.2.1 3.2 2011 PSF yes
|
||||
3.2.2 3.2.1 2011 PSF yes
|
||||
3.2.3 3.2.2 2012 PSF yes
|
||||
3.3.0 3.2 2012 PSF yes
|
||||
|
||||
Footnotes:
|
||||
|
||||
(1) GPL-compatible doesn't mean that we're distributing Python under
|
||||
the GPL. All Python licenses, unlike the GPL, let you distribute
|
||||
a modified version without making your changes open source. The
|
||||
GPL-compatible licenses make it possible to combine Python with
|
||||
other software that is released under the GPL; the others don't.
|
||||
|
||||
(2) According to Richard Stallman, 1.6.1 is not GPL-compatible,
|
||||
because its license has a choice of law clause. According to
|
||||
CNRI, however, Stallman's lawyer has told CNRI's lawyer that 1.6.1
|
||||
is "not incompatible" with the GPL.
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to the many outside volunteers who have worked under Guido's
|
||||
direction to make these releases possible.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
B. TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR ACCESSING OR OTHERWISE USING PYTHON
|
||||
===============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
PYTHON SOFTWARE FOUNDATION LICENSE VERSION 2
|
||||
--------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
1. This LICENSE AGREEMENT is between the Python Software Foundation
|
||||
("PSF"), and the Individual or Organization ("Licensee") accessing and
|
||||
otherwise using this software ("Python") in source or binary form and
|
||||
its associated documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Subject to the terms and conditions of this License Agreement, PSF hereby
|
||||
grants Licensee a nonexclusive, royalty-free, world-wide license to reproduce,
|
||||
analyze, test, perform and/or display publicly, prepare derivative works,
|
||||
distribute, and otherwise use Python alone or in any derivative version,
|
||||
provided, however, that PSF's License Agreement and PSF's notice of copyright,
|
||||
i.e., "Copyright (c) 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010,
|
||||
2011, 2012 Python Software Foundation; All Rights Reserved" are retained in Python
|
||||
alone or in any derivative version prepared by Licensee.
|
||||
|
||||
3. In the event Licensee prepares a derivative work that is based on
|
||||
or incorporates Python or any part thereof, and wants to make
|
||||
the derivative work available to others as provided herein, then
|
||||
Licensee hereby agrees to include in any such work a brief summary of
|
||||
the changes made to Python.
|
||||
|
||||
4. PSF is making Python available to Licensee on an "AS IS"
|
||||
basis. PSF MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED. BY WAY OF EXAMPLE, BUT NOT LIMITATION, PSF MAKES NO AND
|
||||
DISCLAIMS ANY REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
|
||||
FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR THAT THE USE OF PYTHON WILL NOT
|
||||
INFRINGE ANY THIRD PARTY RIGHTS.
|
||||
|
||||
5. PSF SHALL NOT BE LIABLE TO LICENSEE OR ANY OTHER USERS OF PYTHON
|
||||
FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR LOSS AS
|
||||
A RESULT OF MODIFYING, DISTRIBUTING, OR OTHERWISE USING PYTHON,
|
||||
OR ANY DERIVATIVE THEREOF, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY THEREOF.
|
||||
|
||||
6. This License Agreement will automatically terminate upon a material
|
||||
breach of its terms and conditions.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Nothing in this License Agreement shall be deemed to create any
|
||||
relationship of agency, partnership, or joint venture between PSF and
|
||||
Licensee. This License Agreement does not grant permission to use PSF
|
||||
trademarks or trade name in a trademark sense to endorse or promote
|
||||
products or services of Licensee, or any third party.
|
||||
|
||||
8. By copying, installing or otherwise using Python, Licensee
|
||||
agrees to be bound by the terms and conditions of this License
|
||||
Agreement.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BEOPEN.COM LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR PYTHON 2.0
|
||||
-------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
BEOPEN PYTHON OPEN SOURCE LICENSE AGREEMENT VERSION 1
|
||||
|
||||
1. This LICENSE AGREEMENT is between BeOpen.com ("BeOpen"), having an
|
||||
office at 160 Saratoga Avenue, Santa Clara, CA 95051, and the
|
||||
Individual or Organization ("Licensee") accessing and otherwise using
|
||||
this software in source or binary form and its associated
|
||||
documentation ("the Software").
|
||||
|
||||
2. Subject to the terms and conditions of this BeOpen Python License
|
||||
Agreement, BeOpen hereby grants Licensee a non-exclusive,
|
||||
royalty-free, world-wide license to reproduce, analyze, test, perform
|
||||
and/or display publicly, prepare derivative works, distribute, and
|
||||
otherwise use the Software alone or in any derivative version,
|
||||
provided, however, that the BeOpen Python License is retained in the
|
||||
Software, alone or in any derivative version prepared by Licensee.
|
||||
|
||||
3. BeOpen is making the Software available to Licensee on an "AS IS"
|
||||
basis. BEOPEN MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED. BY WAY OF EXAMPLE, BUT NOT LIMITATION, BEOPEN MAKES NO AND
|
||||
DISCLAIMS ANY REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
|
||||
FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR THAT THE USE OF THE SOFTWARE WILL NOT
|
||||
INFRINGE ANY THIRD PARTY RIGHTS.
|
||||
|
||||
4. BEOPEN SHALL NOT BE LIABLE TO LICENSEE OR ANY OTHER USERS OF THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR LOSS
|
||||
AS A RESULT OF USING, MODIFYING OR DISTRIBUTING THE SOFTWARE, OR ANY
|
||||
DERIVATIVE THEREOF, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY THEREOF.
|
||||
|
||||
5. This License Agreement will automatically terminate upon a material
|
||||
breach of its terms and conditions.
|
||||
|
||||
6. This License Agreement shall be governed by and interpreted in all
|
||||
respects by the law of the State of California, excluding conflict of
|
||||
law provisions. Nothing in this License Agreement shall be deemed to
|
||||
create any relationship of agency, partnership, or joint venture
|
||||
between BeOpen and Licensee. This License Agreement does not grant
|
||||
permission to use BeOpen trademarks or trade names in a trademark
|
||||
sense to endorse or promote products or services of Licensee, or any
|
||||
third party. As an exception, the "BeOpen Python" logos available at
|
||||
http://www.pythonlabs.com/logos.html may be used according to the
|
||||
permissions granted on that web page.
|
||||
|
||||
7. By copying, installing or otherwise using the software, Licensee
|
||||
agrees to be bound by the terms and conditions of this License
|
||||
Agreement.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
CNRI LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR PYTHON 1.6.1
|
||||
---------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
1. This LICENSE AGREEMENT is between the Corporation for National
|
||||
Research Initiatives, having an office at 1895 Preston White Drive,
|
||||
Reston, VA 20191 ("CNRI"), and the Individual or Organization
|
||||
("Licensee") accessing and otherwise using Python 1.6.1 software in
|
||||
source or binary form and its associated documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Subject to the terms and conditions of this License Agreement, CNRI
|
||||
hereby grants Licensee a nonexclusive, royalty-free, world-wide
|
||||
license to reproduce, analyze, test, perform and/or display publicly,
|
||||
prepare derivative works, distribute, and otherwise use Python 1.6.1
|
||||
alone or in any derivative version, provided, however, that CNRI's
|
||||
License Agreement and CNRI's notice of copyright, i.e., "Copyright (c)
|
||||
1995-2001 Corporation for National Research Initiatives; All Rights
|
||||
Reserved" are retained in Python 1.6.1 alone or in any derivative
|
||||
version prepared by Licensee. Alternately, in lieu of CNRI's License
|
||||
Agreement, Licensee may substitute the following text (omitting the
|
||||
quotes): "Python 1.6.1 is made available subject to the terms and
|
||||
conditions in CNRI's License Agreement. This Agreement together with
|
||||
Python 1.6.1 may be located on the Internet using the following
|
||||
unique, persistent identifier (known as a handle): 1895.22/1013. This
|
||||
Agreement may also be obtained from a proxy server on the Internet
|
||||
using the following URL: http://hdl.handle.net/1895.22/1013".
|
||||
|
||||
3. In the event Licensee prepares a derivative work that is based on
|
||||
or incorporates Python 1.6.1 or any part thereof, and wants to make
|
||||
the derivative work available to others as provided herein, then
|
||||
Licensee hereby agrees to include in any such work a brief summary of
|
||||
the changes made to Python 1.6.1.
|
||||
|
||||
4. CNRI is making Python 1.6.1 available to Licensee on an "AS IS"
|
||||
basis. CNRI MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED. BY WAY OF EXAMPLE, BUT NOT LIMITATION, CNRI MAKES NO AND
|
||||
DISCLAIMS ANY REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
|
||||
FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR THAT THE USE OF PYTHON 1.6.1 WILL NOT
|
||||
INFRINGE ANY THIRD PARTY RIGHTS.
|
||||
|
||||
5. CNRI SHALL NOT BE LIABLE TO LICENSEE OR ANY OTHER USERS OF PYTHON
|
||||
1.6.1 FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR LOSS AS
|
||||
A RESULT OF MODIFYING, DISTRIBUTING, OR OTHERWISE USING PYTHON 1.6.1,
|
||||
OR ANY DERIVATIVE THEREOF, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY THEREOF.
|
||||
|
||||
6. This License Agreement will automatically terminate upon a material
|
||||
breach of its terms and conditions.
|
||||
|
||||
7. This License Agreement shall be governed by the federal
|
||||
intellectual property law of the United States, including without
|
||||
limitation the federal copyright law, and, to the extent such
|
||||
U.S. federal law does not apply, by the law of the Commonwealth of
|
||||
Virginia, excluding Virginia's conflict of law provisions.
|
||||
Notwithstanding the foregoing, with regard to derivative works based
|
||||
on Python 1.6.1 that incorporate non-separable material that was
|
||||
previously distributed under the GNU General Public License (GPL), the
|
||||
law of the Commonwealth of Virginia shall govern this License
|
||||
Agreement only as to issues arising under or with respect to
|
||||
Paragraphs 4, 5, and 7 of this License Agreement. Nothing in this
|
||||
License Agreement shall be deemed to create any relationship of
|
||||
agency, partnership, or joint venture between CNRI and Licensee. This
|
||||
License Agreement does not grant permission to use CNRI trademarks or
|
||||
trade name in a trademark sense to endorse or promote products or
|
||||
services of Licensee, or any third party.
|
||||
|
||||
8. By clicking on the "ACCEPT" button where indicated, or by copying,
|
||||
installing or otherwise using Python 1.6.1, Licensee agrees to be
|
||||
bound by the terms and conditions of this License Agreement.
|
||||
|
||||
ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
CWI LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR PYTHON 0.9.0 THROUGH 1.2
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 1991 - 1995, Stichting Mathematisch Centrum Amsterdam,
|
||||
The Netherlands. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Permission to use, copy, modify, and distribute this software and its
|
||||
documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby granted,
|
||||
provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and that
|
||||
both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear in
|
||||
supporting documentation, and that the name of Stichting Mathematisch
|
||||
Centrum or CWI not be used in advertising or publicity pertaining to
|
||||
distribution of the software without specific, written prior
|
||||
permission.
|
||||
|
||||
STICHTING MATHEMATISCH CENTRUM DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES WITH REGARD TO
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
|
||||
FITNESS, IN NO EVENT SHALL STICHTING MATHEMATISCH CENTRUM BE LIABLE
|
||||
FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES
|
||||
WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER IN AN
|
||||
ACTION OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE OR OTHER TORTIOUS ACTION, ARISING OUT
|
||||
OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
|
||||
886
extlib/libfmt/doc/syntax.md
vendored
Normal file
886
extlib/libfmt/doc/syntax.md
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,886 @@
|
||||
# Format String Syntax
|
||||
|
||||
Formatting functions such as [`fmt::format`](api.md#format) and [`fmt::print`](
|
||||
api.md#print) use the same format string syntax described in this section.
|
||||
|
||||
Format strings contain "replacement fields" surrounded by curly braces `{}`.
|
||||
Anything that is not contained in braces is considered literal text, which is
|
||||
copied unchanged to the output. If you need to include a brace character in
|
||||
the literal text, it can be escaped by doubling: `{{` and `}}`.
|
||||
|
||||
The grammar for a replacement field is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="replacement-field"></a>
|
||||
<pre><code class="language-json"
|
||||
>replacement_field ::= "{" [arg_id] [":" (<a href="#format-spec"
|
||||
>format_spec</a> | <a href="#chrono-format-spec">chrono_format_spec</a>)] "}"
|
||||
arg_id ::= integer | identifier
|
||||
integer ::= digit+
|
||||
digit ::= "0"..."9"
|
||||
identifier ::= id_start id_continue*
|
||||
id_start ::= "a"..."z" | "A"..."Z" | "_"
|
||||
id_continue ::= id_start | digit</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
In less formal terms, the replacement field can start with an *arg_id* that
|
||||
specifies the argument whose value is to be formatted and inserted into the
|
||||
output instead of the replacement field. The *arg_id* is optionally followed
|
||||
by a *format_spec*, which is preceded by a colon `':'`. These specify a
|
||||
non-default format for the replacement value.
|
||||
|
||||
See also the [Format Specification
|
||||
Mini-Language](#format-specification-mini-language) section.
|
||||
|
||||
If the numerical arg_ids in a format string are 0, 1, 2, ... in sequence,
|
||||
they can all be omitted (not just some) and the numbers 0, 1, 2, ... will be
|
||||
automatically inserted in that order.
|
||||
|
||||
Named arguments can be referred to by their names or indices.
|
||||
|
||||
Some simple format string examples:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
"First, thou shalt count to {0}" // References the first argument
|
||||
"Bring me a {}" // Implicitly references the first argument
|
||||
"From {} to {}" // Same as "From {0} to {1}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The *format_spec* field contains a specification of how the value should
|
||||
be presented, including such details as field width, alignment, padding,
|
||||
decimal precision and so on. Each value type can define its own
|
||||
"formatting mini-language" or interpretation of the *format_spec*.
|
||||
|
||||
Most built-in types support a common formatting mini-language, which is
|
||||
described in the next section.
|
||||
|
||||
A *format_spec* field can also include nested replacement fields in
|
||||
certain positions within it. These nested replacement fields can contain
|
||||
only an argument id; format specifications are not allowed. This allows
|
||||
the formatting of a value to be dynamically specified.
|
||||
|
||||
See the [Format Examples](#format-examples) section for some examples.
|
||||
|
||||
## Format Specification Mini-Language
|
||||
|
||||
"Format specifications" are used within replacement fields contained within a
|
||||
format string to define how individual values are presented. Each formattable
|
||||
type may define how the format specification is to be interpreted.
|
||||
|
||||
Most built-in types implement the following options for format
|
||||
specifications, although some of the formatting options are only
|
||||
supported by the numeric types.
|
||||
|
||||
The general form of a *standard format specifier* is:
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="format-spec"></a>
|
||||
<pre><code class="language-json"
|
||||
>format_spec ::= [[fill]align][sign]["#"]["0"][width]["." precision]["L"][type]
|
||||
fill ::= <a character other than '{' or '}'>
|
||||
align ::= "<" | ">" | "^"
|
||||
sign ::= "+" | "-" | " "
|
||||
width ::= <a href="#replacement-field">integer</a> | "{" [<a
|
||||
href="#replacement-field">arg_id</a>] "}"
|
||||
precision ::= <a href="#replacement-field">integer</a> | "{" [<a
|
||||
href="#replacement-field">arg_id</a>] "}"
|
||||
type ::= "a" | "A" | "b" | "B" | "c" | "d" | "e" | "E" | "f" | "F" |
|
||||
"g" | "G" | "o" | "p" | "s" | "x" | "X" | "?"</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
The *fill* character can be any Unicode code point other than `'{'` or `'}'`.
|
||||
The presence of a fill character is signaled by the character following it,
|
||||
which must be one of the alignment options. If the second character of
|
||||
*format_spec* is not a valid alignment option, then it is assumed that both
|
||||
the fill character and the alignment option are absent.
|
||||
|
||||
The meaning of the various alignment options is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Option</th>
|
||||
<th>Meaning</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'<'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Forces the field to be left-aligned within the available space (this is the
|
||||
default for most objects).
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'>'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Forces the field to be right-aligned within the available space (this is
|
||||
the default for numbers).
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'^'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Forces the field to be centered within the available space.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
Note that unless a minimum field width is defined, the field width will
|
||||
always be the same size as the data to fill it, so that the alignment
|
||||
option has no meaning in this case.
|
||||
|
||||
The *sign* option is only valid for floating point and signed integer types,
|
||||
and can be one of the following:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Option</th>
|
||||
<th>Meaning</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'+'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Indicates that a sign should be used for both nonnegative as well as
|
||||
negative numbers.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'-'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Indicates that a sign should be used only for negative numbers (this is the
|
||||
default behavior).
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>space</td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Indicates that a leading space should be used on nonnegative numbers, and a
|
||||
minus sign on negative numbers.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
The `'#'` option causes the "alternate form" to be used for the
|
||||
conversion. The alternate form is defined differently for different
|
||||
types. This option is only valid for integer and floating-point types.
|
||||
For integers, when binary, octal, or hexadecimal output is used, this
|
||||
option adds the prefix respective `"0b"` (`"0B"`), `"0"`, or `"0x"`
|
||||
(`"0X"`) to the output value. Whether the prefix is lower-case or
|
||||
upper-case is determined by the case of the type specifier, for example,
|
||||
the prefix `"0x"` is used for the type `'x'` and `"0X"` is used for
|
||||
`'X'`. For floating-point numbers the alternate form causes the result
|
||||
of the conversion to always contain a decimal-point character, even if
|
||||
no digits follow it. Normally, a decimal-point character appears in the
|
||||
result of these conversions only if a digit follows it. In addition, for
|
||||
`'g'` and `'G'` conversions, trailing zeros are not removed from the
|
||||
result.
|
||||
|
||||
*width* is a decimal integer defining the minimum field width. If not
|
||||
specified, then the field width will be determined by the content.
|
||||
|
||||
Preceding the *width* field by a zero (`'0'`) character enables
|
||||
sign-aware zero-padding for numeric types. It forces the padding to be
|
||||
placed after the sign or base (if any) but before the digits. This is
|
||||
used for printing fields in the form "+000000120". This option is only
|
||||
valid for numeric types and it has no effect on formatting of infinity
|
||||
and NaN. This option is ignored when any alignment specifier is present.
|
||||
|
||||
The *precision* is a decimal number indicating how many digits should be
|
||||
displayed after the decimal point for a floating-point value formatted
|
||||
with `'f'` and `'F'`, or before and after the decimal point for a
|
||||
floating-point value formatted with `'g'` or `'G'`. For non-number types
|
||||
the field indicates the maximum field size - in other words, how many
|
||||
characters will be used from the field content. The *precision* is not
|
||||
allowed for integer, character, Boolean, and pointer values. Note that a
|
||||
C string must be null-terminated even if precision is specified.
|
||||
|
||||
The `'L'` option uses the current locale setting to insert the appropriate
|
||||
number separator characters. This option is only valid for numeric types.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, the *type* determines how the data should be presented.
|
||||
|
||||
The available string presentation types are:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Type</th>
|
||||
<th>Meaning</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'s'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
String format. This is the default type for strings and may be omitted.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'?'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Debug format. The string is quoted and special characters escaped.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>none</td>
|
||||
<td>The same as <code>'s'</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
The available character presentation types are:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Type</th>
|
||||
<th>Meaning</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'c'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Character format. This is the default type for characters and may be
|
||||
omitted.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'?'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Debug format. The character is quoted and special characters escaped.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>none</td>
|
||||
<td>The same as <code>'c'</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
The available integer presentation types are:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Type</th>
|
||||
<th>Meaning</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'b'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Binary format. Outputs the number in base 2. Using the <code>'#'</code>
|
||||
option with this type adds the prefix <code>"0b"</code> to the output value.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'B'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Binary format. Outputs the number in base 2. Using the <code>'#'</code>
|
||||
option with this type adds the prefix <code>"0B"</code> to the output value.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'c'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Character format. Outputs the number as a character.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'d'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Decimal integer. Outputs the number in base 10.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'o'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Octal format. Outputs the number in base 8.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'x'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Hex format. Outputs the number in base 16, using lower-case letters for the
|
||||
digits above 9. Using the <code>'#'</code> option with this type adds the
|
||||
prefix <code>"0x"</code> to the output value.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'X'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Hex format. Outputs the number in base 16, using upper-case letters for the
|
||||
digits above 9. Using the <code>'#'</code> option with this type adds the
|
||||
prefix <code>"0X"</code> to the output value.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>none</td>
|
||||
<td>The same as <code>'d'</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
Integer presentation types can also be used with character and Boolean values
|
||||
with the only exception that `'c'` cannot be used with `bool`. Boolean values
|
||||
are formatted using textual representation, either `true` or `false`, if the
|
||||
presentation type is not specified.
|
||||
|
||||
The available presentation types for floating-point values are:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Type</th>
|
||||
<th>Meaning</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'a'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Hexadecimal floating point format. Prints the number in base 16 with
|
||||
prefix <code>"0x"</code> and lower-case letters for digits above 9.
|
||||
Uses <code>'p'</code> to indicate the exponent.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'A'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Same as <code>'a'</code> except it uses upper-case letters for the
|
||||
prefix, digits above 9 and to indicate the exponent.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'e'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Exponent notation. Prints the number in scientific notation using
|
||||
the letter 'e' to indicate the exponent.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'E'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Exponent notation. Same as <code>'e'</code> except it uses an
|
||||
upper-case <code>'E'</code> as the separator character.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'f'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Fixed point. Displays the number as a fixed-point number.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'F'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Fixed point. Same as <code>'f'</code>, but converts <code>nan</code>
|
||||
to <code>NAN</code> and <code>inf</code> to <code>INF</code>.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'g'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<p>General format. For a given precision <code>p >= 1</code>,
|
||||
this rounds the number to <code>p</code> significant digits and then
|
||||
formats the result in either fixed-point format or in scientific
|
||||
notation, depending on its magnitude.</p>
|
||||
<p>A precision of <code>0</code> is treated as equivalent to a precision
|
||||
of <code>1</code>.</p>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'G'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
General format. Same as <code>'g'</code> except switches to
|
||||
<code>'E'</code> if the number gets too large. The representations of
|
||||
infinity and NaN are uppercased, too.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>none</td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Similar to <code>'g'</code>, except that the default precision is as
|
||||
high as needed to represent the particular value.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
The available presentation types for pointers are:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Type</th>
|
||||
<th>Meaning</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'p'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Pointer format. This is the default type for pointers and may be omitted.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>none</td>
|
||||
<td>The same as <code>'p'</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
## Chrono Format Specifications
|
||||
|
||||
Format specifications for chrono duration and time point types as well as
|
||||
`std::tm` have the following syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
<a id="chrono-format-spec"></a>
|
||||
<pre><code class="language-json"
|
||||
>chrono_format_spec ::= [[<a href="#format-spec">fill</a>]<a href="#format-spec"
|
||||
>align</a>][<a href="#format-spec">width</a>]["." <a href="#format-spec"
|
||||
>precision</a>][chrono_specs]
|
||||
chrono_specs ::= conversion_spec |
|
||||
chrono_specs (conversion_spec | literal_char)
|
||||
conversion_spec ::= "%" [padding_modifier] [locale_modifier] chrono_type
|
||||
literal_char ::= <a character other than '{', '}' or '%'>
|
||||
padding_modifier ::= "-" | "_" | "0"
|
||||
locale_modifier ::= "E" | "O"
|
||||
chrono_type ::= "a" | "A" | "b" | "B" | "c" | "C" | "d" | "D" | "e" |
|
||||
"F" | "g" | "G" | "h" | "H" | "I" | "j" | "m" | "M" |
|
||||
"n" | "p" | "q" | "Q" | "r" | "R" | "S" | "t" | "T" |
|
||||
"u" | "U" | "V" | "w" | "W" | "x" | "X" | "y" | "Y" |
|
||||
"z" | "Z" | "%"</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
Literal chars are copied unchanged to the output. Precision is valid only
|
||||
for `std::chrono::duration` types with a floating-point representation type.
|
||||
|
||||
The available presentation types (*chrono_type*) are:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th>Type</th>
|
||||
<th>Meaning</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'a'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The abbreviated weekday name, e.g. "Sat". If the value does not contain a
|
||||
valid weekday, an exception of type <code>format_error</code> is thrown.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'A'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The full weekday name, e.g. "Saturday". If the value does not contain a
|
||||
valid weekday, an exception of type <code>format_error</code> is thrown.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'b'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The abbreviated month name, e.g. "Nov". If the value does not contain a
|
||||
valid month, an exception of type <code>format_error</code> is thrown.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'B'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The full month name, e.g. "November". If the value does not contain a valid
|
||||
month, an exception of type <code>format_error</code> is thrown.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'c'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The date and time representation, e.g. "Sat Nov 12 22:04:00 1955". The
|
||||
modified command <code>%Ec</code> produces the locale's alternate date and
|
||||
time representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'C'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The year divided by 100 using floored division, e.g. "19". If the result
|
||||
is a single decimal digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command
|
||||
<code>%EC</code> produces the locale's alternative representation of the
|
||||
century.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'d'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The day of month as a decimal number. If the result is a single decimal
|
||||
digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command <code>%Od</code>
|
||||
produces the locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'D'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Equivalent to <code>%m/%d/%y</code>, e.g. "11/12/55".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'e'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The day of month as a decimal number. If the result is a single decimal
|
||||
digit, it is prefixed with a space. The modified command <code>%Oe</code>
|
||||
produces the locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'F'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Equivalent to <code>%Y-%m-%d</code>, e.g. "1955-11-12".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'g'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The last two decimal digits of the ISO week-based year. If the result is a
|
||||
single digit it is prefixed by 0.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'G'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The ISO week-based year as a decimal number. If the result is less than
|
||||
four digits it is left-padded with 0 to four digits.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'h'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Equivalent to <code>%b</code>, e.g. "Nov".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'H'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number. If the result is a single
|
||||
digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command <code>%OH</code>
|
||||
produces the locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'I'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number. If the result is a single
|
||||
digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command <code>%OI</code>
|
||||
produces the locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'j'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
If the type being formatted is a specialization of duration, the decimal
|
||||
number of days without padding. Otherwise, the day of the year as a decimal
|
||||
number. Jan 1 is 001. If the result is less than three digits, it is
|
||||
left-padded with 0 to three digits.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'m'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The month as a decimal number. Jan is 01. If the result is a single digit,
|
||||
it is prefixed with 0. The modified command <code>%Om</code> produces the
|
||||
locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'M'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The minute as a decimal number. If the result is a single digit, it
|
||||
is prefixed with 0. The modified command <code>%OM</code> produces the
|
||||
locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'n'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>A new-line character.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'p'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>The AM/PM designations associated with a 12-hour clock.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'q'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>The duration's unit suffix.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'Q'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The duration's numeric value (as if extracted via <code>.count()</code>).
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'r'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>The 12-hour clock time, e.g. "10:04:00 PM".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'R'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Equivalent to <code>%H:%M</code>, e.g. "22:04".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'S'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
Seconds as a decimal number. If the number of seconds is less than 10, the
|
||||
result is prefixed with 0. If the precision of the input cannot be exactly
|
||||
represented with seconds, then the format is a decimal floating-point number
|
||||
with a fixed format and a precision matching that of the precision of the
|
||||
input (or to a microseconds precision if the conversion to floating-point
|
||||
decimal seconds cannot be made within 18 fractional digits). The modified
|
||||
command <code>%OS</code> produces the locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'t'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>A horizontal-tab character.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'T'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>Equivalent to <code>%H:%M:%S</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'u'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The ISO weekday as a decimal number (1-7), where Monday is 1. The modified
|
||||
command <code>%Ou</code> produces the locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'U'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The week number of the year as a decimal number. The first Sunday of the
|
||||
year is the first day of week 01. Days of the same year prior to that are
|
||||
in week 00. If the result is a single digit, it is prefixed with 0.
|
||||
The modified command <code>%OU</code> produces the locale's alternative
|
||||
representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'V'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The ISO week-based week number as a decimal number. If the result is a
|
||||
single digit, it is prefixed with 0. The modified command <code>%OV</code>
|
||||
produces the locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'w'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The weekday as a decimal number (0-6), where Sunday is 0. The modified
|
||||
command <code>%Ow</code> produces the locale's alternative representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'W'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The week number of the year as a decimal number. The first Monday of the
|
||||
year is the first day of week 01. Days of the same year prior to that are
|
||||
in week 00. If the result is a single digit, it is prefixed with 0.
|
||||
The modified command <code>%OW</code> produces the locale's alternative
|
||||
representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'x'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The date representation, e.g. "11/12/55". The modified command
|
||||
<code>%Ex</code> produces the locale's alternate date representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'X'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The time representation, e.g. "10:04:00". The modified command
|
||||
<code>%EX</code> produces the locale's alternate time representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'y'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The last two decimal digits of the year. If the result is a single digit
|
||||
it is prefixed by 0. The modified command <code>%Oy</code> produces the
|
||||
locale's alternative representation. The modified command <code>%Ey</code>
|
||||
produces the locale's alternative representation of offset from
|
||||
<code>%EC</code> (year only).
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'Y'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The year as a decimal number. If the result is less than four digits it is
|
||||
left-padded with 0 to four digits. The modified command <code>%EY</code>
|
||||
produces the locale's alternative full year representation.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'z'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The offset from UTC in the ISO 8601:2004 format. For example -0430 refers
|
||||
to 4 hours 30 minutes behind UTC. If the offset is zero, +0000 is used.
|
||||
The modified commands <code>%Ez</code> and <code>%Oz</code> insert a
|
||||
<code>:</code> between the hours and minutes: -04:30. If the offset
|
||||
information is not available, an exception of type
|
||||
<code>format_error</code> is thrown.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'Z'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
The time zone abbreviation. If the time zone abbreviation is not available,
|
||||
an exception of type <code>format_error</code> is thrown.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><code>'%'</code></td>
|
||||
<td>A % character.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
Specifiers that have a calendaric component such as `'d'` (the day of month)
|
||||
are valid only for `std::tm` and time points but not durations.
|
||||
|
||||
The available padding modifiers (*padding_modifier*) are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Type | Meaning |
|
||||
|-------|-----------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `'_'` | Pad a numeric result with spaces. |
|
||||
| `'-'` | Do not pad a numeric result string. |
|
||||
| `'0'` | Pad a numeric result string with zeros. |
|
||||
|
||||
These modifiers are only supported for the `'H'`, `'I'`, `'M'`, `'S'`, `'U'`,
|
||||
`'V'`, `'W'`, `'Y'`, `'d'`, `'j'` and `'m'` presentation types.
|
||||
|
||||
## Range Format Specifications
|
||||
|
||||
Format specifications for range types have the following syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><code class="language-json"
|
||||
>range_format_spec ::= ["n"][range_type][range_underlying_spec]</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
The `'n'` option formats the range without the opening and closing brackets.
|
||||
|
||||
The available presentation types for `range_type` are:
|
||||
|
||||
| Type | Meaning |
|
||||
|--------|------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| none | Default format. |
|
||||
| `'s'` | String format. The range is formatted as a string. |
|
||||
| `'?s'` | Debug format. The range is formatted as an escaped string. |
|
||||
|
||||
If `range_type` is `'s'` or `'?s'`, the range element type must be a character
|
||||
type. The `'n'` option and `range_underlying_spec` are mutually exclusive with
|
||||
`'s'` and `'?s'`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `range_underlying_spec` is parsed based on the formatter of the range's
|
||||
element type.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, a range of characters or strings is printed escaped and quoted.
|
||||
But if any `range_underlying_spec` is provided (even if it is empty), then the
|
||||
characters or strings are printed according to the provided specification.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::print("{}", std::vector{10, 20, 30});
|
||||
// Output: [10, 20, 30]
|
||||
fmt::print("{::#x}", std::vector{10, 20, 30});
|
||||
// Output: [0xa, 0x14, 0x1e]
|
||||
fmt::print("{}", std::vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'});
|
||||
// Output: ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
|
||||
fmt::print("{:n}", std::vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'});
|
||||
// Output: 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'
|
||||
fmt::print("{:s}", std::vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'});
|
||||
// Output: "hello"
|
||||
fmt::print("{:?s}", std::vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\n'});
|
||||
// Output: "hello\n"
|
||||
fmt::print("{::}", std::vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'});
|
||||
// Output: [h, e, l, l, o]
|
||||
fmt::print("{::d}", std::vector{'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'});
|
||||
// Output: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Format Examples
|
||||
|
||||
This section contains examples of the format syntax and comparison with
|
||||
the printf formatting.
|
||||
|
||||
In most of the cases the syntax is similar to the printf formatting,
|
||||
with the addition of the `{}` and with `:` used instead of `%`. For
|
||||
example, `"%03.2f"` can be translated to `"{:03.2f}"`.
|
||||
|
||||
The new format syntax also supports new and different options, shown in
|
||||
the following examples.
|
||||
|
||||
Accessing arguments by position:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::format("{0}, {1}, {2}", 'a', 'b', 'c');
|
||||
// Result: "a, b, c"
|
||||
fmt::format("{}, {}, {}", 'a', 'b', 'c');
|
||||
// Result: "a, b, c"
|
||||
fmt::format("{2}, {1}, {0}", 'a', 'b', 'c');
|
||||
// Result: "c, b, a"
|
||||
fmt::format("{0}{1}{0}", "abra", "cad"); // arguments' indices can be repeated
|
||||
// Result: "abracadabra"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Aligning the text and specifying a width:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::format("{:<30}", "left aligned");
|
||||
// Result: "left aligned "
|
||||
fmt::format("{:>30}", "right aligned");
|
||||
// Result: " right aligned"
|
||||
fmt::format("{:^30}", "centered");
|
||||
// Result: " centered "
|
||||
fmt::format("{:*^30}", "centered"); // use '*' as a fill char
|
||||
// Result: "***********centered***********"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dynamic width:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::format("{:<{}}", "left aligned", 30);
|
||||
// Result: "left aligned "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dynamic precision:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::format("{:.{}f}", 3.14, 1);
|
||||
// Result: "3.1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Replacing `%+f`, `%-f`, and `% f` and specifying a sign:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::format("{:+f}; {:+f}", 3.14, -3.14); // show it always
|
||||
// Result: "+3.140000; -3.140000"
|
||||
fmt::format("{: f}; {: f}", 3.14, -3.14); // show a space for positive numbers
|
||||
// Result: " 3.140000; -3.140000"
|
||||
fmt::format("{:-f}; {:-f}", 3.14, -3.14); // show only the minus -- same as '{:f}; {:f}'
|
||||
// Result: "3.140000; -3.140000"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Replacing `%x` and `%o` and converting the value to different bases:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::format("int: {0:d}; hex: {0:x}; oct: {0:o}; bin: {0:b}", 42);
|
||||
// Result: "int: 42; hex: 2a; oct: 52; bin: 101010"
|
||||
// with 0x or 0 or 0b as prefix:
|
||||
fmt::format("int: {0:d}; hex: {0:#x}; oct: {0:#o}; bin: {0:#b}", 42);
|
||||
// Result: "int: 42; hex: 0x2a; oct: 052; bin: 0b101010"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Padded hex byte with prefix and always prints both hex characters:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::format("{:#04x}", 0);
|
||||
// Result: "0x00"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Box drawing using Unicode fill:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
fmt::print(
|
||||
"┌{0:─^{2}}┐\n"
|
||||
"│{1: ^{2}}│\n"
|
||||
"└{0:─^{2}}┘\n", "", "Hello, world!", 20);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
prints:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
┌────────────────────┐
|
||||
│ Hello, world! │
|
||||
└────────────────────┘
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Using type-specific formatting:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/chrono.h>
|
||||
|
||||
auto t = tm();
|
||||
t.tm_year = 2010 - 1900;
|
||||
t.tm_mon = 7;
|
||||
t.tm_mday = 4;
|
||||
t.tm_hour = 12;
|
||||
t.tm_min = 15;
|
||||
t.tm_sec = 58;
|
||||
fmt::print("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t);
|
||||
// Prints: 2010-08-04 12:15:58
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Using the comma as a thousands separator:
|
||||
|
||||
```c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
|
||||
auto s = fmt::format(std::locale("en_US.UTF-8"), "{:L}", 1234567890);
|
||||
// s == "1,234,567,890"
|
||||
```
|
||||
220
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/args.h
vendored
Normal file
220
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/args.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - dynamic argument lists
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_ARGS_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_ARGS_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <functional> // std::reference_wrapper
|
||||
# include <memory> // std::unique_ptr
|
||||
# include <vector>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h" // std_string_view
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct is_reference_wrapper : std::false_type {};
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct is_reference_wrapper<std::reference_wrapper<T>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> auto unwrap(const T& v) -> const T& { return v; }
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto unwrap(const std::reference_wrapper<T>& v) -> const T& {
|
||||
return static_cast<const T&>(v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// node is defined outside dynamic_arg_list to workaround a C2504 bug in MSVC
|
||||
// 2022 (v17.10.0).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Workaround for clang's -Wweak-vtables. Unlike for regular classes, for
|
||||
// templates it doesn't complain about inability to deduce single translation
|
||||
// unit for placing vtable. So node is made a fake template.
|
||||
template <typename = void> struct node {
|
||||
virtual ~node() = default;
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<node<>> next;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class dynamic_arg_list {
|
||||
template <typename T> struct typed_node : node<> {
|
||||
T value;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Arg>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR typed_node(const Arg& arg) : value(arg) {}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR typed_node(const basic_string_view<Char>& arg)
|
||||
: value(arg.data(), arg.size()) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<node<>> head_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Arg> auto push(const Arg& arg) -> const T& {
|
||||
auto new_node = std::unique_ptr<typed_node<T>>(new typed_node<T>(arg));
|
||||
auto& value = new_node->value;
|
||||
new_node->next = std::move(head_);
|
||||
head_ = std::move(new_node);
|
||||
return value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* A dynamic list of formatting arguments with storage.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* It can be implicitly converted into `fmt::basic_format_args` for passing
|
||||
* into type-erased formatting functions such as `fmt::vformat`.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename Context> class dynamic_format_arg_store {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using char_type = typename Context::char_type;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct need_copy {
|
||||
static constexpr detail::type mapped_type =
|
||||
detail::mapped_type_constant<T, char_type>::value;
|
||||
|
||||
enum {
|
||||
value = !(detail::is_reference_wrapper<T>::value ||
|
||||
std::is_same<T, basic_string_view<char_type>>::value ||
|
||||
std::is_same<T, detail::std_string_view<char_type>>::value ||
|
||||
(mapped_type != detail::type::cstring_type &&
|
||||
mapped_type != detail::type::string_type &&
|
||||
mapped_type != detail::type::custom_type))
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
using stored_t = conditional_t<
|
||||
std::is_convertible<T, std::basic_string<char_type>>::value &&
|
||||
!detail::is_reference_wrapper<T>::value,
|
||||
std::basic_string<char_type>, T>;
|
||||
|
||||
// Storage of basic_format_arg must be contiguous.
|
||||
std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>> data_;
|
||||
std::vector<detail::named_arg_info<char_type>> named_info_;
|
||||
|
||||
// Storage of arguments not fitting into basic_format_arg must grow
|
||||
// without relocation because items in data_ refer to it.
|
||||
detail::dynamic_arg_list dynamic_args_;
|
||||
|
||||
friend class basic_format_args<Context>;
|
||||
|
||||
auto data() const -> const basic_format_arg<Context>* {
|
||||
return named_info_.empty() ? data_.data() : data_.data() + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> void emplace_arg(const T& arg) {
|
||||
data_.emplace_back(arg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
void emplace_arg(const detail::named_arg<char_type, T>& arg) {
|
||||
if (named_info_.empty())
|
||||
data_.insert(data_.begin(), basic_format_arg<Context>(nullptr, 0));
|
||||
data_.emplace_back(detail::unwrap(arg.value));
|
||||
auto pop_one = [](std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>>* data) {
|
||||
data->pop_back();
|
||||
};
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<std::vector<basic_format_arg<Context>>, decltype(pop_one)>
|
||||
guard{&data_, pop_one};
|
||||
named_info_.push_back({arg.name, static_cast<int>(data_.size() - 2u)});
|
||||
data_[0] = {named_info_.data(), named_info_.size()};
|
||||
guard.release();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
constexpr dynamic_format_arg_store() = default;
|
||||
|
||||
operator basic_format_args<Context>() const {
|
||||
return basic_format_args<Context>(data(), static_cast<int>(data_.size()),
|
||||
!named_info_.empty());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Adds an argument into the dynamic store for later passing to a formatting
|
||||
* function.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Note that custom types and string types (but not string views) are copied
|
||||
* into the store dynamically allocating memory if necessary.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store;
|
||||
* store.push_back(42);
|
||||
* store.push_back("abc");
|
||||
* store.push_back(1.5f);
|
||||
* std::string result = fmt::vformat("{} and {} and {}", store);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename T> void push_back(const T& arg) {
|
||||
if (detail::const_check(need_copy<T>::value))
|
||||
emplace_arg(dynamic_args_.push<stored_t<T>>(arg));
|
||||
else
|
||||
emplace_arg(detail::unwrap(arg));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Adds a reference to the argument into the dynamic store for later passing
|
||||
* to a formatting function.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::dynamic_format_arg_store<fmt::format_context> store;
|
||||
* char band[] = "Rolling Stones";
|
||||
* store.push_back(std::cref(band));
|
||||
* band[9] = 'c'; // Changing str affects the output.
|
||||
* std::string result = fmt::vformat("{}", store);
|
||||
* // result == "Rolling Scones"
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename T> void push_back(std::reference_wrapper<T> arg) {
|
||||
static_assert(
|
||||
need_copy<T>::value,
|
||||
"objects of built-in types and string views are always copied");
|
||||
emplace_arg(arg.get());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Adds named argument into the dynamic store for later passing to a
|
||||
* formatting function. `std::reference_wrapper` is supported to avoid
|
||||
* copying of the argument. The name is always copied into the store.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
void push_back(const detail::named_arg<char_type, T>& arg) {
|
||||
const char_type* arg_name =
|
||||
dynamic_args_.push<std::basic_string<char_type>>(arg.name).c_str();
|
||||
if (detail::const_check(need_copy<T>::value)) {
|
||||
emplace_arg(
|
||||
fmt::arg(arg_name, dynamic_args_.push<stored_t<T>>(arg.value)));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
emplace_arg(fmt::arg(arg_name, arg.value));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Erase all elements from the store.
|
||||
void clear() {
|
||||
data_.clear();
|
||||
named_info_.clear();
|
||||
dynamic_args_ = {};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Reserves space to store at least `new_cap` arguments including
|
||||
/// `new_cap_named` named arguments.
|
||||
void reserve(size_t new_cap, size_t new_cap_named) {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(new_cap >= new_cap_named,
|
||||
"set of arguments includes set of named arguments");
|
||||
data_.reserve(new_cap);
|
||||
named_info_.reserve(new_cap_named);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Returns the number of elements in the store.
|
||||
size_t size() const noexcept { return data_.size(); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // FMT_ARGS_H_
|
||||
2958
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/base.h
vendored
Normal file
2958
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/base.h
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
2338
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/chrono.h
vendored
Normal file
2338
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/chrono.h
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
610
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/color.h
vendored
Normal file
610
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/color.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,610 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - color support
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2018 - present, Victor Zverovich and fmt contributors
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_COLOR_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_COLOR_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
|
||||
enum class color : uint32_t {
|
||||
alice_blue = 0xF0F8FF, // rgb(240,248,255)
|
||||
antique_white = 0xFAEBD7, // rgb(250,235,215)
|
||||
aqua = 0x00FFFF, // rgb(0,255,255)
|
||||
aquamarine = 0x7FFFD4, // rgb(127,255,212)
|
||||
azure = 0xF0FFFF, // rgb(240,255,255)
|
||||
beige = 0xF5F5DC, // rgb(245,245,220)
|
||||
bisque = 0xFFE4C4, // rgb(255,228,196)
|
||||
black = 0x000000, // rgb(0,0,0)
|
||||
blanched_almond = 0xFFEBCD, // rgb(255,235,205)
|
||||
blue = 0x0000FF, // rgb(0,0,255)
|
||||
blue_violet = 0x8A2BE2, // rgb(138,43,226)
|
||||
brown = 0xA52A2A, // rgb(165,42,42)
|
||||
burly_wood = 0xDEB887, // rgb(222,184,135)
|
||||
cadet_blue = 0x5F9EA0, // rgb(95,158,160)
|
||||
chartreuse = 0x7FFF00, // rgb(127,255,0)
|
||||
chocolate = 0xD2691E, // rgb(210,105,30)
|
||||
coral = 0xFF7F50, // rgb(255,127,80)
|
||||
cornflower_blue = 0x6495ED, // rgb(100,149,237)
|
||||
cornsilk = 0xFFF8DC, // rgb(255,248,220)
|
||||
crimson = 0xDC143C, // rgb(220,20,60)
|
||||
cyan = 0x00FFFF, // rgb(0,255,255)
|
||||
dark_blue = 0x00008B, // rgb(0,0,139)
|
||||
dark_cyan = 0x008B8B, // rgb(0,139,139)
|
||||
dark_golden_rod = 0xB8860B, // rgb(184,134,11)
|
||||
dark_gray = 0xA9A9A9, // rgb(169,169,169)
|
||||
dark_green = 0x006400, // rgb(0,100,0)
|
||||
dark_khaki = 0xBDB76B, // rgb(189,183,107)
|
||||
dark_magenta = 0x8B008B, // rgb(139,0,139)
|
||||
dark_olive_green = 0x556B2F, // rgb(85,107,47)
|
||||
dark_orange = 0xFF8C00, // rgb(255,140,0)
|
||||
dark_orchid = 0x9932CC, // rgb(153,50,204)
|
||||
dark_red = 0x8B0000, // rgb(139,0,0)
|
||||
dark_salmon = 0xE9967A, // rgb(233,150,122)
|
||||
dark_sea_green = 0x8FBC8F, // rgb(143,188,143)
|
||||
dark_slate_blue = 0x483D8B, // rgb(72,61,139)
|
||||
dark_slate_gray = 0x2F4F4F, // rgb(47,79,79)
|
||||
dark_turquoise = 0x00CED1, // rgb(0,206,209)
|
||||
dark_violet = 0x9400D3, // rgb(148,0,211)
|
||||
deep_pink = 0xFF1493, // rgb(255,20,147)
|
||||
deep_sky_blue = 0x00BFFF, // rgb(0,191,255)
|
||||
dim_gray = 0x696969, // rgb(105,105,105)
|
||||
dodger_blue = 0x1E90FF, // rgb(30,144,255)
|
||||
fire_brick = 0xB22222, // rgb(178,34,34)
|
||||
floral_white = 0xFFFAF0, // rgb(255,250,240)
|
||||
forest_green = 0x228B22, // rgb(34,139,34)
|
||||
fuchsia = 0xFF00FF, // rgb(255,0,255)
|
||||
gainsboro = 0xDCDCDC, // rgb(220,220,220)
|
||||
ghost_white = 0xF8F8FF, // rgb(248,248,255)
|
||||
gold = 0xFFD700, // rgb(255,215,0)
|
||||
golden_rod = 0xDAA520, // rgb(218,165,32)
|
||||
gray = 0x808080, // rgb(128,128,128)
|
||||
green = 0x008000, // rgb(0,128,0)
|
||||
green_yellow = 0xADFF2F, // rgb(173,255,47)
|
||||
honey_dew = 0xF0FFF0, // rgb(240,255,240)
|
||||
hot_pink = 0xFF69B4, // rgb(255,105,180)
|
||||
indian_red = 0xCD5C5C, // rgb(205,92,92)
|
||||
indigo = 0x4B0082, // rgb(75,0,130)
|
||||
ivory = 0xFFFFF0, // rgb(255,255,240)
|
||||
khaki = 0xF0E68C, // rgb(240,230,140)
|
||||
lavender = 0xE6E6FA, // rgb(230,230,250)
|
||||
lavender_blush = 0xFFF0F5, // rgb(255,240,245)
|
||||
lawn_green = 0x7CFC00, // rgb(124,252,0)
|
||||
lemon_chiffon = 0xFFFACD, // rgb(255,250,205)
|
||||
light_blue = 0xADD8E6, // rgb(173,216,230)
|
||||
light_coral = 0xF08080, // rgb(240,128,128)
|
||||
light_cyan = 0xE0FFFF, // rgb(224,255,255)
|
||||
light_golden_rod_yellow = 0xFAFAD2, // rgb(250,250,210)
|
||||
light_gray = 0xD3D3D3, // rgb(211,211,211)
|
||||
light_green = 0x90EE90, // rgb(144,238,144)
|
||||
light_pink = 0xFFB6C1, // rgb(255,182,193)
|
||||
light_salmon = 0xFFA07A, // rgb(255,160,122)
|
||||
light_sea_green = 0x20B2AA, // rgb(32,178,170)
|
||||
light_sky_blue = 0x87CEFA, // rgb(135,206,250)
|
||||
light_slate_gray = 0x778899, // rgb(119,136,153)
|
||||
light_steel_blue = 0xB0C4DE, // rgb(176,196,222)
|
||||
light_yellow = 0xFFFFE0, // rgb(255,255,224)
|
||||
lime = 0x00FF00, // rgb(0,255,0)
|
||||
lime_green = 0x32CD32, // rgb(50,205,50)
|
||||
linen = 0xFAF0E6, // rgb(250,240,230)
|
||||
magenta = 0xFF00FF, // rgb(255,0,255)
|
||||
maroon = 0x800000, // rgb(128,0,0)
|
||||
medium_aquamarine = 0x66CDAA, // rgb(102,205,170)
|
||||
medium_blue = 0x0000CD, // rgb(0,0,205)
|
||||
medium_orchid = 0xBA55D3, // rgb(186,85,211)
|
||||
medium_purple = 0x9370DB, // rgb(147,112,219)
|
||||
medium_sea_green = 0x3CB371, // rgb(60,179,113)
|
||||
medium_slate_blue = 0x7B68EE, // rgb(123,104,238)
|
||||
medium_spring_green = 0x00FA9A, // rgb(0,250,154)
|
||||
medium_turquoise = 0x48D1CC, // rgb(72,209,204)
|
||||
medium_violet_red = 0xC71585, // rgb(199,21,133)
|
||||
midnight_blue = 0x191970, // rgb(25,25,112)
|
||||
mint_cream = 0xF5FFFA, // rgb(245,255,250)
|
||||
misty_rose = 0xFFE4E1, // rgb(255,228,225)
|
||||
moccasin = 0xFFE4B5, // rgb(255,228,181)
|
||||
navajo_white = 0xFFDEAD, // rgb(255,222,173)
|
||||
navy = 0x000080, // rgb(0,0,128)
|
||||
old_lace = 0xFDF5E6, // rgb(253,245,230)
|
||||
olive = 0x808000, // rgb(128,128,0)
|
||||
olive_drab = 0x6B8E23, // rgb(107,142,35)
|
||||
orange = 0xFFA500, // rgb(255,165,0)
|
||||
orange_red = 0xFF4500, // rgb(255,69,0)
|
||||
orchid = 0xDA70D6, // rgb(218,112,214)
|
||||
pale_golden_rod = 0xEEE8AA, // rgb(238,232,170)
|
||||
pale_green = 0x98FB98, // rgb(152,251,152)
|
||||
pale_turquoise = 0xAFEEEE, // rgb(175,238,238)
|
||||
pale_violet_red = 0xDB7093, // rgb(219,112,147)
|
||||
papaya_whip = 0xFFEFD5, // rgb(255,239,213)
|
||||
peach_puff = 0xFFDAB9, // rgb(255,218,185)
|
||||
peru = 0xCD853F, // rgb(205,133,63)
|
||||
pink = 0xFFC0CB, // rgb(255,192,203)
|
||||
plum = 0xDDA0DD, // rgb(221,160,221)
|
||||
powder_blue = 0xB0E0E6, // rgb(176,224,230)
|
||||
purple = 0x800080, // rgb(128,0,128)
|
||||
rebecca_purple = 0x663399, // rgb(102,51,153)
|
||||
red = 0xFF0000, // rgb(255,0,0)
|
||||
rosy_brown = 0xBC8F8F, // rgb(188,143,143)
|
||||
royal_blue = 0x4169E1, // rgb(65,105,225)
|
||||
saddle_brown = 0x8B4513, // rgb(139,69,19)
|
||||
salmon = 0xFA8072, // rgb(250,128,114)
|
||||
sandy_brown = 0xF4A460, // rgb(244,164,96)
|
||||
sea_green = 0x2E8B57, // rgb(46,139,87)
|
||||
sea_shell = 0xFFF5EE, // rgb(255,245,238)
|
||||
sienna = 0xA0522D, // rgb(160,82,45)
|
||||
silver = 0xC0C0C0, // rgb(192,192,192)
|
||||
sky_blue = 0x87CEEB, // rgb(135,206,235)
|
||||
slate_blue = 0x6A5ACD, // rgb(106,90,205)
|
||||
slate_gray = 0x708090, // rgb(112,128,144)
|
||||
snow = 0xFFFAFA, // rgb(255,250,250)
|
||||
spring_green = 0x00FF7F, // rgb(0,255,127)
|
||||
steel_blue = 0x4682B4, // rgb(70,130,180)
|
||||
tan = 0xD2B48C, // rgb(210,180,140)
|
||||
teal = 0x008080, // rgb(0,128,128)
|
||||
thistle = 0xD8BFD8, // rgb(216,191,216)
|
||||
tomato = 0xFF6347, // rgb(255,99,71)
|
||||
turquoise = 0x40E0D0, // rgb(64,224,208)
|
||||
violet = 0xEE82EE, // rgb(238,130,238)
|
||||
wheat = 0xF5DEB3, // rgb(245,222,179)
|
||||
white = 0xFFFFFF, // rgb(255,255,255)
|
||||
white_smoke = 0xF5F5F5, // rgb(245,245,245)
|
||||
yellow = 0xFFFF00, // rgb(255,255,0)
|
||||
yellow_green = 0x9ACD32 // rgb(154,205,50)
|
||||
}; // enum class color
|
||||
|
||||
enum class terminal_color : uint8_t {
|
||||
black = 30,
|
||||
red,
|
||||
green,
|
||||
yellow,
|
||||
blue,
|
||||
magenta,
|
||||
cyan,
|
||||
white,
|
||||
bright_black = 90,
|
||||
bright_red,
|
||||
bright_green,
|
||||
bright_yellow,
|
||||
bright_blue,
|
||||
bright_magenta,
|
||||
bright_cyan,
|
||||
bright_white
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
enum class emphasis : uint8_t {
|
||||
bold = 1,
|
||||
faint = 1 << 1,
|
||||
italic = 1 << 2,
|
||||
underline = 1 << 3,
|
||||
blink = 1 << 4,
|
||||
reverse = 1 << 5,
|
||||
conceal = 1 << 6,
|
||||
strikethrough = 1 << 7,
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// rgb is a struct for red, green and blue colors.
|
||||
// Using the name "rgb" makes some editors show the color in a tooltip.
|
||||
struct rgb {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR rgb() : r(0), g(0), b(0) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR rgb(uint8_t r_, uint8_t g_, uint8_t b_) : r(r_), g(g_), b(b_) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR rgb(uint32_t hex)
|
||||
: r((hex >> 16) & 0xFF), g((hex >> 8) & 0xFF), b(hex & 0xFF) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR rgb(color hex)
|
||||
: r((uint32_t(hex) >> 16) & 0xFF),
|
||||
g((uint32_t(hex) >> 8) & 0xFF),
|
||||
b(uint32_t(hex) & 0xFF) {}
|
||||
uint8_t r;
|
||||
uint8_t g;
|
||||
uint8_t b;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
// color is a struct of either a rgb color or a terminal color.
|
||||
struct color_type {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type() noexcept : is_rgb(), value{} {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(color rgb_color) noexcept : is_rgb(true), value{} {
|
||||
value.rgb_color = static_cast<uint32_t>(rgb_color);
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(rgb rgb_color) noexcept : is_rgb(true), value{} {
|
||||
value.rgb_color = (static_cast<uint32_t>(rgb_color.r) << 16) |
|
||||
(static_cast<uint32_t>(rgb_color.g) << 8) | rgb_color.b;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR color_type(terminal_color term_color) noexcept
|
||||
: is_rgb(), value{} {
|
||||
value.term_color = static_cast<uint8_t>(term_color);
|
||||
}
|
||||
bool is_rgb;
|
||||
union color_union {
|
||||
uint8_t term_color;
|
||||
uint32_t rgb_color;
|
||||
} value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
/// A text style consisting of foreground and background colors and emphasis.
|
||||
class text_style {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style(emphasis em = emphasis()) noexcept
|
||||
: set_foreground_color(), set_background_color(), ems(em) {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator|=(const text_style& rhs) -> text_style& {
|
||||
if (!set_foreground_color) {
|
||||
set_foreground_color = rhs.set_foreground_color;
|
||||
foreground_color = rhs.foreground_color;
|
||||
} else if (rhs.set_foreground_color) {
|
||||
if (!foreground_color.is_rgb || !rhs.foreground_color.is_rgb)
|
||||
report_error("can't OR a terminal color");
|
||||
foreground_color.value.rgb_color |= rhs.foreground_color.value.rgb_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!set_background_color) {
|
||||
set_background_color = rhs.set_background_color;
|
||||
background_color = rhs.background_color;
|
||||
} else if (rhs.set_background_color) {
|
||||
if (!background_color.is_rgb || !rhs.background_color.is_rgb)
|
||||
report_error("can't OR a terminal color");
|
||||
background_color.value.rgb_color |= rhs.background_color.value.rgb_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ems = static_cast<emphasis>(static_cast<uint8_t>(ems) |
|
||||
static_cast<uint8_t>(rhs.ems));
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator|(text_style lhs, const text_style& rhs)
|
||||
-> text_style {
|
||||
return lhs |= rhs;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto has_foreground() const noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
return set_foreground_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto has_background() const noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
return set_background_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto has_emphasis() const noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
return static_cast<uint8_t>(ems) != 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_foreground() const noexcept -> detail::color_type {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(has_foreground(), "no foreground specified for this style");
|
||||
return foreground_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_background() const noexcept -> detail::color_type {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(has_background(), "no background specified for this style");
|
||||
return background_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_emphasis() const noexcept -> emphasis {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(has_emphasis(), "no emphasis specified for this style");
|
||||
return ems;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style(bool is_foreground,
|
||||
detail::color_type text_color) noexcept
|
||||
: set_foreground_color(), set_background_color(), ems() {
|
||||
if (is_foreground) {
|
||||
foreground_color = text_color;
|
||||
set_foreground_color = true;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
background_color = text_color;
|
||||
set_background_color = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR auto fg(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style;
|
||||
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR auto bg(detail::color_type background) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style;
|
||||
|
||||
detail::color_type foreground_color;
|
||||
detail::color_type background_color;
|
||||
bool set_foreground_color;
|
||||
bool set_background_color;
|
||||
emphasis ems;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/// Creates a text style from the foreground (text) color.
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto fg(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style {
|
||||
return text_style(true, foreground);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Creates a text style from the background color.
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto bg(detail::color_type background) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style {
|
||||
return text_style(false, background);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto operator|(emphasis lhs, emphasis rhs) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style {
|
||||
return text_style(lhs) | rhs;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct ansi_color_escape {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape(color_type text_color,
|
||||
const char* esc) noexcept {
|
||||
// If we have a terminal color, we need to output another escape code
|
||||
// sequence.
|
||||
if (!text_color.is_rgb) {
|
||||
bool is_background = esc == string_view("\x1b[48;2;");
|
||||
uint32_t value = text_color.value.term_color;
|
||||
// Background ASCII codes are the same as the foreground ones but with
|
||||
// 10 more.
|
||||
if (is_background) value += 10u;
|
||||
|
||||
size_t index = 0;
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('\x1b');
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('[');
|
||||
|
||||
if (value >= 100u) {
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('1');
|
||||
value %= 100u;
|
||||
}
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('0' + value / 10u);
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('0' + value % 10u);
|
||||
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('m');
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('\0');
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
|
||||
buffer[i] = static_cast<Char>(esc[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
rgb color(text_color.value.rgb_color);
|
||||
to_esc(color.r, buffer + 7, ';');
|
||||
to_esc(color.g, buffer + 11, ';');
|
||||
to_esc(color.b, buffer + 15, 'm');
|
||||
buffer[19] = static_cast<Char>(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape(emphasis em) noexcept {
|
||||
uint8_t em_codes[num_emphases] = {};
|
||||
if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::bold)) em_codes[0] = 1;
|
||||
if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::faint)) em_codes[1] = 2;
|
||||
if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::italic)) em_codes[2] = 3;
|
||||
if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::underline)) em_codes[3] = 4;
|
||||
if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::blink)) em_codes[4] = 5;
|
||||
if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::reverse)) em_codes[5] = 7;
|
||||
if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::conceal)) em_codes[6] = 8;
|
||||
if (has_emphasis(em, emphasis::strikethrough)) em_codes[7] = 9;
|
||||
|
||||
size_t index = 0;
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < num_emphases; ++i) {
|
||||
if (!em_codes[i]) continue;
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('\x1b');
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('[');
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('0' + em_codes[i]);
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>('m');
|
||||
}
|
||||
buffer[index++] = static_cast<Char>(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR operator const Char*() const noexcept { return buffer; }
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto begin() const noexcept -> const Char* { return buffer; }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto end() const noexcept -> const Char* {
|
||||
return buffer + basic_string_view<Char>(buffer).size();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
static constexpr size_t num_emphases = 8;
|
||||
Char buffer[7u + 3u * num_emphases + 1u];
|
||||
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR void to_esc(uint8_t c, Char* out,
|
||||
char delimiter) noexcept {
|
||||
out[0] = static_cast<Char>('0' + c / 100);
|
||||
out[1] = static_cast<Char>('0' + c / 10 % 10);
|
||||
out[2] = static_cast<Char>('0' + c % 10);
|
||||
out[3] = static_cast<Char>(delimiter);
|
||||
}
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR auto has_emphasis(emphasis em, emphasis mask) noexcept
|
||||
-> bool {
|
||||
return static_cast<uint8_t>(em) & static_cast<uint8_t>(mask);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto make_foreground_color(color_type foreground) noexcept
|
||||
-> ansi_color_escape<Char> {
|
||||
return ansi_color_escape<Char>(foreground, "\x1b[38;2;");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto make_background_color(color_type background) noexcept
|
||||
-> ansi_color_escape<Char> {
|
||||
return ansi_color_escape<Char>(background, "\x1b[48;2;");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto make_emphasis(emphasis em) noexcept
|
||||
-> ansi_color_escape<Char> {
|
||||
return ansi_color_escape<Char>(em);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> inline void reset_color(buffer<Char>& buffer) {
|
||||
auto reset_color = string_view("\x1b[0m");
|
||||
buffer.append(reset_color.begin(), reset_color.end());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct styled_arg : view {
|
||||
const T& value;
|
||||
text_style style;
|
||||
styled_arg(const T& v, text_style s) : value(v), style(s) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, const text_style& ts,
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
basic_format_args<buffered_context<Char>> args) {
|
||||
bool has_style = false;
|
||||
if (ts.has_emphasis()) {
|
||||
has_style = true;
|
||||
auto emphasis = make_emphasis<Char>(ts.get_emphasis());
|
||||
buf.append(emphasis.begin(), emphasis.end());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (ts.has_foreground()) {
|
||||
has_style = true;
|
||||
auto foreground = make_foreground_color<Char>(ts.get_foreground());
|
||||
buf.append(foreground.begin(), foreground.end());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (ts.has_background()) {
|
||||
has_style = true;
|
||||
auto background = make_background_color<Char>(ts.get_background());
|
||||
buf.append(background.begin(), background.end());
|
||||
}
|
||||
vformat_to(buf, fmt, args);
|
||||
if (has_style) reset_color<Char>(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
inline void vprint(FILE* f, const text_style& ts, string_view fmt,
|
||||
format_args args) {
|
||||
auto buf = memory_buffer();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, fmt, args);
|
||||
print(f, FMT_STRING("{}"), string_view(buf.begin(), buf.size()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Formats a string and prints it to the specified file stream using ANSI
|
||||
* escape sequences to specify text formatting.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::print(fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red),
|
||||
* "Elapsed time: {0:.2f} seconds", 1.23);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
void print(FILE* f, const text_style& ts, format_string<T...> fmt,
|
||||
T&&... args) {
|
||||
vprint(f, ts, fmt.str, vargs<T...>{{args...}});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Formats a string and prints it to stdout using ANSI escape sequences to
|
||||
* specify text formatting.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::print(fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red),
|
||||
* "Elapsed time: {0:.2f} seconds", 1.23);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
void print(const text_style& ts, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
return print(stdout, ts, fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline auto vformat(const text_style& ts, string_view fmt, format_args args)
|
||||
-> std::string {
|
||||
auto buf = memory_buffer();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, fmt, args);
|
||||
return fmt::to_string(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Formats arguments and returns the result as a string using ANSI escape
|
||||
* sequences to specify text formatting.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* ```
|
||||
* #include <fmt/color.h>
|
||||
* std::string message = fmt::format(fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red),
|
||||
* "The answer is {}", 42);
|
||||
* ```
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
inline auto format(const text_style& ts, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args)
|
||||
-> std::string {
|
||||
return fmt::vformat(ts, fmt.str, vargs<T...>{{args...}});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Formats a string with the given text_style and writes the output to `out`.
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char>::value)>
|
||||
auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, const text_style& ts, string_view fmt,
|
||||
format_args args) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
auto&& buf = detail::get_buffer<char>(out);
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, fmt, args);
|
||||
return detail::get_iterator(buf, out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Formats arguments with the given text style, writes the result to the output
|
||||
* iterator `out` and returns the iterator past the end of the output range.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* std::vector<char> out;
|
||||
* fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out),
|
||||
* fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red), "{}", 42);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename... T,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char>::value)>
|
||||
inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const text_style& ts,
|
||||
format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
return vformat_to(out, ts, fmt.str, vargs<T...>{{args...}});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<detail::styled_arg<T>, Char> : formatter<T, Char> {
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const detail::styled_arg<T>& arg, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
const auto& ts = arg.style;
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
|
||||
bool has_style = false;
|
||||
if (ts.has_emphasis()) {
|
||||
has_style = true;
|
||||
auto emphasis = detail::make_emphasis<Char>(ts.get_emphasis());
|
||||
out = detail::copy<Char>(emphasis.begin(), emphasis.end(), out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (ts.has_foreground()) {
|
||||
has_style = true;
|
||||
auto foreground =
|
||||
detail::make_foreground_color<Char>(ts.get_foreground());
|
||||
out = detail::copy<Char>(foreground.begin(), foreground.end(), out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (ts.has_background()) {
|
||||
has_style = true;
|
||||
auto background =
|
||||
detail::make_background_color<Char>(ts.get_background());
|
||||
out = detail::copy<Char>(background.begin(), background.end(), out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
out = formatter<T, Char>::format(arg.value, ctx);
|
||||
if (has_style) {
|
||||
auto reset_color = string_view("\x1b[0m");
|
||||
out = detail::copy<Char>(reset_color.begin(), reset_color.end(), out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Returns an argument that will be formatted using ANSI escape sequences,
|
||||
* to be used in a formatting function.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::print("Elapsed time: {0:.2f} seconds",
|
||||
* fmt::styled(1.23, fmt::fg(fmt::color::green) |
|
||||
* fmt::bg(fmt::color::blue)));
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto styled(const T& value, text_style ts)
|
||||
-> detail::styled_arg<remove_cvref_t<T>> {
|
||||
return detail::styled_arg<remove_cvref_t<T>>{value, ts};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_EXPORT
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // FMT_COLOR_H_
|
||||
551
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/compile.h
vendored
Normal file
551
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/compile.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,551 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - experimental format string compilation
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich and fmt contributors
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_COMPILE_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_COMPILE_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <iterator> // std::back_inserter
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
// A compile-time string which is compiled into fast formatting code.
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT class compiled_string {};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S>
|
||||
struct is_compiled_string : std::is_base_of<compiled_string, S> {};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Converts a string literal `s` into a format string that will be parsed at
|
||||
* compile time and converted into efficient formatting code. Requires C++17
|
||||
* `constexpr if` compiler support.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // Converts 42 into std::string using the most efficient method and no
|
||||
* // runtime format string processing.
|
||||
* std::string s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction)
|
||||
# define FMT_COMPILE(s) FMT_STRING_IMPL(s, fmt::compiled_string)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_COMPILE(s) FMT_STRING(s)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS
|
||||
template <typename Char, size_t N, fmt::detail::fixed_string<Char, N> Str>
|
||||
struct udl_compiled_string : compiled_string {
|
||||
using char_type = Char;
|
||||
constexpr explicit operator basic_string_view<char_type>() const {
|
||||
return {Str.data, N - 1};
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename... Tail>
|
||||
auto first(const T& value, const Tail&...) -> const T& {
|
||||
return value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction)
|
||||
template <typename... Args> struct type_list {};
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns a reference to the argument at index N from [first, rest...].
|
||||
template <int N, typename T, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr const auto& get([[maybe_unused]] const T& first,
|
||||
[[maybe_unused]] const Args&... rest) {
|
||||
static_assert(N < 1 + sizeof...(Args), "index is out of bounds");
|
||||
if constexpr (N == 0)
|
||||
return first;
|
||||
else
|
||||
return detail::get<N - 1>(rest...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS
|
||||
template <int N, typename T, typename... Args, typename Char>
|
||||
constexpr auto get_arg_index_by_name(basic_string_view<Char> name) -> int {
|
||||
if constexpr (is_static_named_arg<T>()) {
|
||||
if (name == T::name) return N;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if constexpr (sizeof...(Args) > 0)
|
||||
return get_arg_index_by_name<N + 1, Args...>(name);
|
||||
(void)name; // Workaround an MSVC bug about "unused" parameter.
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... Args, typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_arg_index_by_name(basic_string_view<Char> name) -> int {
|
||||
# if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS
|
||||
if constexpr (sizeof...(Args) > 0)
|
||||
return get_arg_index_by_name<0, Args...>(name);
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
(void)name;
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr int get_arg_index_by_name(basic_string_view<Char> name,
|
||||
type_list<Args...>) {
|
||||
return get_arg_index_by_name<Args...>(name);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <int N, typename> struct get_type_impl;
|
||||
|
||||
template <int N, typename... Args> struct get_type_impl<N, type_list<Args...>> {
|
||||
using type =
|
||||
remove_cvref_t<decltype(detail::get<N>(std::declval<Args>()...))>;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <int N, typename T>
|
||||
using get_type = typename get_type_impl<N, T>::type;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct is_compiled_format : std::false_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct text {
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> data;
|
||||
using char_type = Char;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&...) const {
|
||||
return write<Char>(out, data);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct is_compiled_format<text<Char>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
constexpr text<Char> make_text(basic_string_view<Char> s, size_t pos,
|
||||
size_t size) {
|
||||
return {{&s[pos], size}};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct code_unit {
|
||||
Char value;
|
||||
using char_type = Char;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&...) const {
|
||||
*out++ = value;
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// This ensures that the argument type is convertible to `const T&`.
|
||||
template <typename T, int N, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr const T& get_arg_checked(const Args&... args) {
|
||||
const auto& arg = detail::get<N>(args...);
|
||||
if constexpr (detail::is_named_arg<remove_cvref_t<decltype(arg)>>()) {
|
||||
return arg.value;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return arg;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct is_compiled_format<code_unit<Char>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
// A replacement field that refers to argument N.
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename T, int N> struct field {
|
||||
using char_type = Char;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const {
|
||||
const T& arg = get_arg_checked<T, N>(args...);
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_convertible<T, basic_string_view<Char>>::value) {
|
||||
auto s = basic_string_view<Char>(arg);
|
||||
return copy<Char>(s.begin(), s.end(), out);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return write<Char>(out, arg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename T, int N>
|
||||
struct is_compiled_format<field<Char, T, N>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
// A replacement field that refers to argument with name.
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct runtime_named_field {
|
||||
using char_type = Char;
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> name;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename T>
|
||||
constexpr static bool try_format_argument(
|
||||
OutputIt& out,
|
||||
// [[maybe_unused]] due to unused-but-set-parameter warning in GCC 7,8,9
|
||||
[[maybe_unused]] basic_string_view<Char> arg_name, const T& arg) {
|
||||
if constexpr (is_named_arg<typename std::remove_cv<T>::type>::value) {
|
||||
if (arg_name == arg.name) {
|
||||
out = write<Char>(out, arg.value);
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const {
|
||||
bool found = (try_format_argument(out, name, args) || ...);
|
||||
if (!found) {
|
||||
FMT_THROW(format_error("argument with specified name is not found"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct is_compiled_format<runtime_named_field<Char>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
// A replacement field that refers to argument N and has format specifiers.
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename T, int N> struct spec_field {
|
||||
using char_type = Char;
|
||||
formatter<T, Char> fmt;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr FMT_INLINE OutputIt format(OutputIt out,
|
||||
const Args&... args) const {
|
||||
const auto& vargs =
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>>(args...);
|
||||
basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char> ctx(out, vargs);
|
||||
return fmt.format(get_arg_checked<T, N>(args...), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename T, int N>
|
||||
struct is_compiled_format<spec_field<Char, T, N>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename L, typename R> struct concat {
|
||||
L lhs;
|
||||
R rhs;
|
||||
using char_type = typename L::char_type;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename... Args>
|
||||
constexpr OutputIt format(OutputIt out, const Args&... args) const {
|
||||
out = lhs.format(out, args...);
|
||||
return rhs.format(out, args...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename L, typename R>
|
||||
struct is_compiled_format<concat<L, R>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename L, typename R>
|
||||
constexpr concat<L, R> make_concat(L lhs, R rhs) {
|
||||
return {lhs, rhs};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct unknown_format {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
constexpr size_t parse_text(basic_string_view<Char> str, size_t pos) {
|
||||
for (size_t size = str.size(); pos != size; ++pos) {
|
||||
if (str[pos] == '{' || str[pos] == '}') break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pos;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Args, size_t POS, int ID, typename S>
|
||||
constexpr auto compile_format_string(S fmt);
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Args, size_t POS, int ID, typename T, typename S>
|
||||
constexpr auto parse_tail(T head, S fmt) {
|
||||
if constexpr (POS != basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>(fmt).size()) {
|
||||
constexpr auto tail = compile_format_string<Args, POS, ID>(fmt);
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same<remove_cvref_t<decltype(tail)>,
|
||||
unknown_format>())
|
||||
return tail;
|
||||
else
|
||||
return make_concat(head, tail);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return head;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char> struct parse_specs_result {
|
||||
formatter<T, Char> fmt;
|
||||
size_t end;
|
||||
int next_arg_id;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
enum { manual_indexing_id = -1 };
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
constexpr parse_specs_result<T, Char> parse_specs(basic_string_view<Char> str,
|
||||
size_t pos, int next_arg_id) {
|
||||
str.remove_prefix(pos);
|
||||
auto ctx =
|
||||
compile_parse_context<Char>(str, max_value<int>(), nullptr, next_arg_id);
|
||||
auto f = formatter<T, Char>();
|
||||
auto end = f.parse(ctx);
|
||||
return {f, pos + fmt::detail::to_unsigned(end - str.data()),
|
||||
next_arg_id == 0 ? manual_indexing_id : ctx.next_arg_id()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct arg_id_handler {
|
||||
arg_id_kind kind;
|
||||
arg_ref<Char> arg_id;
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr int on_auto() {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(false, "handler cannot be used with automatic indexing");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
constexpr int on_index(int id) {
|
||||
kind = arg_id_kind::index;
|
||||
arg_id = arg_ref<Char>(id);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
constexpr int on_name(basic_string_view<Char> id) {
|
||||
kind = arg_id_kind::name;
|
||||
arg_id = arg_ref<Char>(id);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct parse_arg_id_result {
|
||||
arg_id_kind kind;
|
||||
arg_ref<Char> arg_id;
|
||||
const Char* arg_id_end;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <int ID, typename Char>
|
||||
constexpr auto parse_arg_id(const Char* begin, const Char* end) {
|
||||
auto handler = arg_id_handler<Char>{arg_id_kind::none, arg_ref<Char>{}};
|
||||
auto arg_id_end = parse_arg_id(begin, end, handler);
|
||||
return parse_arg_id_result<Char>{handler.kind, handler.arg_id, arg_id_end};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Enable = void> struct field_type {
|
||||
using type = remove_cvref_t<T>;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct field_type<T, enable_if_t<detail::is_named_arg<T>::value>> {
|
||||
using type = remove_cvref_t<decltype(T::value)>;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Args, size_t END_POS, int ARG_INDEX, int NEXT_ID,
|
||||
typename S>
|
||||
constexpr auto parse_replacement_field_then_tail(S fmt) {
|
||||
using char_type = typename S::char_type;
|
||||
constexpr auto str = basic_string_view<char_type>(fmt);
|
||||
constexpr char_type c = END_POS != str.size() ? str[END_POS] : char_type();
|
||||
if constexpr (c == '}') {
|
||||
return parse_tail<Args, END_POS + 1, NEXT_ID>(
|
||||
field<char_type, typename field_type<T>::type, ARG_INDEX>(), fmt);
|
||||
} else if constexpr (c != ':') {
|
||||
FMT_THROW(format_error("expected ':'"));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
constexpr auto result = parse_specs<typename field_type<T>::type>(
|
||||
str, END_POS + 1, NEXT_ID == manual_indexing_id ? 0 : NEXT_ID);
|
||||
if constexpr (result.end >= str.size() || str[result.end] != '}') {
|
||||
FMT_THROW(format_error("expected '}'"));
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return parse_tail<Args, result.end + 1, result.next_arg_id>(
|
||||
spec_field<char_type, typename field_type<T>::type, ARG_INDEX>{
|
||||
result.fmt},
|
||||
fmt);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compiles a non-empty format string and returns the compiled representation
|
||||
// or unknown_format() on unrecognized input.
|
||||
template <typename Args, size_t POS, int ID, typename S>
|
||||
constexpr auto compile_format_string(S fmt) {
|
||||
using char_type = typename S::char_type;
|
||||
constexpr auto str = basic_string_view<char_type>(fmt);
|
||||
if constexpr (str[POS] == '{') {
|
||||
if constexpr (POS + 1 == str.size())
|
||||
FMT_THROW(format_error("unmatched '{' in format string"));
|
||||
if constexpr (str[POS + 1] == '{') {
|
||||
return parse_tail<Args, POS + 2, ID>(make_text(str, POS, 1), fmt);
|
||||
} else if constexpr (str[POS + 1] == '}' || str[POS + 1] == ':') {
|
||||
static_assert(ID != manual_indexing_id,
|
||||
"cannot switch from manual to automatic argument indexing");
|
||||
constexpr auto next_id =
|
||||
ID != manual_indexing_id ? ID + 1 : manual_indexing_id;
|
||||
return parse_replacement_field_then_tail<get_type<ID, Args>, Args,
|
||||
POS + 1, ID, next_id>(fmt);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
constexpr auto arg_id_result =
|
||||
parse_arg_id<ID>(str.data() + POS + 1, str.data() + str.size());
|
||||
constexpr auto arg_id_end_pos = arg_id_result.arg_id_end - str.data();
|
||||
constexpr char_type c =
|
||||
arg_id_end_pos != str.size() ? str[arg_id_end_pos] : char_type();
|
||||
static_assert(c == '}' || c == ':', "missing '}' in format string");
|
||||
if constexpr (arg_id_result.kind == arg_id_kind::index) {
|
||||
static_assert(
|
||||
ID == manual_indexing_id || ID == 0,
|
||||
"cannot switch from automatic to manual argument indexing");
|
||||
constexpr auto arg_index = arg_id_result.arg_id.index;
|
||||
return parse_replacement_field_then_tail<get_type<arg_index, Args>,
|
||||
Args, arg_id_end_pos,
|
||||
arg_index, manual_indexing_id>(
|
||||
fmt);
|
||||
} else if constexpr (arg_id_result.kind == arg_id_kind::name) {
|
||||
constexpr auto arg_index =
|
||||
get_arg_index_by_name(arg_id_result.arg_id.name, Args{});
|
||||
if constexpr (arg_index >= 0) {
|
||||
constexpr auto next_id =
|
||||
ID != manual_indexing_id ? ID + 1 : manual_indexing_id;
|
||||
return parse_replacement_field_then_tail<
|
||||
decltype(get_type<arg_index, Args>::value), Args, arg_id_end_pos,
|
||||
arg_index, next_id>(fmt);
|
||||
} else if constexpr (c == '}') {
|
||||
return parse_tail<Args, arg_id_end_pos + 1, ID>(
|
||||
runtime_named_field<char_type>{arg_id_result.arg_id.name}, fmt);
|
||||
} else if constexpr (c == ':') {
|
||||
return unknown_format(); // no type info for specs parsing
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if constexpr (str[POS] == '}') {
|
||||
if constexpr (POS + 1 == str.size())
|
||||
FMT_THROW(format_error("unmatched '}' in format string"));
|
||||
return parse_tail<Args, POS + 2, ID>(make_text(str, POS, 1), fmt);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
constexpr auto end = parse_text(str, POS + 1);
|
||||
if constexpr (end - POS > 1) {
|
||||
return parse_tail<Args, end, ID>(make_text(str, POS, end - POS), fmt);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return parse_tail<Args, end, ID>(code_unit<char_type>{str[POS]}, fmt);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... Args, typename S,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
constexpr auto compile(S fmt) {
|
||||
constexpr auto str = basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>(fmt);
|
||||
if constexpr (str.size() == 0) {
|
||||
return detail::make_text(str, 0, 0);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
constexpr auto result =
|
||||
detail::compile_format_string<detail::type_list<Args...>, 0, 0>(fmt);
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction)
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr) && defined(__cpp_return_type_deduction)
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename CompiledFormat, typename... Args,
|
||||
typename Char = typename CompiledFormat::char_type,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_format<CompiledFormat>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_INLINE std::basic_string<Char> format(const CompiledFormat& cf,
|
||||
const Args&... args) {
|
||||
auto s = std::basic_string<Char>();
|
||||
cf.format(std::back_inserter(s), args...);
|
||||
return s;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename CompiledFormat, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_format<CompiledFormat>::value)>
|
||||
constexpr FMT_INLINE OutputIt format_to(OutputIt out, const CompiledFormat& cf,
|
||||
const Args&... args) {
|
||||
return cf.format(out, args...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_INLINE std::basic_string<typename S::char_type> format(const S&,
|
||||
Args&&... args) {
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same<typename S::char_type, char>::value) {
|
||||
constexpr auto str = basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>(S());
|
||||
if constexpr (str.size() == 2 && str[0] == '{' && str[1] == '}') {
|
||||
const auto& first = detail::first(args...);
|
||||
if constexpr (detail::is_named_arg<
|
||||
remove_cvref_t<decltype(first)>>::value) {
|
||||
return fmt::to_string(first.value);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return fmt::to_string(first);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
constexpr auto compiled = detail::compile<Args...>(S());
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same<remove_cvref_t<decltype(compiled)>,
|
||||
detail::unknown_format>()) {
|
||||
return fmt::format(
|
||||
static_cast<basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>>(S()),
|
||||
std::forward<Args>(args)...);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return fmt::format(compiled, std::forward<Args>(args)...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR OutputIt format_to(OutputIt out, const S&, Args&&... args) {
|
||||
constexpr auto compiled = detail::compile<Args...>(S());
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same<remove_cvref_t<decltype(compiled)>,
|
||||
detail::unknown_format>()) {
|
||||
return fmt::format_to(
|
||||
out, static_cast<basic_string_view<typename S::char_type>>(S()),
|
||||
std::forward<Args>(args)...);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return fmt::format_to(out, compiled, std::forward<Args>(args)...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
auto format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, const S& fmt, Args&&... args)
|
||||
-> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> {
|
||||
using traits = detail::fixed_buffer_traits;
|
||||
auto buf = detail::iterator_buffer<OutputIt, char, traits>(out, n);
|
||||
fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), fmt, std::forward<Args>(args)...);
|
||||
return {buf.out(), buf.count()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto formatted_size(const S& fmt, const Args&... args)
|
||||
-> size_t {
|
||||
auto buf = detail::counting_buffer<>();
|
||||
fmt::format_to(appender(buf), fmt, args...);
|
||||
return buf.count();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
void print(std::FILE* f, const S& fmt, const Args&... args) {
|
||||
auto buf = memory_buffer();
|
||||
fmt::format_to(appender(buf), fmt, args...);
|
||||
detail::print(f, {buf.data(), buf.size()});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
void print(const S& fmt, const Args&... args) {
|
||||
print(stdout, fmt, args...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS
|
||||
inline namespace literals {
|
||||
template <detail::fixed_string Str> constexpr auto operator""_cf() {
|
||||
using char_t = remove_cvref_t<decltype(Str.data[0])>;
|
||||
return detail::udl_compiled_string<char_t, sizeof(Str.data) / sizeof(char_t),
|
||||
Str>();
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace literals
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_EXPORT
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // FMT_COMPILE_H_
|
||||
5
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/core.h
vendored
Normal file
5
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/core.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
// This file is only provided for compatibility and may be removed in future
|
||||
// versions. Use fmt/base.h if you don't need fmt::format and fmt/format.h
|
||||
// otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
1949
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/format-inl.h
vendored
Normal file
1949
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/format-inl.h
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
4232
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/format.h
vendored
Normal file
4232
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/format.h
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
427
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/os.h
vendored
Normal file
427
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/os.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,427 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - optional OS-specific functionality
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_OS_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_OS_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <cerrno>
|
||||
# include <cstddef>
|
||||
# include <cstdio>
|
||||
# include <system_error> // std::system_error
|
||||
|
||||
# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<xlocale.h>)
|
||||
# include <xlocale.h> // LC_NUMERIC_MASK on macOS
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif // FMT_MODULE
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
// UWP doesn't provide _pipe.
|
||||
# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("winapifamily.h")
|
||||
# include <winapifamily.h>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# if (FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<fcntl.h>) || defined(__APPLE__) || \
|
||||
defined(__linux__)) && \
|
||||
(!defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) || \
|
||||
(WINAPI_FAMILY == WINAPI_FAMILY_DESKTOP_APP))
|
||||
# include <fcntl.h> // for O_RDONLY
|
||||
# define FMT_USE_FCNTL 1
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# define FMT_USE_FCNTL 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_POSIX
|
||||
# if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__)
|
||||
// Fix warnings about deprecated symbols.
|
||||
# define FMT_POSIX(call) _##call
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# define FMT_POSIX(call) call
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Calls to system functions are wrapped in FMT_SYSTEM for testability.
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_SYSTEM
|
||||
# define FMT_HAS_SYSTEM
|
||||
# define FMT_POSIX_CALL(call) FMT_SYSTEM(call)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_SYSTEM(call) ::call
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
// Fix warnings about deprecated symbols.
|
||||
# define FMT_POSIX_CALL(call) ::_##call
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# define FMT_POSIX_CALL(call) ::call
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Retries the expression while it evaluates to error_result and errno
|
||||
// equals to EINTR.
|
||||
#ifndef _WIN32
|
||||
# define FMT_RETRY_VAL(result, expression, error_result) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
(result) = (expression); \
|
||||
} while ((result) == (error_result) && errno == EINTR)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_RETRY_VAL(result, expression, error_result) result = (expression)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#define FMT_RETRY(result, expression) FMT_RETRY_VAL(result, expression, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* A reference to a null-terminated string. It can be constructed from a C
|
||||
* string or `std::string`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* You can use one of the following type aliases for common character types:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* +---------------+-----------------------------+
|
||||
* | Type | Definition |
|
||||
* +===============+=============================+
|
||||
* | cstring_view | basic_cstring_view<char> |
|
||||
* +---------------+-----------------------------+
|
||||
* | wcstring_view | basic_cstring_view<wchar_t> |
|
||||
* +---------------+-----------------------------+
|
||||
*
|
||||
* This class is most useful as a parameter type for functions that wrap C APIs.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename Char> class basic_cstring_view {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
const Char* data_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
/// Constructs a string reference object from a C string.
|
||||
basic_cstring_view(const Char* s) : data_(s) {}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Constructs a string reference from an `std::string` object.
|
||||
basic_cstring_view(const std::basic_string<Char>& s) : data_(s.c_str()) {}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Returns the pointer to a C string.
|
||||
auto c_str() const -> const Char* { return data_; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
using cstring_view = basic_cstring_view<char>;
|
||||
using wcstring_view = basic_cstring_view<wchar_t>;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
FMT_API const std::error_category& system_category() noexcept;
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
FMT_API void format_windows_error(buffer<char>& out, int error_code,
|
||||
const char* message) noexcept;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_API std::system_error vwindows_error(int error_code, string_view fmt,
|
||||
format_args args);
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Constructs a `std::system_error` object with the description of the form
|
||||
*
|
||||
* <message>: <system-message>
|
||||
*
|
||||
* where `<message>` is the formatted message and `<system-message>` is the
|
||||
* system message corresponding to the error code.
|
||||
* `error_code` is a Windows error code as given by `GetLastError`.
|
||||
* If `error_code` is not a valid error code such as -1, the system message
|
||||
* will look like "error -1".
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* // This throws a system_error with the description
|
||||
* // cannot open file 'madeup': The system cannot find the file
|
||||
* specified.
|
||||
* // or similar (system message may vary).
|
||||
* const char *filename = "madeup";
|
||||
* LPOFSTRUCT of = LPOFSTRUCT();
|
||||
* HFILE file = OpenFile(filename, &of, OF_READ);
|
||||
* if (file == HFILE_ERROR) {
|
||||
* throw fmt::windows_error(GetLastError(),
|
||||
* "cannot open file '{}'", filename);
|
||||
* }
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
auto windows_error(int error_code, string_view message, const T&... args)
|
||||
-> std::system_error {
|
||||
return vwindows_error(error_code, message, vargs<T...>{{args...}});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reports a Windows error without throwing an exception.
|
||||
// Can be used to report errors from destructors.
|
||||
FMT_API void report_windows_error(int error_code, const char* message) noexcept;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
inline auto system_category() noexcept -> const std::error_category& {
|
||||
return std::system_category();
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // _WIN32
|
||||
|
||||
// std::system is not available on some platforms such as iOS (#2248).
|
||||
#ifdef __OSX__
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>>
|
||||
void say(const S& fmt, Args&&... args) {
|
||||
std::system(format("say \"{}\"", format(fmt, args...)).c_str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// A buffered file.
|
||||
class buffered_file {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
FILE* file_;
|
||||
|
||||
friend class file;
|
||||
|
||||
inline explicit buffered_file(FILE* f) : file_(f) {}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
buffered_file(const buffered_file&) = delete;
|
||||
void operator=(const buffered_file&) = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
// Constructs a buffered_file object which doesn't represent any file.
|
||||
inline buffered_file() noexcept : file_(nullptr) {}
|
||||
|
||||
// Destroys the object closing the file it represents if any.
|
||||
FMT_API ~buffered_file() noexcept;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
inline buffered_file(buffered_file&& other) noexcept : file_(other.file_) {
|
||||
other.file_ = nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline auto operator=(buffered_file&& other) -> buffered_file& {
|
||||
close();
|
||||
file_ = other.file_;
|
||||
other.file_ = nullptr;
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Opens a file.
|
||||
FMT_API buffered_file(cstring_view filename, cstring_view mode);
|
||||
|
||||
// Closes the file.
|
||||
FMT_API void close();
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the pointer to a FILE object representing this file.
|
||||
inline auto get() const noexcept -> FILE* { return file_; }
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_API auto descriptor() const -> int;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
inline void print(string_view fmt, const T&... args) {
|
||||
fmt::vargs<T...> vargs = {{args...}};
|
||||
detail::is_locking<T...>() ? fmt::vprint_buffered(file_, fmt, vargs)
|
||||
: fmt::vprint(file_, fmt, vargs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
|
||||
// A file. Closed file is represented by a file object with descriptor -1.
|
||||
// Methods that are not declared with noexcept may throw
|
||||
// fmt::system_error in case of failure. Note that some errors such as
|
||||
// closing the file multiple times will cause a crash on Windows rather
|
||||
// than an exception. You can get standard behavior by overriding the
|
||||
// invalid parameter handler with _set_invalid_parameter_handler.
|
||||
class FMT_API file {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
int fd_; // File descriptor.
|
||||
|
||||
// Constructs a file object with a given descriptor.
|
||||
explicit file(int fd) : fd_(fd) {}
|
||||
|
||||
friend struct pipe;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
// Possible values for the oflag argument to the constructor.
|
||||
enum {
|
||||
RDONLY = FMT_POSIX(O_RDONLY), // Open for reading only.
|
||||
WRONLY = FMT_POSIX(O_WRONLY), // Open for writing only.
|
||||
RDWR = FMT_POSIX(O_RDWR), // Open for reading and writing.
|
||||
CREATE = FMT_POSIX(O_CREAT), // Create if the file doesn't exist.
|
||||
APPEND = FMT_POSIX(O_APPEND), // Open in append mode.
|
||||
TRUNC = FMT_POSIX(O_TRUNC) // Truncate the content of the file.
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Constructs a file object which doesn't represent any file.
|
||||
inline file() noexcept : fd_(-1) {}
|
||||
|
||||
// Opens a file and constructs a file object representing this file.
|
||||
file(cstring_view path, int oflag);
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
file(const file&) = delete;
|
||||
void operator=(const file&) = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
inline file(file&& other) noexcept : fd_(other.fd_) { other.fd_ = -1; }
|
||||
|
||||
// Move assignment is not noexcept because close may throw.
|
||||
inline auto operator=(file&& other) -> file& {
|
||||
close();
|
||||
fd_ = other.fd_;
|
||||
other.fd_ = -1;
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Destroys the object closing the file it represents if any.
|
||||
~file() noexcept;
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the file descriptor.
|
||||
inline auto descriptor() const noexcept -> int { return fd_; }
|
||||
|
||||
// Closes the file.
|
||||
void close();
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the file size. The size has signed type for consistency with
|
||||
// stat::st_size.
|
||||
auto size() const -> long long;
|
||||
|
||||
// Attempts to read count bytes from the file into the specified buffer.
|
||||
auto read(void* buffer, size_t count) -> size_t;
|
||||
|
||||
// Attempts to write count bytes from the specified buffer to the file.
|
||||
auto write(const void* buffer, size_t count) -> size_t;
|
||||
|
||||
// Duplicates a file descriptor with the dup function and returns
|
||||
// the duplicate as a file object.
|
||||
static auto dup(int fd) -> file;
|
||||
|
||||
// Makes fd be the copy of this file descriptor, closing fd first if
|
||||
// necessary.
|
||||
void dup2(int fd);
|
||||
|
||||
// Makes fd be the copy of this file descriptor, closing fd first if
|
||||
// necessary.
|
||||
void dup2(int fd, std::error_code& ec) noexcept;
|
||||
|
||||
// Creates a buffered_file object associated with this file and detaches
|
||||
// this file object from the file.
|
||||
auto fdopen(const char* mode) -> buffered_file;
|
||||
|
||||
# if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__)
|
||||
// Opens a file and constructs a file object representing this file by
|
||||
// wcstring_view filename. Windows only.
|
||||
static file open_windows_file(wcstring_view path, int oflag);
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct FMT_API pipe {
|
||||
file read_end;
|
||||
file write_end;
|
||||
|
||||
// Creates a pipe setting up read_end and write_end file objects for reading
|
||||
// and writing respectively.
|
||||
pipe();
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the memory page size.
|
||||
auto getpagesize() -> long;
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
struct buffer_size {
|
||||
constexpr buffer_size() = default;
|
||||
size_t value = 0;
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator=(size_t val) const -> buffer_size {
|
||||
auto bs = buffer_size();
|
||||
bs.value = val;
|
||||
return bs;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct ostream_params {
|
||||
int oflag = file::WRONLY | file::CREATE | file::TRUNC;
|
||||
size_t buffer_size = BUFSIZ > 32768 ? BUFSIZ : 32768;
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr ostream_params() {}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
ostream_params(T... params, int new_oflag) : ostream_params(params...) {
|
||||
oflag = new_oflag;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
ostream_params(T... params, detail::buffer_size bs)
|
||||
: ostream_params(params...) {
|
||||
this->buffer_size = bs.value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intel has a bug that results in failure to deduce a constructor
|
||||
// for empty parameter packs.
|
||||
# if defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && __INTEL_COMPILER < 2000
|
||||
ostream_params(int new_oflag) : oflag(new_oflag) {}
|
||||
ostream_params(detail::buffer_size bs) : buffer_size(bs.value) {}
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_INLINE_VARIABLE constexpr auto buffer_size = detail::buffer_size();
|
||||
|
||||
/// A fast buffered output stream for writing from a single thread. Writing from
|
||||
/// multiple threads without external synchronization may result in a data race.
|
||||
class FMT_API ostream : private detail::buffer<char> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
file file_;
|
||||
|
||||
ostream(cstring_view path, const detail::ostream_params& params);
|
||||
|
||||
static void grow(buffer<char>& buf, size_t);
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
ostream(ostream&& other) noexcept;
|
||||
~ostream();
|
||||
|
||||
operator writer() {
|
||||
detail::buffer<char>& buf = *this;
|
||||
return buf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void flush() {
|
||||
if (size() == 0) return;
|
||||
file_.write(data(), size() * sizeof(data()[0]));
|
||||
clear();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
friend auto output_file(cstring_view path, T... params) -> ostream;
|
||||
|
||||
inline void close() {
|
||||
flush();
|
||||
file_.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Formats `args` according to specifications in `fmt` and writes the
|
||||
/// output to the file.
|
||||
template <typename... T> void print(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
vformat_to(appender(*this), fmt.str, vargs<T...>{{args...}});
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Opens a file for writing. Supported parameters passed in `params`:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* - `<integer>`: Flags passed to [open](
|
||||
* https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/007904875/functions/open.html)
|
||||
* (`file::WRONLY | file::CREATE | file::TRUNC` by default)
|
||||
* - `buffer_size=<integer>`: Output buffer size
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* auto out = fmt::output_file("guide.txt");
|
||||
* out.print("Don't {}", "Panic");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
inline auto output_file(cstring_view path, T... params) -> ostream {
|
||||
return {path, detail::ostream_params(params...)};
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_EXPORT
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // FMT_OS_H_
|
||||
166
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/ostream.h
vendored
Normal file
166
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/ostream.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - std::ostream support
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_OSTREAM_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_OSTREAM_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <fstream> // std::filebuf
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
# ifdef __GLIBCXX__
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_sync_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# include <io.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "chrono.h" // formatbuf
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _MSVC_STL_UPDATE
|
||||
# define FMT_MSVC_STL_UPDATE _MSVC_STL_UPDATE
|
||||
#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER < 1912 // VS 15.5
|
||||
# define FMT_MSVC_STL_UPDATE _MSVC_LANG
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_MSVC_STL_UPDATE 0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate a unique explicit instantion in every translation unit using a tag
|
||||
// type in an anonymous namespace.
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
struct file_access_tag {};
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
template <typename Tag, typename BufType, FILE* BufType::*FileMemberPtr>
|
||||
class file_access {
|
||||
friend auto get_file(BufType& obj) -> FILE* { return obj.*FileMemberPtr; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_MSVC_STL_UPDATE
|
||||
template class file_access<file_access_tag, std::filebuf,
|
||||
&std::filebuf::_Myfile>;
|
||||
auto get_file(std::filebuf&) -> FILE*;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Write the content of buf to os.
|
||||
// It is a separate function rather than a part of vprint to simplify testing.
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
void write_buffer(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, buffer<Char>& buf) {
|
||||
const Char* buf_data = buf.data();
|
||||
using unsigned_streamsize = make_unsigned_t<std::streamsize>;
|
||||
unsigned_streamsize size = buf.size();
|
||||
unsigned_streamsize max_size = to_unsigned(max_value<std::streamsize>());
|
||||
do {
|
||||
unsigned_streamsize n = size <= max_size ? size : max_size;
|
||||
os.write(buf_data, static_cast<std::streamsize>(n));
|
||||
buf_data += n;
|
||||
size -= n;
|
||||
} while (size != 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct streamed_view {
|
||||
const T& value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
// Formats an object of type T that has an overloaded ostream operator<<.
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct basic_ostream_formatter : formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char> {
|
||||
void set_debug_format() = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Context>
|
||||
auto format(const T& value, Context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto buffer = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
auto&& formatbuf = detail::formatbuf<std::basic_streambuf<Char>>(buffer);
|
||||
auto&& output = std::basic_ostream<Char>(&formatbuf);
|
||||
output.imbue(std::locale::classic()); // The default is always unlocalized.
|
||||
output << value;
|
||||
output.exceptions(std::ios_base::failbit | std::ios_base::badbit);
|
||||
return formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char>::format(
|
||||
{buffer.data(), buffer.size()}, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
using ostream_formatter = basic_ostream_formatter<char>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<detail::streamed_view<T>, Char>
|
||||
: basic_ostream_formatter<Char> {
|
||||
template <typename Context>
|
||||
auto format(detail::streamed_view<T> view, Context& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return basic_ostream_formatter<Char>::format(view.value, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Returns a view that formats `value` via an ostream `operator<<`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::print("Current thread id: {}\n",
|
||||
* fmt::streamed(std::this_thread::get_id()));
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
constexpr auto streamed(const T& value) -> detail::streamed_view<T> {
|
||||
return {value};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void vprint(std::ostream& os, string_view fmt, format_args args) {
|
||||
auto buffer = memory_buffer();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buffer, fmt, args);
|
||||
FILE* f = nullptr;
|
||||
#if FMT_MSVC_STL_UPDATE && FMT_USE_RTTI
|
||||
if (auto* buf = dynamic_cast<std::filebuf*>(os.rdbuf()))
|
||||
f = detail::get_file(*buf);
|
||||
#elif defined(_WIN32) && defined(__GLIBCXX__) && FMT_USE_RTTI
|
||||
auto* rdbuf = os.rdbuf();
|
||||
if (auto* sfbuf = dynamic_cast<__gnu_cxx::stdio_sync_filebuf<char>*>(rdbuf))
|
||||
f = sfbuf->file();
|
||||
else if (auto* fbuf = dynamic_cast<__gnu_cxx::stdio_filebuf<char>*>(rdbuf))
|
||||
f = fbuf->file();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
if (f) {
|
||||
int fd = _fileno(f);
|
||||
if (_isatty(fd)) {
|
||||
os.flush();
|
||||
if (detail::write_console(fd, {buffer.data(), buffer.size()})) return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
detail::ignore_unused(f);
|
||||
detail::write_buffer(os, buffer);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Prints formatted data to the stream `os`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::print(cerr, "Don't {}!", "panic");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT template <typename... T>
|
||||
void print(std::ostream& os, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
fmt::vargs<T...> vargs = {{args...}};
|
||||
if (detail::use_utf8) return vprint(os, fmt.str, vargs);
|
||||
auto buffer = memory_buffer();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buffer, fmt.str, vargs);
|
||||
detail::write_buffer(os, buffer);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT template <typename... T>
|
||||
void println(std::ostream& os, format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
fmt::print(os, "{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // FMT_OSTREAM_H_
|
||||
633
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/printf.h
vendored
Normal file
633
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/printf.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,633 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - legacy printf implementation
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - 2016, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_PRINTF_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_PRINTF_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <algorithm> // std::max
|
||||
# include <limits> // std::numeric_limits
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct printf_formatter {
|
||||
printf_formatter() = delete;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> class basic_printf_context {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
basic_appender<Char> out_;
|
||||
basic_format_args<basic_printf_context> args_;
|
||||
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<Char, char>::value ||
|
||||
std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value,
|
||||
"Unsupported code unit type.");
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using char_type = Char;
|
||||
using parse_context_type = parse_context<Char>;
|
||||
template <typename T> using formatter_type = printf_formatter<T>;
|
||||
enum { builtin_types = 1 };
|
||||
|
||||
/// Constructs a `printf_context` object. References to the arguments are
|
||||
/// stored in the context object so make sure they have appropriate lifetimes.
|
||||
basic_printf_context(basic_appender<Char> out,
|
||||
basic_format_args<basic_printf_context> args)
|
||||
: out_(out), args_(args) {}
|
||||
|
||||
auto out() -> basic_appender<Char> { return out_; }
|
||||
void advance_to(basic_appender<Char>) {}
|
||||
|
||||
auto locale() -> detail::locale_ref { return {}; }
|
||||
|
||||
auto arg(int id) const -> basic_format_arg<basic_printf_context> {
|
||||
return args_.get(id);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
// Return the result via the out param to workaround gcc bug 77539.
|
||||
template <bool IS_CONSTEXPR, typename T, typename Ptr = const T*>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto find(Ptr first, Ptr last, T value, Ptr& out) -> bool {
|
||||
for (out = first; out != last; ++out) {
|
||||
if (*out == value) return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
inline auto find<false, char>(const char* first, const char* last, char value,
|
||||
const char*& out) -> bool {
|
||||
out =
|
||||
static_cast<const char*>(memchr(first, value, to_unsigned(last - first)));
|
||||
return out != nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Checks if a value fits in int - used to avoid warnings about comparing
|
||||
// signed and unsigned integers.
|
||||
template <bool IsSigned> struct int_checker {
|
||||
template <typename T> static auto fits_in_int(T value) -> bool {
|
||||
unsigned max = to_unsigned(max_value<int>());
|
||||
return value <= max;
|
||||
}
|
||||
inline static auto fits_in_int(bool) -> bool { return true; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct int_checker<true> {
|
||||
template <typename T> static auto fits_in_int(T value) -> bool {
|
||||
return value >= (std::numeric_limits<int>::min)() &&
|
||||
value <= max_value<int>();
|
||||
}
|
||||
inline static auto fits_in_int(int) -> bool { return true; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct printf_precision_handler {
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto operator()(T value) -> int {
|
||||
if (!int_checker<std::numeric_limits<T>::is_signed>::fits_in_int(value))
|
||||
report_error("number is too big");
|
||||
return (std::max)(static_cast<int>(value), 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto operator()(T) -> int {
|
||||
report_error("precision is not integer");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// An argument visitor that returns true iff arg is a zero integer.
|
||||
struct is_zero_int {
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto operator()(T value) -> bool {
|
||||
return value == 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto operator()(T) -> bool {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct make_unsigned_or_bool : std::make_unsigned<T> {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct make_unsigned_or_bool<bool> {
|
||||
using type = bool;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Context> class arg_converter {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using char_type = typename Context::char_type;
|
||||
|
||||
basic_format_arg<Context>& arg_;
|
||||
char_type type_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
arg_converter(basic_format_arg<Context>& arg, char_type type)
|
||||
: arg_(arg), type_(type) {}
|
||||
|
||||
void operator()(bool value) {
|
||||
if (type_ != 's') operator()<bool>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename U, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<U>::value)>
|
||||
void operator()(U value) {
|
||||
bool is_signed = type_ == 'd' || type_ == 'i';
|
||||
using target_type = conditional_t<std::is_same<T, void>::value, U, T>;
|
||||
if (const_check(sizeof(target_type) <= sizeof(int))) {
|
||||
// Extra casts are used to silence warnings.
|
||||
using unsigned_type = typename make_unsigned_or_bool<target_type>::type;
|
||||
if (is_signed)
|
||||
arg_ = static_cast<int>(static_cast<target_type>(value));
|
||||
else
|
||||
arg_ = static_cast<unsigned>(static_cast<unsigned_type>(value));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// glibc's printf doesn't sign extend arguments of smaller types:
|
||||
// std::printf("%lld", -42); // prints "4294967254"
|
||||
// but we don't have to do the same because it's a UB.
|
||||
if (is_signed)
|
||||
arg_ = static_cast<long long>(value);
|
||||
else
|
||||
arg_ = static_cast<typename make_unsigned_or_bool<U>::type>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename U, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<U>::value)>
|
||||
void operator()(U) {} // No conversion needed for non-integral types.
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Converts an integer argument to T for printf, if T is an integral type.
|
||||
// If T is void, the argument is converted to corresponding signed or unsigned
|
||||
// type depending on the type specifier: 'd' and 'i' - signed, other -
|
||||
// unsigned).
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Context, typename Char>
|
||||
void convert_arg(basic_format_arg<Context>& arg, Char type) {
|
||||
arg.visit(arg_converter<T, Context>(arg, type));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Converts an integer argument to char for printf.
|
||||
template <typename Context> class char_converter {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
basic_format_arg<Context>& arg_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit char_converter(basic_format_arg<Context>& arg) : arg_(arg) {}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
void operator()(T value) {
|
||||
arg_ = static_cast<typename Context::char_type>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
void operator()(T) {} // No conversion needed for non-integral types.
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// An argument visitor that return a pointer to a C string if argument is a
|
||||
// string or null otherwise.
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct get_cstring {
|
||||
template <typename T> auto operator()(T) -> const Char* { return nullptr; }
|
||||
auto operator()(const Char* s) -> const Char* { return s; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Checks if an argument is a valid printf width specifier and sets
|
||||
// left alignment if it is negative.
|
||||
class printf_width_handler {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
format_specs& specs_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
inline explicit printf_width_handler(format_specs& specs) : specs_(specs) {}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto operator()(T value) -> unsigned {
|
||||
auto width = static_cast<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<T>>(value);
|
||||
if (detail::is_negative(value)) {
|
||||
specs_.set_align(align::left);
|
||||
width = 0 - width;
|
||||
}
|
||||
unsigned int_max = to_unsigned(max_value<int>());
|
||||
if (width > int_max) report_error("number is too big");
|
||||
return static_cast<unsigned>(width);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto operator()(T) -> unsigned {
|
||||
report_error("width is not integer");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Workaround for a bug with the XL compiler when initializing
|
||||
// printf_arg_formatter's base class.
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
auto make_arg_formatter(basic_appender<Char> iter, format_specs& s)
|
||||
-> arg_formatter<Char> {
|
||||
return {iter, s, locale_ref()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The `printf` argument formatter.
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
class printf_arg_formatter : public arg_formatter<Char> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using base = arg_formatter<Char>;
|
||||
using context_type = basic_printf_context<Char>;
|
||||
|
||||
context_type& context_;
|
||||
|
||||
void write_null_pointer(bool is_string = false) {
|
||||
auto s = this->specs;
|
||||
s.set_type(presentation_type::none);
|
||||
write_bytes<Char>(this->out, is_string ? "(null)" : "(nil)", s);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> void write(T value) {
|
||||
detail::write<Char>(this->out, value, this->specs, this->locale);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
printf_arg_formatter(basic_appender<Char> iter, format_specs& s,
|
||||
context_type& ctx)
|
||||
: base(make_arg_formatter(iter, s)), context_(ctx) {}
|
||||
|
||||
void operator()(monostate value) { write(value); }
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
void operator()(T value) {
|
||||
// MSVC2013 fails to compile separate overloads for bool and Char so use
|
||||
// std::is_same instead.
|
||||
if (!std::is_same<T, Char>::value) {
|
||||
write(value);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
format_specs s = this->specs;
|
||||
if (s.type() != presentation_type::none &&
|
||||
s.type() != presentation_type::chr) {
|
||||
return (*this)(static_cast<int>(value));
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.set_sign(sign::none);
|
||||
s.clear_alt();
|
||||
s.set_fill(' '); // Ignore '0' flag for char types.
|
||||
// align::numeric needs to be overwritten here since the '0' flag is
|
||||
// ignored for non-numeric types
|
||||
if (s.align() == align::none || s.align() == align::numeric)
|
||||
s.set_align(align::right);
|
||||
detail::write<Char>(this->out, static_cast<Char>(value), s);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value)>
|
||||
void operator()(T value) {
|
||||
write(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void operator()(const char* value) {
|
||||
if (value)
|
||||
write(value);
|
||||
else
|
||||
write_null_pointer(this->specs.type() != presentation_type::pointer);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void operator()(const wchar_t* value) {
|
||||
if (value)
|
||||
write(value);
|
||||
else
|
||||
write_null_pointer(this->specs.type() != presentation_type::pointer);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void operator()(basic_string_view<Char> value) { write(value); }
|
||||
|
||||
void operator()(const void* value) {
|
||||
if (value)
|
||||
write(value);
|
||||
else
|
||||
write_null_pointer();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void operator()(typename basic_format_arg<context_type>::handle handle) {
|
||||
auto parse_ctx = parse_context<Char>({});
|
||||
handle.format(parse_ctx, context_);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
void parse_flags(format_specs& specs, const Char*& it, const Char* end) {
|
||||
for (; it != end; ++it) {
|
||||
switch (*it) {
|
||||
case '-': specs.set_align(align::left); break;
|
||||
case '+': specs.set_sign(sign::plus); break;
|
||||
case '0': specs.set_fill('0'); break;
|
||||
case ' ':
|
||||
if (specs.sign() != sign::plus) specs.set_sign(sign::space);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case '#': specs.set_alt(); break;
|
||||
default: return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename GetArg>
|
||||
auto parse_header(const Char*& it, const Char* end, format_specs& specs,
|
||||
GetArg get_arg) -> int {
|
||||
int arg_index = -1;
|
||||
Char c = *it;
|
||||
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
|
||||
// Parse an argument index (if followed by '$') or a width possibly
|
||||
// preceded with '0' flag(s).
|
||||
int value = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, -1);
|
||||
if (it != end && *it == '$') { // value is an argument index
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
arg_index = value != -1 ? value : max_value<int>();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (c == '0') specs.set_fill('0');
|
||||
if (value != 0) {
|
||||
// Nonzero value means that we parsed width and don't need to
|
||||
// parse it or flags again, so return now.
|
||||
if (value == -1) report_error("number is too big");
|
||||
specs.width = value;
|
||||
return arg_index;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
parse_flags(specs, it, end);
|
||||
// Parse width.
|
||||
if (it != end) {
|
||||
if (*it >= '0' && *it <= '9') {
|
||||
specs.width = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, -1);
|
||||
if (specs.width == -1) report_error("number is too big");
|
||||
} else if (*it == '*') {
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
specs.width = static_cast<int>(
|
||||
get_arg(-1).visit(detail::printf_width_handler(specs)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return arg_index;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline auto parse_printf_presentation_type(char c, type t, bool& upper)
|
||||
-> presentation_type {
|
||||
using pt = presentation_type;
|
||||
constexpr auto integral_set = sint_set | uint_set | bool_set | char_set;
|
||||
switch (c) {
|
||||
case 'd': return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::dec : pt::none;
|
||||
case 'o': return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::oct : pt::none;
|
||||
case 'X': upper = true; FMT_FALLTHROUGH;
|
||||
case 'x': return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::hex : pt::none;
|
||||
case 'E': upper = true; FMT_FALLTHROUGH;
|
||||
case 'e': return in(t, float_set) ? pt::exp : pt::none;
|
||||
case 'F': upper = true; FMT_FALLTHROUGH;
|
||||
case 'f': return in(t, float_set) ? pt::fixed : pt::none;
|
||||
case 'G': upper = true; FMT_FALLTHROUGH;
|
||||
case 'g': return in(t, float_set) ? pt::general : pt::none;
|
||||
case 'A': upper = true; FMT_FALLTHROUGH;
|
||||
case 'a': return in(t, float_set) ? pt::hexfloat : pt::none;
|
||||
case 'c': return in(t, integral_set) ? pt::chr : pt::none;
|
||||
case 's': return in(t, string_set | cstring_set) ? pt::string : pt::none;
|
||||
case 'p': return in(t, pointer_set | cstring_set) ? pt::pointer : pt::none;
|
||||
default: return pt::none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Context>
|
||||
void vprintf(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> format,
|
||||
basic_format_args<Context> args) {
|
||||
using iterator = basic_appender<Char>;
|
||||
auto out = iterator(buf);
|
||||
auto context = basic_printf_context<Char>(out, args);
|
||||
auto parse_ctx = parse_context<Char>(format);
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the argument with specified index or, if arg_index is -1, the next
|
||||
// argument.
|
||||
auto get_arg = [&](int arg_index) {
|
||||
if (arg_index < 0)
|
||||
arg_index = parse_ctx.next_arg_id();
|
||||
else
|
||||
parse_ctx.check_arg_id(--arg_index);
|
||||
return detail::get_arg(context, arg_index);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const Char* start = parse_ctx.begin();
|
||||
const Char* end = parse_ctx.end();
|
||||
auto it = start;
|
||||
while (it != end) {
|
||||
if (!find<false, Char>(it, end, '%', it)) {
|
||||
it = end; // find leaves it == nullptr if it doesn't find '%'.
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
Char c = *it++;
|
||||
if (it != end && *it == c) {
|
||||
write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(start, to_unsigned(it - start)));
|
||||
start = ++it;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(start, to_unsigned(it - 1 - start)));
|
||||
|
||||
auto specs = format_specs();
|
||||
specs.set_align(align::right);
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse argument index, flags and width.
|
||||
int arg_index = parse_header(it, end, specs, get_arg);
|
||||
if (arg_index == 0) report_error("argument not found");
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse precision.
|
||||
if (it != end && *it == '.') {
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
c = it != end ? *it : 0;
|
||||
if ('0' <= c && c <= '9') {
|
||||
specs.precision = parse_nonnegative_int(it, end, 0);
|
||||
} else if (c == '*') {
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
specs.precision =
|
||||
static_cast<int>(get_arg(-1).visit(printf_precision_handler()));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
specs.precision = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto arg = get_arg(arg_index);
|
||||
// For d, i, o, u, x, and X conversion specifiers, if a precision is
|
||||
// specified, the '0' flag is ignored
|
||||
if (specs.precision >= 0 && is_integral_type(arg.type())) {
|
||||
// Ignore '0' for non-numeric types or if '-' present.
|
||||
specs.set_fill(' ');
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (specs.precision >= 0 && arg.type() == type::cstring_type) {
|
||||
auto str = arg.visit(get_cstring<Char>());
|
||||
auto str_end = str + specs.precision;
|
||||
auto nul = std::find(str, str_end, Char());
|
||||
auto sv = basic_string_view<Char>(
|
||||
str, to_unsigned(nul != str_end ? nul - str : specs.precision));
|
||||
arg = sv;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (specs.alt() && arg.visit(is_zero_int())) specs.clear_alt();
|
||||
if (specs.fill_unit<Char>() == '0') {
|
||||
if (is_arithmetic_type(arg.type()) && specs.align() != align::left) {
|
||||
specs.set_align(align::numeric);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Ignore '0' flag for non-numeric types or if '-' flag is also present.
|
||||
specs.set_fill(' ');
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse length and convert the argument to the required type.
|
||||
c = it != end ? *it++ : 0;
|
||||
Char t = it != end ? *it : 0;
|
||||
switch (c) {
|
||||
case 'h':
|
||||
if (t == 'h') {
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
t = it != end ? *it : 0;
|
||||
convert_arg<signed char>(arg, t);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
convert_arg<short>(arg, t);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'l':
|
||||
if (t == 'l') {
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
t = it != end ? *it : 0;
|
||||
convert_arg<long long>(arg, t);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
convert_arg<long>(arg, t);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'j': convert_arg<intmax_t>(arg, t); break;
|
||||
case 'z': convert_arg<size_t>(arg, t); break;
|
||||
case 't': convert_arg<std::ptrdiff_t>(arg, t); break;
|
||||
case 'L':
|
||||
// printf produces garbage when 'L' is omitted for long double, no
|
||||
// need to do the same.
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default: --it; convert_arg<void>(arg, c);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse type.
|
||||
if (it == end) report_error("invalid format string");
|
||||
char type = static_cast<char>(*it++);
|
||||
if (is_integral_type(arg.type())) {
|
||||
// Normalize type.
|
||||
switch (type) {
|
||||
case 'i':
|
||||
case 'u': type = 'd'; break;
|
||||
case 'c':
|
||||
arg.visit(char_converter<basic_printf_context<Char>>(arg));
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
bool upper = false;
|
||||
specs.set_type(parse_printf_presentation_type(type, arg.type(), upper));
|
||||
if (specs.type() == presentation_type::none)
|
||||
report_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
if (upper) specs.set_upper();
|
||||
|
||||
start = it;
|
||||
|
||||
// Format argument.
|
||||
arg.visit(printf_arg_formatter<Char>(out, specs, context));
|
||||
}
|
||||
write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(start, to_unsigned(it - start)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
using printf_context = basic_printf_context<char>;
|
||||
using wprintf_context = basic_printf_context<wchar_t>;
|
||||
|
||||
using printf_args = basic_format_args<printf_context>;
|
||||
using wprintf_args = basic_format_args<wprintf_context>;
|
||||
|
||||
/// Constructs an `format_arg_store` object that contains references to
|
||||
/// arguments and can be implicitly converted to `printf_args`.
|
||||
template <typename Char = char, typename... T>
|
||||
inline auto make_printf_args(T&... args)
|
||||
-> decltype(fmt::make_format_args<basic_printf_context<Char>>(args...)) {
|
||||
return fmt::make_format_args<basic_printf_context<Char>>(args...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct vprintf_args {
|
||||
using type = basic_format_args<basic_printf_context<Char>>;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
inline auto vsprintf(basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
typename vprintf_args<Char>::type args)
|
||||
-> std::basic_string<Char> {
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
detail::vprintf(buf, fmt, args);
|
||||
return {buf.data(), buf.size()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Formats `args` according to specifications in `fmt` and returns the result
|
||||
* as as string.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* std::string message = fmt::sprintf("The answer is %d", 42);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... T, typename Char = detail::char_t<S>>
|
||||
inline auto sprintf(const S& fmt, const T&... args) -> std::basic_string<Char> {
|
||||
return vsprintf(detail::to_string_view(fmt),
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<basic_printf_context<Char>>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
inline auto vfprintf(std::FILE* f, basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
typename vprintf_args<Char>::type args) -> int {
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
detail::vprintf(buf, fmt, args);
|
||||
size_t size = buf.size();
|
||||
return std::fwrite(buf.data(), sizeof(Char), size, f) < size
|
||||
? -1
|
||||
: static_cast<int>(size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Formats `args` according to specifications in `fmt` and writes the output
|
||||
* to `f`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::fprintf(stderr, "Don't %s!", "panic");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... T, typename Char = detail::char_t<S>>
|
||||
inline auto fprintf(std::FILE* f, const S& fmt, const T&... args) -> int {
|
||||
return vfprintf(f, detail::to_string_view(fmt),
|
||||
make_printf_args<Char>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_DEPRECATED inline auto vprintf(basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
typename vprintf_args<Char>::type args)
|
||||
-> int {
|
||||
return vfprintf(stdout, fmt, args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Formats `args` according to specifications in `fmt` and writes the output
|
||||
* to `stdout`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::printf("Elapsed time: %.2f seconds", 1.23);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
inline auto printf(string_view fmt, const T&... args) -> int {
|
||||
return vfprintf(stdout, fmt, make_printf_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
FMT_DEPRECATED inline auto printf(basic_string_view<wchar_t> fmt,
|
||||
const T&... args) -> int {
|
||||
return vfprintf(stdout, fmt, make_printf_args<wchar_t>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_EXPORT
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // FMT_PRINTF_H_
|
||||
848
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/ranges.h
vendored
Normal file
848
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/ranges.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,848 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - range and tuple support
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich and {fmt} contributors
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_RANGES_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_RANGES_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <initializer_list>
|
||||
# include <iterator>
|
||||
# include <string>
|
||||
# include <tuple>
|
||||
# include <type_traits>
|
||||
# include <utility>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
enum class range_format { disabled, map, set, sequence, string, debug_string };
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> class is_map {
|
||||
template <typename U> static auto check(U*) -> typename U::mapped_type;
|
||||
template <typename> static void check(...);
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
!std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> class is_set {
|
||||
template <typename U> static auto check(U*) -> typename U::key_type;
|
||||
template <typename> static void check(...);
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
!std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value && !is_map<T>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// C array overload
|
||||
template <typename T, std::size_t N>
|
||||
auto range_begin(const T (&arr)[N]) -> const T* {
|
||||
return arr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename T, std::size_t N>
|
||||
auto range_end(const T (&arr)[N]) -> const T* {
|
||||
return arr + N;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Enable = void>
|
||||
struct has_member_fn_begin_end_t : std::false_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct has_member_fn_begin_end_t<T, void_t<decltype(*std::declval<T>().begin()),
|
||||
decltype(std::declval<T>().end())>>
|
||||
: std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
// Member function overloads.
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto range_begin(T&& rng) -> decltype(static_cast<T&&>(rng).begin()) {
|
||||
return static_cast<T&&>(rng).begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto range_end(T&& rng) -> decltype(static_cast<T&&>(rng).end()) {
|
||||
return static_cast<T&&>(rng).end();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ADL overloads. Only participate in overload resolution if member functions
|
||||
// are not found.
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto range_begin(T&& rng)
|
||||
-> enable_if_t<!has_member_fn_begin_end_t<T&&>::value,
|
||||
decltype(begin(static_cast<T&&>(rng)))> {
|
||||
return begin(static_cast<T&&>(rng));
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto range_end(T&& rng) -> enable_if_t<!has_member_fn_begin_end_t<T&&>::value,
|
||||
decltype(end(static_cast<T&&>(rng)))> {
|
||||
return end(static_cast<T&&>(rng));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Enable = void>
|
||||
struct has_const_begin_end : std::false_type {};
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Enable = void>
|
||||
struct has_mutable_begin_end : std::false_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct has_const_begin_end<
|
||||
T, void_t<decltype(*detail::range_begin(
|
||||
std::declval<const remove_cvref_t<T>&>())),
|
||||
decltype(detail::range_end(
|
||||
std::declval<const remove_cvref_t<T>&>()))>>
|
||||
: std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct has_mutable_begin_end<
|
||||
T, void_t<decltype(*detail::range_begin(std::declval<T&>())),
|
||||
decltype(detail::range_end(std::declval<T&>())),
|
||||
// the extra int here is because older versions of MSVC don't
|
||||
// SFINAE properly unless there are distinct types
|
||||
int>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename _ = void> struct is_range_ : std::false_type {};
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct is_range_<T, void>
|
||||
: std::integral_constant<bool, (has_const_begin_end<T>::value ||
|
||||
has_mutable_begin_end<T>::value)> {};
|
||||
|
||||
// tuple_size and tuple_element check.
|
||||
template <typename T> class is_tuple_like_ {
|
||||
template <typename U, typename V = typename std::remove_cv<U>::type>
|
||||
static auto check(U* p) -> decltype(std::tuple_size<V>::value, 0);
|
||||
template <typename> static void check(...);
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
!std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Check for integer_sequence
|
||||
#if defined(__cpp_lib_integer_sequence) || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1900
|
||||
template <typename T, T... N>
|
||||
using integer_sequence = std::integer_sequence<T, N...>;
|
||||
template <size_t... N> using index_sequence = std::index_sequence<N...>;
|
||||
template <size_t N> using make_index_sequence = std::make_index_sequence<N>;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
template <typename T, T... N> struct integer_sequence {
|
||||
using value_type = T;
|
||||
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR auto size() -> size_t { return sizeof...(N); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t... N> using index_sequence = integer_sequence<size_t, N...>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, size_t N, T... Ns>
|
||||
struct make_integer_sequence : make_integer_sequence<T, N - 1, N - 1, Ns...> {};
|
||||
template <typename T, T... Ns>
|
||||
struct make_integer_sequence<T, 0, Ns...> : integer_sequence<T, Ns...> {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t N>
|
||||
using make_index_sequence = make_integer_sequence<size_t, N>;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
using tuple_index_sequence = make_index_sequence<std::tuple_size<T>::value>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename C, bool = is_tuple_like_<T>::value>
|
||||
class is_tuple_formattable_ {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value = false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
template <typename T, typename C> class is_tuple_formattable_<T, C, true> {
|
||||
template <size_t... Is>
|
||||
static auto all_true(index_sequence<Is...>,
|
||||
integer_sequence<bool, (Is >= 0)...>) -> std::true_type;
|
||||
static auto all_true(...) -> std::false_type;
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t... Is>
|
||||
static auto check(index_sequence<Is...>) -> decltype(all_true(
|
||||
index_sequence<Is...>{},
|
||||
integer_sequence<bool,
|
||||
(is_formattable<typename std::tuple_element<Is, T>::type,
|
||||
C>::value)...>{}));
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
decltype(check(tuple_index_sequence<T>{}))::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Tuple, typename F, size_t... Is>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void for_each(index_sequence<Is...>, Tuple&& t, F&& f) {
|
||||
using std::get;
|
||||
// Using a free function get<Is>(Tuple) now.
|
||||
const int unused[] = {0, ((void)f(get<Is>(t)), 0)...};
|
||||
ignore_unused(unused);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Tuple, typename F>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void for_each(Tuple&& t, F&& f) {
|
||||
for_each(tuple_index_sequence<remove_cvref_t<Tuple>>(),
|
||||
std::forward<Tuple>(t), std::forward<F>(f));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Tuple1, typename Tuple2, typename F, size_t... Is>
|
||||
void for_each2(index_sequence<Is...>, Tuple1&& t1, Tuple2&& t2, F&& f) {
|
||||
using std::get;
|
||||
const int unused[] = {0, ((void)f(get<Is>(t1), get<Is>(t2)), 0)...};
|
||||
ignore_unused(unused);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Tuple1, typename Tuple2, typename F>
|
||||
void for_each2(Tuple1&& t1, Tuple2&& t2, F&& f) {
|
||||
for_each2(tuple_index_sequence<remove_cvref_t<Tuple1>>(),
|
||||
std::forward<Tuple1>(t1), std::forward<Tuple2>(t2),
|
||||
std::forward<F>(f));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
namespace tuple {
|
||||
// Workaround a bug in MSVC 2019 (v140).
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename... T>
|
||||
using result_t = std::tuple<formatter<remove_cvref_t<T>, Char>...>;
|
||||
|
||||
using std::get;
|
||||
template <typename Tuple, typename Char, std::size_t... Is>
|
||||
auto get_formatters(index_sequence<Is...>)
|
||||
-> result_t<Char, decltype(get<Is>(std::declval<Tuple>()))...>;
|
||||
} // namespace tuple
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_MSC_VERSION && FMT_MSC_VERSION < 1920
|
||||
// Older MSVC doesn't get the reference type correctly for arrays.
|
||||
template <typename R> struct range_reference_type_impl {
|
||||
using type = decltype(*detail::range_begin(std::declval<R&>()));
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, std::size_t N> struct range_reference_type_impl<T[N]> {
|
||||
using type = T&;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
using range_reference_type = typename range_reference_type_impl<T>::type;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
template <typename Range>
|
||||
using range_reference_type =
|
||||
decltype(*detail::range_begin(std::declval<Range&>()));
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// We don't use the Range's value_type for anything, but we do need the Range's
|
||||
// reference type, with cv-ref stripped.
|
||||
template <typename Range>
|
||||
using uncvref_type = remove_cvref_t<range_reference_type<Range>>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Formatter>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto maybe_set_debug_format(Formatter& f, bool set)
|
||||
-> decltype(f.set_debug_format(set)) {
|
||||
f.set_debug_format(set);
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename Formatter>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void maybe_set_debug_format(Formatter&, ...) {}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct range_format_kind_
|
||||
: std::integral_constant<range_format,
|
||||
std::is_same<uncvref_type<T>, T>::value
|
||||
? range_format::disabled
|
||||
: is_map<T>::value ? range_format::map
|
||||
: is_set<T>::value ? range_format::set
|
||||
: range_format::sequence> {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <range_format K>
|
||||
using range_format_constant = std::integral_constant<range_format, K>;
|
||||
|
||||
// These are not generic lambdas for compatibility with C++11.
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct parse_empty_specs {
|
||||
template <typename Formatter> FMT_CONSTEXPR void operator()(Formatter& f) {
|
||||
f.parse(ctx);
|
||||
detail::maybe_set_debug_format(f, true);
|
||||
}
|
||||
parse_context<Char>& ctx;
|
||||
};
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext> struct format_tuple_element {
|
||||
using char_type = typename FormatContext::char_type;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
void operator()(const formatter<T, char_type>& f, const T& v) {
|
||||
if (i > 0) ctx.advance_to(detail::copy<char_type>(separator, ctx.out()));
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(f.format(v, ctx));
|
||||
++i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
FormatContext& ctx;
|
||||
basic_string_view<char_type> separator;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct is_tuple_like {
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
detail::is_tuple_like_<T>::value && !detail::is_range_<T>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename C> struct is_tuple_formattable {
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
detail::is_tuple_formattable_<T, C>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Tuple, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<Tuple, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<fmt::is_tuple_like<Tuple>::value &&
|
||||
fmt::is_tuple_formattable<Tuple, Char>::value>> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
decltype(detail::tuple::get_formatters<Tuple, Char>(
|
||||
detail::tuple_index_sequence<Tuple>())) formatters_;
|
||||
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> separator_ = detail::string_literal<Char, ',', ' '>{};
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> opening_bracket_ =
|
||||
detail::string_literal<Char, '('>{};
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> closing_bracket_ =
|
||||
detail::string_literal<Char, ')'>{};
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR formatter() {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_separator(basic_string_view<Char> sep) {
|
||||
separator_ = sep;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_brackets(basic_string_view<Char> open,
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> close) {
|
||||
opening_bracket_ = open;
|
||||
closing_bracket_ = close;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin();
|
||||
auto end = ctx.end();
|
||||
if (it != end && detail::to_ascii(*it) == 'n') {
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
set_brackets({}, {});
|
||||
set_separator({});
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (it != end && *it != '}') report_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(it);
|
||||
detail::for_each(formatters_, detail::parse_empty_specs<Char>{ctx});
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const Tuple& value, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(detail::copy<Char>(opening_bracket_, ctx.out()));
|
||||
detail::for_each2(
|
||||
formatters_, value,
|
||||
detail::format_tuple_element<FormatContext>{0, ctx, separator_});
|
||||
return detail::copy<Char>(closing_bracket_, ctx.out());
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char> struct is_range {
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
detail::is_range_<T>::value && !detail::has_to_string_view<T>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Element>
|
||||
using range_formatter_type = formatter<remove_cvref_t<Element>, Char>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename R>
|
||||
using maybe_const_range =
|
||||
conditional_t<has_const_begin_end<R>::value, const R, R>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename R, typename Char>
|
||||
struct is_formattable_delayed
|
||||
: is_formattable<uncvref_type<maybe_const_range<R>>, Char> {};
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename...> struct conjunction : std::true_type {};
|
||||
template <typename P> struct conjunction<P> : P {};
|
||||
template <typename P1, typename... Pn>
|
||||
struct conjunction<P1, Pn...>
|
||||
: conditional_t<bool(P1::value), conjunction<Pn...>, P1> {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char, typename Enable = void>
|
||||
struct range_formatter;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct range_formatter<
|
||||
T, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<conjunction<std::is_same<T, remove_cvref_t<T>>,
|
||||
is_formattable<T, Char>>::value>> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
detail::range_formatter_type<Char, T> underlying_;
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> separator_ = detail::string_literal<Char, ',', ' '>{};
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> opening_bracket_ =
|
||||
detail::string_literal<Char, '['>{};
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> closing_bracket_ =
|
||||
detail::string_literal<Char, ']'>{};
|
||||
bool is_debug = false;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Output, typename It, typename Sentinel, typename U = T,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<U, Char>::value)>
|
||||
auto write_debug_string(Output& out, It it, Sentinel end) const -> Output {
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
for (; it != end; ++it) buf.push_back(*it);
|
||||
auto specs = format_specs();
|
||||
specs.set_type(presentation_type::debug);
|
||||
return detail::write<Char>(
|
||||
out, basic_string_view<Char>(buf.data(), buf.size()), specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Output, typename It, typename Sentinel, typename U = T,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<U, Char>::value)>
|
||||
auto write_debug_string(Output& out, It, Sentinel) const -> Output {
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR range_formatter() {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto underlying() -> detail::range_formatter_type<Char, T>& {
|
||||
return underlying_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_separator(basic_string_view<Char> sep) {
|
||||
separator_ = sep;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_brackets(basic_string_view<Char> open,
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> close) {
|
||||
opening_bracket_ = open;
|
||||
closing_bracket_ = close;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin();
|
||||
auto end = ctx.end();
|
||||
detail::maybe_set_debug_format(underlying_, true);
|
||||
if (it == end) return underlying_.parse(ctx);
|
||||
|
||||
switch (detail::to_ascii(*it)) {
|
||||
case 'n':
|
||||
set_brackets({}, {});
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case '?':
|
||||
is_debug = true;
|
||||
set_brackets({}, {});
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
if (it == end || *it != 's') report_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
FMT_FALLTHROUGH;
|
||||
case 's':
|
||||
if (!std::is_same<T, Char>::value)
|
||||
report_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
if (!is_debug) {
|
||||
set_brackets(detail::string_literal<Char, '"'>{},
|
||||
detail::string_literal<Char, '"'>{});
|
||||
set_separator({});
|
||||
detail::maybe_set_debug_format(underlying_, false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (it != end && *it != '}') {
|
||||
if (*it != ':') report_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
detail::maybe_set_debug_format(underlying_, false);
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(it);
|
||||
return underlying_.parse(ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename R, typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(R&& range, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
auto it = detail::range_begin(range);
|
||||
auto end = detail::range_end(range);
|
||||
if (is_debug) return write_debug_string(out, std::move(it), end);
|
||||
|
||||
out = detail::copy<Char>(opening_bracket_, out);
|
||||
int i = 0;
|
||||
for (; it != end; ++it) {
|
||||
if (i > 0) out = detail::copy<Char>(separator_, out);
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(out);
|
||||
auto&& item = *it; // Need an lvalue
|
||||
out = underlying_.format(item, ctx);
|
||||
++i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
out = detail::copy<Char>(closing_bracket_, out);
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char, typename Enable = void>
|
||||
struct range_format_kind
|
||||
: conditional_t<
|
||||
is_range<T, Char>::value, detail::range_format_kind_<T>,
|
||||
std::integral_constant<range_format, range_format::disabled>> {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename R, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<
|
||||
R, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<conjunction<
|
||||
bool_constant<
|
||||
range_format_kind<R, Char>::value != range_format::disabled &&
|
||||
range_format_kind<R, Char>::value != range_format::map &&
|
||||
range_format_kind<R, Char>::value != range_format::string &&
|
||||
range_format_kind<R, Char>::value != range_format::debug_string>,
|
||||
detail::is_formattable_delayed<R, Char>>::value>> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using range_type = detail::maybe_const_range<R>;
|
||||
range_formatter<detail::uncvref_type<range_type>, Char> range_formatter_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using nonlocking = void;
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR formatter() {
|
||||
if (detail::const_check(range_format_kind<R, Char>::value !=
|
||||
range_format::set))
|
||||
return;
|
||||
range_formatter_.set_brackets(detail::string_literal<Char, '{'>{},
|
||||
detail::string_literal<Char, '}'>{});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
return range_formatter_.parse(ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(range_type& range, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return range_formatter_.format(range, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// A map formatter.
|
||||
template <typename R, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<
|
||||
R, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<range_format_kind<R, Char>::value == range_format::map>> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using map_type = detail::maybe_const_range<R>;
|
||||
using element_type = detail::uncvref_type<map_type>;
|
||||
|
||||
decltype(detail::tuple::get_formatters<element_type, Char>(
|
||||
detail::tuple_index_sequence<element_type>())) formatters_;
|
||||
bool no_delimiters_ = false;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR formatter() {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin();
|
||||
auto end = ctx.end();
|
||||
if (it != end) {
|
||||
if (detail::to_ascii(*it) == 'n') {
|
||||
no_delimiters_ = true;
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (it != end && *it != '}') {
|
||||
if (*it != ':') report_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(it);
|
||||
}
|
||||
detail::for_each(formatters_, detail::parse_empty_specs<Char>{ctx});
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(map_type& map, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> open = detail::string_literal<Char, '{'>{};
|
||||
if (!no_delimiters_) out = detail::copy<Char>(open, out);
|
||||
int i = 0;
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> sep = detail::string_literal<Char, ',', ' '>{};
|
||||
for (auto&& value : map) {
|
||||
if (i > 0) out = detail::copy<Char>(sep, out);
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(out);
|
||||
detail::for_each2(formatters_, value,
|
||||
detail::format_tuple_element<FormatContext>{
|
||||
0, ctx, detail::string_literal<Char, ':', ' '>{}});
|
||||
++i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> close = detail::string_literal<Char, '}'>{};
|
||||
if (!no_delimiters_) out = detail::copy<Char>(close, out);
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// A (debug_)string formatter.
|
||||
template <typename R, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<
|
||||
R, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<range_format_kind<R, Char>::value == range_format::string ||
|
||||
range_format_kind<R, Char>::value ==
|
||||
range_format::debug_string>> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using range_type = detail::maybe_const_range<R>;
|
||||
using string_type =
|
||||
conditional_t<std::is_constructible<
|
||||
detail::std_string_view<Char>,
|
||||
decltype(detail::range_begin(std::declval<R>())),
|
||||
decltype(detail::range_end(std::declval<R>()))>::value,
|
||||
detail::std_string_view<Char>, std::basic_string<Char>>;
|
||||
|
||||
formatter<string_type, Char> underlying_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
return underlying_.parse(ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(range_type& range, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
if (detail::const_check(range_format_kind<R, Char>::value ==
|
||||
range_format::debug_string))
|
||||
*out++ = '"';
|
||||
out = underlying_.format(
|
||||
string_type{detail::range_begin(range), detail::range_end(range)}, ctx);
|
||||
if (detail::const_check(range_format_kind<R, Char>::value ==
|
||||
range_format::debug_string))
|
||||
*out++ = '"';
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename It, typename Sentinel, typename Char = char>
|
||||
struct join_view : detail::view {
|
||||
It begin;
|
||||
Sentinel end;
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> sep;
|
||||
|
||||
join_view(It b, Sentinel e, basic_string_view<Char> s)
|
||||
: begin(std::move(b)), end(e), sep(s) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename It, typename Sentinel, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<join_view<It, Sentinel, Char>, Char> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using value_type =
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_ranges
|
||||
std::iter_value_t<It>;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
typename std::iterator_traits<It>::value_type;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
formatter<remove_cvref_t<value_type>, Char> value_formatter_;
|
||||
|
||||
using view = conditional_t<std::is_copy_constructible<It>::value,
|
||||
const join_view<It, Sentinel, Char>,
|
||||
join_view<It, Sentinel, Char>>;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using nonlocking = void;
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
return value_formatter_.parse(ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(view& value, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
using iter =
|
||||
conditional_t<std::is_copy_constructible<view>::value, It, It&>;
|
||||
iter it = value.begin;
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
if (it == value.end) return out;
|
||||
out = value_formatter_.format(*it, ctx);
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
while (it != value.end) {
|
||||
out = detail::copy<Char>(value.sep.begin(), value.sep.end(), out);
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(out);
|
||||
out = value_formatter_.format(*it, ctx);
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Tuple> struct tuple_join_view : detail::view {
|
||||
const Tuple& tuple;
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> sep;
|
||||
|
||||
tuple_join_view(const Tuple& t, basic_string_view<Char> s)
|
||||
: tuple(t), sep{s} {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Define FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS to enable experimental format specifiers
|
||||
// support in tuple_join. It is disabled by default because of issues with
|
||||
// the dynamic width and precision.
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS
|
||||
# define FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS 0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Tuple>
|
||||
struct formatter<tuple_join_view<Char, Tuple>, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<is_tuple_like<Tuple>::value>> {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
return do_parse(ctx, std::tuple_size<Tuple>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const tuple_join_view<Char, Tuple>& value,
|
||||
FormatContext& ctx) const -> typename FormatContext::iterator {
|
||||
return do_format(value, ctx, std::tuple_size<Tuple>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
decltype(detail::tuple::get_formatters<Tuple, Char>(
|
||||
detail::tuple_index_sequence<Tuple>())) formatters_;
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto do_parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx,
|
||||
std::integral_constant<size_t, 0>)
|
||||
-> const Char* {
|
||||
return ctx.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t N>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto do_parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx,
|
||||
std::integral_constant<size_t, N>)
|
||||
-> const Char* {
|
||||
auto end = ctx.begin();
|
||||
#if FMT_TUPLE_JOIN_SPECIFIERS
|
||||
end = std::get<std::tuple_size<Tuple>::value - N>(formatters_).parse(ctx);
|
||||
if (N > 1) {
|
||||
auto end1 = do_parse(ctx, std::integral_constant<size_t, N - 1>());
|
||||
if (end != end1)
|
||||
report_error("incompatible format specs for tuple elements");
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return end;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto do_format(const tuple_join_view<Char, Tuple>&, FormatContext& ctx,
|
||||
std::integral_constant<size_t, 0>) const ->
|
||||
typename FormatContext::iterator {
|
||||
return ctx.out();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext, size_t N>
|
||||
auto do_format(const tuple_join_view<Char, Tuple>& value, FormatContext& ctx,
|
||||
std::integral_constant<size_t, N>) const ->
|
||||
typename FormatContext::iterator {
|
||||
using std::get;
|
||||
auto out =
|
||||
std::get<std::tuple_size<Tuple>::value - N>(formatters_)
|
||||
.format(get<std::tuple_size<Tuple>::value - N>(value.tuple), ctx);
|
||||
if (N <= 1) return out;
|
||||
out = detail::copy<Char>(value.sep, out);
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(out);
|
||||
return do_format(value, ctx, std::integral_constant<size_t, N - 1>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
// Check if T has an interface like a container adaptor (e.g. std::stack,
|
||||
// std::queue, std::priority_queue).
|
||||
template <typename T> class is_container_adaptor_like {
|
||||
template <typename U> static auto check(U* p) -> typename U::container_type;
|
||||
template <typename> static void check(...);
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
!std::is_void<decltype(check<T>(nullptr))>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Container> struct all {
|
||||
const Container& c;
|
||||
auto begin() const -> typename Container::const_iterator { return c.begin(); }
|
||||
auto end() const -> typename Container::const_iterator { return c.end(); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<
|
||||
T, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<conjunction<detail::is_container_adaptor_like<T>,
|
||||
bool_constant<range_format_kind<T, Char>::value ==
|
||||
range_format::disabled>>::value>>
|
||||
: formatter<detail::all<typename T::container_type>, Char> {
|
||||
using all = detail::all<typename T::container_type>;
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const T& t, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
struct getter : T {
|
||||
static auto get(const T& t) -> all {
|
||||
return {t.*(&getter::c)}; // Access c through the derived class.
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
return formatter<all>::format(getter::get(t), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
|
||||
/// Returns a view that formats the iterator range `[begin, end)` with elements
|
||||
/// separated by `sep`.
|
||||
template <typename It, typename Sentinel>
|
||||
auto join(It begin, Sentinel end, string_view sep) -> join_view<It, Sentinel> {
|
||||
return {std::move(begin), end, sep};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Returns a view that formats `range` with elements separated by `sep`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* auto v = std::vector<int>{1, 2, 3};
|
||||
* fmt::print("{}", fmt::join(v, ", "));
|
||||
* // Output: 1, 2, 3
|
||||
*
|
||||
* `fmt::join` applies passed format specifiers to the range elements:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::print("{:02}", fmt::join(v, ", "));
|
||||
* // Output: 01, 02, 03
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename Range, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_tuple_like<Range>::value)>
|
||||
auto join(Range&& r, string_view sep)
|
||||
-> join_view<decltype(detail::range_begin(r)),
|
||||
decltype(detail::range_end(r))> {
|
||||
return {detail::range_begin(r), detail::range_end(r), sep};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Returns an object that formats `std::tuple` with elements separated by `sep`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* auto t = std::tuple<int, char>{1, 'a'};
|
||||
* fmt::print("{}", fmt::join(t, ", "));
|
||||
* // Output: 1, a
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename Tuple, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_tuple_like<Tuple>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto join(const Tuple& tuple, string_view sep)
|
||||
-> tuple_join_view<char, Tuple> {
|
||||
return {tuple, sep};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Returns an object that formats `std::initializer_list` with elements
|
||||
* separated by `sep`.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* **Example**:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* fmt::print("{}", fmt::join({1, 2, 3}, ", "));
|
||||
* // Output: "1, 2, 3"
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto join(std::initializer_list<T> list, string_view sep)
|
||||
-> join_view<const T*, const T*> {
|
||||
return join(std::begin(list), std::end(list), sep);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_EXPORT
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // FMT_RANGES_H_
|
||||
726
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/std.h
vendored
Normal file
726
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/std.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,726 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - formatters for standard library types
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_STD_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_STD_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
#include "ostream.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <atomic>
|
||||
# include <bitset>
|
||||
# include <complex>
|
||||
# include <cstdlib>
|
||||
# include <exception>
|
||||
# include <functional>
|
||||
# include <memory>
|
||||
# include <thread>
|
||||
# include <type_traits>
|
||||
# include <typeinfo>
|
||||
# include <utility>
|
||||
# include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
// Check FMT_CPLUSPLUS to suppress a bogus warning in MSVC.
|
||||
# if FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201703L
|
||||
# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<filesystem>) && \
|
||||
(!defined(FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM) || FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM != 0)
|
||||
# include <filesystem>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<variant>)
|
||||
# include <variant>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<optional>)
|
||||
# include <optional>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
// Use > instead of >= in the version check because <source_location> may be
|
||||
// available after C++17 but before C++20 is marked as implemented.
|
||||
# if FMT_CPLUSPLUS > 201703L && FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<source_location>)
|
||||
# include <source_location>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# if FMT_CPLUSPLUS > 202002L && FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<expected>)
|
||||
# include <expected>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif // FMT_MODULE
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<version>)
|
||||
# include <version>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// GCC 4 does not support FMT_HAS_INCLUDE.
|
||||
#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<cxxabi.h>) || defined(__GLIBCXX__)
|
||||
# include <cxxabi.h>
|
||||
// Android NDK with gabi++ library on some architectures does not implement
|
||||
// abi::__cxa_demangle().
|
||||
# ifndef __GABIXX_CXXABI_H__
|
||||
# define FMT_HAS_ABI_CXA_DEMANGLE
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// For older Xcode versions, __cpp_lib_xxx flags are inaccurately defined.
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM
|
||||
# ifdef __cpp_lib_filesystem
|
||||
# define FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM __cpp_lib_filesystem
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# define FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT
|
||||
# ifdef __cpp_lib_variant
|
||||
# define FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT __cpp_lib_variant
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# define FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename PathChar>
|
||||
auto get_path_string(const std::filesystem::path& p,
|
||||
const std::basic_string<PathChar>& native) {
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, char> && std::is_same_v<PathChar, wchar_t>)
|
||||
return to_utf8<wchar_t>(native, to_utf8_error_policy::replace);
|
||||
else
|
||||
return p.string<Char>();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename PathChar>
|
||||
void write_escaped_path(basic_memory_buffer<Char>& quoted,
|
||||
const std::filesystem::path& p,
|
||||
const std::basic_string<PathChar>& native) {
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, char> &&
|
||||
std::is_same_v<PathChar, wchar_t>) {
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t>();
|
||||
write_escaped_string<wchar_t>(std::back_inserter(buf), native);
|
||||
bool valid = to_utf8<wchar_t>::convert(quoted, {buf.data(), buf.size()});
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(valid, "invalid utf16");
|
||||
} else if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, PathChar>) {
|
||||
write_escaped_string<std::filesystem::path::value_type>(
|
||||
std::back_inserter(quoted), native);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
write_escaped_string<Char>(std::back_inserter(quoted), p.string<Char>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::filesystem::path, Char> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
format_specs specs_;
|
||||
detail::arg_ref<Char> width_ref_;
|
||||
bool debug_ = false;
|
||||
char path_type_ = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_debug_format(bool set = true) { debug_ = set; }
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) {
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end();
|
||||
if (it == end) return it;
|
||||
|
||||
it = detail::parse_align(it, end, specs_);
|
||||
if (it == end) return it;
|
||||
|
||||
Char c = *it;
|
||||
if ((c >= '0' && c <= '9') || c == '{')
|
||||
it = detail::parse_width(it, end, specs_, width_ref_, ctx);
|
||||
if (it != end && *it == '?') {
|
||||
debug_ = true;
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (it != end && (*it == 'g')) path_type_ = detail::to_ascii(*it++);
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::filesystem::path& p, FormatContext& ctx) const {
|
||||
auto specs = specs_;
|
||||
auto path_string =
|
||||
!path_type_ ? p.native()
|
||||
: p.generic_string<std::filesystem::path::value_type>();
|
||||
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec(specs.dynamic_width(), specs.width, width_ref_,
|
||||
ctx);
|
||||
if (!debug_) {
|
||||
auto s = detail::get_path_string<Char>(p, path_string);
|
||||
return detail::write(ctx.out(), basic_string_view<Char>(s), specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto quoted = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
detail::write_escaped_path(quoted, p, path_string);
|
||||
return detail::write(ctx.out(),
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char>(quoted.data(), quoted.size()),
|
||||
specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class path : public std::filesystem::path {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
auto display_string() const -> std::string {
|
||||
const std::filesystem::path& base = *this;
|
||||
return fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{}"), base);
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto system_string() const -> std::string { return string(); }
|
||||
|
||||
auto generic_display_string() const -> std::string {
|
||||
const std::filesystem::path& base = *this;
|
||||
return fmt::format(FMT_STRING("{:g}"), base);
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto generic_system_string() const -> std::string { return generic_string(); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif // FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <std::size_t N, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::bitset<N>, Char>
|
||||
: nested_formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
// Functor because C++11 doesn't support generic lambdas.
|
||||
struct writer {
|
||||
const std::bitset<N>& bs;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(OutputIt out) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
for (auto pos = N; pos > 0; --pos) {
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, bs[pos - 1] ? Char('1') : Char('0'));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::bitset<N>& bs, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return this->write_padded(ctx, writer{bs});
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::thread::id, Char> : basic_ostream_formatter<Char> {};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_optional
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::optional<T>, Char,
|
||||
std::enable_if_t<is_formattable<T, Char>::value>> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
formatter<T, Char> underlying_;
|
||||
static constexpr basic_string_view<Char> optional =
|
||||
detail::string_literal<Char, 'o', 'p', 't', 'i', 'o', 'n', 'a', 'l',
|
||||
'('>{};
|
||||
static constexpr basic_string_view<Char> none =
|
||||
detail::string_literal<Char, 'n', 'o', 'n', 'e'>{};
|
||||
|
||||
template <class U>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR static auto maybe_set_debug_format(U& u, bool set)
|
||||
-> decltype(u.set_debug_format(set)) {
|
||||
u.set_debug_format(set);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <class U>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR static void maybe_set_debug_format(U&, ...) {}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) {
|
||||
maybe_set_debug_format(underlying_, true);
|
||||
return underlying_.parse(ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::optional<T>& opt, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
if (!opt) return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), none);
|
||||
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, optional);
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(out);
|
||||
out = underlying_.format(*opt, ctx);
|
||||
return detail::write(out, ')');
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_optional
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__cpp_lib_expected) || FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T>
|
||||
auto write_escaped_alternative(OutputIt out, const T& v) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
if constexpr (has_to_string_view<T>::value)
|
||||
return write_escaped_string<Char>(out, detail::to_string_view(v));
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, Char>) return write_escaped_char(out, v);
|
||||
return write<Char>(out, v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_expected
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename T, typename E, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::expected<T, E>, Char,
|
||||
std::enable_if_t<(std::is_void<T>::value ||
|
||||
is_formattable<T, Char>::value) &&
|
||||
is_formattable<E, Char>::value>> {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
return ctx.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::expected<T, E>& value, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
|
||||
if (value.has_value()) {
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, "expected(");
|
||||
if constexpr (!std::is_void<T>::value)
|
||||
out = detail::write_escaped_alternative<Char>(out, *value);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, "unexpected(");
|
||||
out = detail::write_escaped_alternative<Char>(out, value.error());
|
||||
}
|
||||
*out++ = ')';
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_expected
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_source_location
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <> struct formatter<std::source_location> {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<>& ctx) { return ctx.begin(); }
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::source_location& loc, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, loc.file_name());
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, ':');
|
||||
out = detail::write<char>(out, loc.line());
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, ':');
|
||||
out = detail::write<char>(out, loc.column());
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, ": ");
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, loc.function_name());
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
using variant_index_sequence =
|
||||
std::make_index_sequence<std::variant_size<T>::value>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename> struct is_variant_like_ : std::false_type {};
|
||||
template <typename... Types>
|
||||
struct is_variant_like_<std::variant<Types...>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
// formattable element check.
|
||||
template <typename T, typename C> class is_variant_formattable_ {
|
||||
template <std::size_t... Is>
|
||||
static std::conjunction<
|
||||
is_formattable<std::variant_alternative_t<Is, T>, C>...>
|
||||
check(std::index_sequence<Is...>);
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
decltype(check(variant_index_sequence<T>{}))::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct is_variant_like {
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value = detail::is_variant_like_<T>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename C> struct is_variant_formattable {
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
detail::is_variant_formattable_<T, C>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::monostate, Char> {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
return ctx.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::monostate&, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), "monostate");
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename Variant, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<
|
||||
Variant, Char,
|
||||
std::enable_if_t<std::conjunction_v<
|
||||
is_variant_like<Variant>, is_variant_formattable<Variant, Char>>>> {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
return ctx.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const Variant& value, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, "variant(");
|
||||
FMT_TRY {
|
||||
std::visit(
|
||||
[&](const auto& v) {
|
||||
out = detail::write_escaped_alternative<Char>(out, v);
|
||||
},
|
||||
value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CATCH(const std::bad_variant_access&) {
|
||||
detail::write<Char>(out, "valueless by exception");
|
||||
}
|
||||
*out++ = ')';
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif // FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <> struct formatter<std::error_code> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
format_specs specs_;
|
||||
detail::arg_ref<char> width_ref_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<>& ctx) -> const char* {
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end();
|
||||
if (it == end) return it;
|
||||
|
||||
it = detail::parse_align(it, end, specs_);
|
||||
if (it == end) return it;
|
||||
|
||||
char c = *it;
|
||||
if ((c >= '0' && c <= '9') || c == '{')
|
||||
it = detail::parse_width(it, end, specs_, width_ref_, ctx);
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto format(const std::error_code& ec,
|
||||
FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto specs = specs_;
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec(specs.dynamic_width(), specs.width, width_ref_,
|
||||
ctx);
|
||||
memory_buffer buf;
|
||||
buf.append(string_view(ec.category().name()));
|
||||
buf.push_back(':');
|
||||
detail::write<char>(appender(buf), ec.value());
|
||||
return detail::write<char>(ctx.out(), string_view(buf.data(), buf.size()),
|
||||
specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_RTTI
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename OutputIt>
|
||||
auto write_demangled_name(OutputIt out, const std::type_info& ti) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
# ifdef FMT_HAS_ABI_CXA_DEMANGLE
|
||||
int status = 0;
|
||||
std::size_t size = 0;
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<char, void (*)(void*)> demangled_name_ptr(
|
||||
abi::__cxa_demangle(ti.name(), nullptr, &size, &status), &std::free);
|
||||
|
||||
string_view demangled_name_view;
|
||||
if (demangled_name_ptr) {
|
||||
demangled_name_view = demangled_name_ptr.get();
|
||||
|
||||
// Normalization of stdlib inline namespace names.
|
||||
// libc++ inline namespaces.
|
||||
// std::__1::* -> std::*
|
||||
// std::__1::__fs::* -> std::*
|
||||
// libstdc++ inline namespaces.
|
||||
// std::__cxx11::* -> std::*
|
||||
// std::filesystem::__cxx11::* -> std::filesystem::*
|
||||
if (demangled_name_view.starts_with("std::")) {
|
||||
char* begin = demangled_name_ptr.get();
|
||||
char* to = begin + 5; // std::
|
||||
for (char *from = to, *end = begin + demangled_name_view.size();
|
||||
from < end;) {
|
||||
// This is safe, because demangled_name is NUL-terminated.
|
||||
if (from[0] == '_' && from[1] == '_') {
|
||||
char* next = from + 1;
|
||||
while (next < end && *next != ':') next++;
|
||||
if (next[0] == ':' && next[1] == ':') {
|
||||
from = next + 2;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
*to++ = *from++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
demangled_name_view = {begin, detail::to_unsigned(to - begin)};
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
demangled_name_view = string_view(ti.name());
|
||||
}
|
||||
return detail::write_bytes<Char>(out, demangled_name_view);
|
||||
# elif FMT_MSC_VERSION
|
||||
const string_view demangled_name(ti.name());
|
||||
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < demangled_name.size(); ++i) {
|
||||
auto sub = demangled_name;
|
||||
sub.remove_prefix(i);
|
||||
if (sub.starts_with("enum ")) {
|
||||
i += 4;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (sub.starts_with("class ") || sub.starts_with("union ")) {
|
||||
i += 5;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (sub.starts_with("struct ")) {
|
||||
i += 6;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (*sub.begin() != ' ') *out++ = *sub.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
# else
|
||||
return detail::write_bytes<Char>(out, string_view(ti.name()));
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::type_info, Char // DEPRECATED! Mixing code unit types.
|
||||
> {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
return ctx.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Context>
|
||||
auto format(const std::type_info& ti, Context& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return detail::write_demangled_name<Char>(ctx.out(), ti);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<
|
||||
T, Char, // DEPRECATED! Mixing code unit types.
|
||||
typename std::enable_if<std::is_base_of<std::exception, T>::value>::type> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool with_typename_ = false;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin();
|
||||
auto end = ctx.end();
|
||||
if (it == end || *it == '}') return it;
|
||||
if (*it == 't') {
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
with_typename_ = FMT_USE_RTTI != 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Context>
|
||||
auto format(const std::exception& ex, Context& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_RTTI
|
||||
if (with_typename_) {
|
||||
out = detail::write_demangled_name<Char>(out, typeid(ex));
|
||||
*out++ = ':';
|
||||
*out++ = ' ';
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return detail::write_bytes<Char>(out, string_view(ex.what()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Enable = void>
|
||||
struct has_flip : std::false_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct has_flip<T, void_t<decltype(std::declval<T>().flip())>>
|
||||
: std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct is_bit_reference_like {
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
std::is_convertible<T, bool>::value &&
|
||||
std::is_nothrow_assignable<T, bool>::value && has_flip<T>::value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _LIBCPP_VERSION
|
||||
|
||||
// Workaround for libc++ incompatibility with C++ standard.
|
||||
// According to the Standard, `bitset::operator[] const` returns bool.
|
||||
template <typename C>
|
||||
struct is_bit_reference_like<std::__bit_const_reference<C>> {
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value = true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
// We can't use std::vector<bool, Allocator>::reference and
|
||||
// std::bitset<N>::reference because the compiler can't deduce Allocator and N
|
||||
// in partial specialization.
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename BitRef, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<BitRef, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<detail::is_bit_reference_like<BitRef>::value>>
|
||||
: formatter<bool, Char> {
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto format(const BitRef& v, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return formatter<bool, Char>::format(v, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Deleter>
|
||||
auto ptr(const std::unique_ptr<T, Deleter>& p) -> const void* {
|
||||
return p.get();
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename T> auto ptr(const std::shared_ptr<T>& p) -> const void* {
|
||||
return p.get();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::atomic<T>, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<is_formattable<T, Char>::value>>
|
||||
: formatter<T, Char> {
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::atomic<T>& v, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return formatter<T, Char>::format(v.load(), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::atomic_flag, Char> : formatter<bool, Char> {
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::atomic_flag& v, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return formatter<bool, Char>::format(v.test(), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char> struct formatter<std::complex<T>, Char> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
detail::dynamic_format_specs<Char> specs_;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext, typename OutputIt>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto do_format(const std::complex<T>& c,
|
||||
detail::dynamic_format_specs<Char>& specs,
|
||||
FormatContext& ctx, OutputIt out) const
|
||||
-> OutputIt {
|
||||
if (c.real() != 0) {
|
||||
*out++ = Char('(');
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, c.real(), specs, ctx.locale());
|
||||
specs.set_sign(sign::plus);
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, c.imag(), specs, ctx.locale());
|
||||
if (!detail::isfinite(c.imag())) *out++ = Char(' ');
|
||||
*out++ = Char('i');
|
||||
*out++ = Char(')');
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, c.imag(), specs, ctx.locale());
|
||||
if (!detail::isfinite(c.imag())) *out++ = Char(' ');
|
||||
*out++ = Char('i');
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(parse_context<Char>& ctx) -> const Char* {
|
||||
if (ctx.begin() == ctx.end() || *ctx.begin() == '}') return ctx.begin();
|
||||
return parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), specs_, ctx,
|
||||
detail::type_constant<T, Char>::value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::complex<T>& c, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto specs = specs_;
|
||||
if (specs.dynamic()) {
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec(specs.dynamic_width(), specs.width,
|
||||
specs.width_ref, ctx);
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec(specs.dynamic_precision(), specs.precision,
|
||||
specs.precision_ref, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (specs.width == 0) return do_format(c, specs, ctx, ctx.out());
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
|
||||
auto outer_specs = format_specs();
|
||||
outer_specs.width = specs.width;
|
||||
outer_specs.copy_fill_from(specs);
|
||||
outer_specs.set_align(specs.align());
|
||||
|
||||
specs.width = 0;
|
||||
specs.set_fill({});
|
||||
specs.set_align(align::none);
|
||||
|
||||
do_format(c, specs, ctx, basic_appender<Char>(buf));
|
||||
return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(),
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char>(buf.data(), buf.size()),
|
||||
outer_specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::reference_wrapper<T>, Char,
|
||||
enable_if_t<is_formattable<remove_cvref_t<T>, Char>::value>>
|
||||
: formatter<remove_cvref_t<T>, Char> {
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(std::reference_wrapper<T> ref, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return formatter<remove_cvref_t<T>, Char>::format(ref.get(), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif // FMT_STD_H_
|
||||
373
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/xchar.h
vendored
Normal file
373
extlib/libfmt/include/fmt/xchar.h
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,373 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - optional wchar_t and exotic character support
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_XCHAR_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_XCHAR_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#include "color.h"
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
#include "ostream.h"
|
||||
#include "ranges.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <cwchar>
|
||||
# if FMT_USE_LOCALE
|
||||
# include <locale>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
using is_exotic_char = bool_constant<!std::is_same<T, char>::value>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S, typename = void> struct format_string_char {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S>
|
||||
struct format_string_char<
|
||||
S, void_t<decltype(sizeof(detail::to_string_view(std::declval<S>())))>> {
|
||||
using type = char_t<S>;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S>
|
||||
struct format_string_char<
|
||||
S, enable_if_t<std::is_base_of<detail::compile_string, S>::value>> {
|
||||
using type = typename S::char_type;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S>
|
||||
using format_string_char_t = typename format_string_char<S>::type;
|
||||
|
||||
inline auto write_loc(basic_appender<wchar_t> out, loc_value value,
|
||||
const format_specs& specs, locale_ref loc) -> bool {
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_LOCALE
|
||||
auto& numpunct =
|
||||
std::use_facet<std::numpunct<wchar_t>>(loc.get<std::locale>());
|
||||
auto separator = std::wstring();
|
||||
auto grouping = numpunct.grouping();
|
||||
if (!grouping.empty()) separator = std::wstring(1, numpunct.thousands_sep());
|
||||
return value.visit(loc_writer<wchar_t>{out, specs, separator, grouping, {}});
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
|
||||
using wstring_view = basic_string_view<wchar_t>;
|
||||
using wformat_parse_context = parse_context<wchar_t>;
|
||||
using wformat_context = buffered_context<wchar_t>;
|
||||
using wformat_args = basic_format_args<wformat_context>;
|
||||
using wmemory_buffer = basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename... T> struct basic_fstring {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> str_;
|
||||
|
||||
static constexpr int num_static_named_args =
|
||||
detail::count_static_named_args<T...>();
|
||||
|
||||
using checker = detail::format_string_checker<
|
||||
Char, static_cast<int>(sizeof...(T)), num_static_named_args,
|
||||
num_static_named_args != detail::count_named_args<T...>()>;
|
||||
|
||||
using arg_pack = detail::arg_pack<T...>;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using t = basic_fstring;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(
|
||||
std::is_convertible<const S&, basic_string_view<Char>>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEVAL FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE basic_fstring(const S& s) : str_(s) {
|
||||
if (FMT_USE_CONSTEVAL)
|
||||
detail::parse_format_string<Char>(s, checker(s, arg_pack()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename S,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_base_of<detail::compile_string, S>::value&&
|
||||
std::is_same<typename S::char_type, Char>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE basic_fstring(const S&) : str_(S()) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto sv = basic_string_view<Char>(S());
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR int ignore =
|
||||
(parse_format_string(sv, checker(sv, arg_pack())), 0);
|
||||
detail::ignore_unused(ignore);
|
||||
}
|
||||
basic_fstring(runtime_format_string<Char> fmt) : str_(fmt.str) {}
|
||||
|
||||
operator basic_string_view<Char>() const { return str_; }
|
||||
auto get() const -> basic_string_view<Char> { return str_; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename... T>
|
||||
using basic_format_string = basic_fstring<Char, T...>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
using wformat_string = typename basic_format_string<wchar_t, T...>::t;
|
||||
inline auto runtime(wstring_view s) -> runtime_format_string<wchar_t> {
|
||||
return {{s}};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct is_char<wchar_t> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
template <> struct is_char<char16_t> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
template <> struct is_char<char32_t> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_char8_t
|
||||
template <> struct is_char<char8_t> : bool_constant<detail::is_utf8_enabled> {};
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
constexpr auto make_wformat_args(T&... args)
|
||||
-> decltype(fmt::make_format_args<wformat_context>(args...)) {
|
||||
return fmt::make_format_args<wformat_context>(args...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if !FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS
|
||||
inline namespace literals {
|
||||
inline auto operator""_a(const wchar_t* s, size_t) -> detail::udl_arg<wchar_t> {
|
||||
return {s};
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace literals
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename It, typename Sentinel>
|
||||
auto join(It begin, Sentinel end, wstring_view sep)
|
||||
-> join_view<It, Sentinel, wchar_t> {
|
||||
return {begin, end, sep};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Range, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_tuple_like<Range>::value)>
|
||||
auto join(Range&& range, wstring_view sep)
|
||||
-> join_view<decltype(std::begin(range)), decltype(std::end(range)),
|
||||
wchar_t> {
|
||||
return join(std::begin(range), std::end(range), sep);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto join(std::initializer_list<T> list, wstring_view sep)
|
||||
-> join_view<const T*, const T*, wchar_t> {
|
||||
return join(std::begin(list), std::end(list), sep);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Tuple, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_tuple_like<Tuple>::value)>
|
||||
auto join(const Tuple& tuple, basic_string_view<wchar_t> sep)
|
||||
-> tuple_join_view<wchar_t, Tuple> {
|
||||
return {tuple, sep};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value)>
|
||||
auto vformat(basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
typename detail::vformat_args<Char>::type args)
|
||||
-> std::basic_string<Char> {
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, fmt, args);
|
||||
return {buf.data(), buf.size()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
auto format(wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> std::wstring {
|
||||
return vformat(fmt::wstring_view(fmt), fmt::make_wformat_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename... T>
|
||||
auto format_to(OutputIt out, wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args)
|
||||
-> OutputIt {
|
||||
return vformat_to(out, fmt::wstring_view(fmt),
|
||||
fmt::make_wformat_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Pass char_t as a default template parameter instead of using
|
||||
// std::basic_string<char_t<S>> to reduce the symbol size.
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... T,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<Char, char>::value &&
|
||||
!std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value)>
|
||||
auto format(const S& fmt, T&&... args) -> std::basic_string<Char> {
|
||||
return vformat(detail::to_string_view(fmt),
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<buffered_context<Char>>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Locale, typename S,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_locale<Locale>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)>
|
||||
inline auto vformat(const Locale& loc, const S& fmt,
|
||||
typename detail::vformat_args<Char>::type args)
|
||||
-> std::basic_string<Char> {
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, detail::to_string_view(fmt), args,
|
||||
detail::locale_ref(loc));
|
||||
return {buf.data(), buf.size()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Locale, typename S, typename... T,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_locale<Locale>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)>
|
||||
inline auto format(const Locale& loc, const S& fmt, T&&... args)
|
||||
-> std::basic_string<Char> {
|
||||
return vformat(loc, detail::to_string_view(fmt),
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<buffered_context<Char>>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename S,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)>
|
||||
auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, const S& fmt,
|
||||
typename detail::vformat_args<Char>::type args) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
auto&& buf = detail::get_buffer<Char>(out);
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, detail::to_string_view(fmt), args);
|
||||
return detail::get_iterator(buf, out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... T,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value &&
|
||||
!std::is_same<Char, char>::value &&
|
||||
!std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value)>
|
||||
inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const S& fmt, T&&... args) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
return vformat_to(out, detail::to_string_view(fmt),
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<buffered_context<Char>>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Locale, typename S, typename OutputIt, typename... Args,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_locale<Locale>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)>
|
||||
inline auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, const Locale& loc, const S& fmt,
|
||||
typename detail::vformat_args<Char>::type args)
|
||||
-> OutputIt {
|
||||
auto&& buf = detail::get_buffer<Char>(out);
|
||||
vformat_to(buf, detail::to_string_view(fmt), args, detail::locale_ref(loc));
|
||||
return detail::get_iterator(buf, out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Locale, typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... T,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value &&
|
||||
detail::is_locale<Locale>::value &&
|
||||
detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value>
|
||||
inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const Locale& loc, const S& fmt,
|
||||
T&&... args) ->
|
||||
typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type {
|
||||
return vformat_to(out, loc, detail::to_string_view(fmt),
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<buffered_context<Char>>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename Char, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)>
|
||||
inline auto vformat_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
typename detail::vformat_args<Char>::type args)
|
||||
-> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> {
|
||||
using traits = detail::fixed_buffer_traits;
|
||||
auto buf = detail::iterator_buffer<OutputIt, Char, traits>(out, n);
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, fmt, args);
|
||||
return {buf.out(), buf.count()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... T,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)>
|
||||
inline auto format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, const S& fmt, T&&... args)
|
||||
-> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> {
|
||||
return vformat_to_n(out, n, fmt::basic_string_view<Char>(fmt),
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<buffered_context<Char>>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... T,
|
||||
typename Char = detail::format_string_char_t<S>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value)>
|
||||
inline auto formatted_size(const S& fmt, T&&... args) -> size_t {
|
||||
auto buf = detail::counting_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, detail::to_string_view(fmt),
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<buffered_context<Char>>(args...));
|
||||
return buf.count();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void vprint(std::FILE* f, wstring_view fmt, wformat_args args) {
|
||||
auto buf = wmemory_buffer();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, fmt, args);
|
||||
buf.push_back(L'\0');
|
||||
if (std::fputws(buf.data(), f) == -1)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot write to file")));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void vprint(wstring_view fmt, wformat_args args) {
|
||||
vprint(stdout, fmt, args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
void print(std::FILE* f, wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
return vprint(f, wstring_view(fmt), fmt::make_wformat_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T> void print(wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
return vprint(wstring_view(fmt), fmt::make_wformat_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
void println(std::FILE* f, wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
return print(f, L"{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T> void println(wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
return print(L"{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline auto vformat(const text_style& ts, wstring_view fmt, wformat_args args)
|
||||
-> std::wstring {
|
||||
auto buf = wmemory_buffer();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, fmt, args);
|
||||
return {buf.data(), buf.size()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
inline auto format(const text_style& ts, wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args)
|
||||
-> std::wstring {
|
||||
return fmt::vformat(ts, fmt, fmt::make_wformat_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
FMT_DEPRECATED void print(std::FILE* f, const text_style& ts,
|
||||
wformat_string<T...> fmt, const T&... args) {
|
||||
vprint(f, ts, fmt, fmt::make_wformat_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
FMT_DEPRECATED void print(const text_style& ts, wformat_string<T...> fmt,
|
||||
const T&... args) {
|
||||
return print(stdout, ts, fmt, args...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void vprint(std::wostream& os, wstring_view fmt, wformat_args args) {
|
||||
auto buffer = basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t>();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buffer, fmt, args);
|
||||
detail::write_buffer(os, buffer);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
void print(std::wostream& os, wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
vprint(os, fmt, fmt::make_format_args<buffered_context<wchar_t>>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
void println(std::wostream& os, wformat_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
print(os, L"{}\n", fmt::format(fmt, std::forward<T>(args)...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/// Converts `value` to `std::wstring` using the default format for type `T`.
|
||||
template <typename T> inline auto to_wstring(const T& value) -> std::wstring {
|
||||
return format(FMT_STRING(L"{}"), value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_END_EXPORT
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#endif // FMT_XCHAR_H_
|
||||
151
extlib/libfmt/src/fmt.cc
vendored
Normal file
151
extlib/libfmt/src/fmt.cc
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
|
||||
module;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _MSVC_LANG
|
||||
# define FMT_CPLUSPLUS _MSVC_LANG
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_CPLUSPLUS __cplusplus
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Put all implementation-provided headers into the global module fragment
|
||||
// to prevent attachment to this module.
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_IMPORT_STD
|
||||
# include <algorithm>
|
||||
# include <bitset>
|
||||
# include <chrono>
|
||||
# include <cmath>
|
||||
# include <complex>
|
||||
# include <cstddef>
|
||||
# include <cstdint>
|
||||
# include <cstdio>
|
||||
# include <cstdlib>
|
||||
# include <cstring>
|
||||
# include <ctime>
|
||||
# include <exception>
|
||||
# if FMT_CPLUSPLUS > 202002L
|
||||
# include <expected>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# include <filesystem>
|
||||
# include <fstream>
|
||||
# include <functional>
|
||||
# include <iterator>
|
||||
# include <limits>
|
||||
# include <locale>
|
||||
# include <memory>
|
||||
# include <optional>
|
||||
# include <ostream>
|
||||
# include <source_location>
|
||||
# include <stdexcept>
|
||||
# include <string>
|
||||
# include <string_view>
|
||||
# include <system_error>
|
||||
# include <thread>
|
||||
# include <type_traits>
|
||||
# include <typeinfo>
|
||||
# include <utility>
|
||||
# include <variant>
|
||||
# include <vector>
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# include <limits.h>
|
||||
# include <stdint.h>
|
||||
# include <stdio.h>
|
||||
# include <time.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#include <cerrno>
|
||||
#include <climits>
|
||||
#include <version>
|
||||
|
||||
#if __has_include(<cxxabi.h>)
|
||||
# include <cxxabi.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) || defined(__MINGW32__)
|
||||
# include <intrin.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#if defined __APPLE__ || defined(__FreeBSD__)
|
||||
# include <xlocale.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#if __has_include(<winapifamily.h>)
|
||||
# include <winapifamily.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#if (__has_include(<fcntl.h>) || defined(__APPLE__) || \
|
||||
defined(__linux__)) && \
|
||||
(!defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) || (WINAPI_FAMILY == WINAPI_FAMILY_DESKTOP_APP))
|
||||
# include <fcntl.h>
|
||||
# include <sys/stat.h>
|
||||
# include <sys/types.h>
|
||||
# ifndef _WIN32
|
||||
# include <unistd.h>
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# include <io.h>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
# if defined(__GLIBCXX__)
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_sync_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
|
||||
# include <windows.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
export module fmt;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_IMPORT_STD
|
||||
import std;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#define FMT_EXPORT export
|
||||
#define FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT export {
|
||||
#define FMT_END_EXPORT }
|
||||
|
||||
// If you define FMT_ATTACH_TO_GLOBAL_MODULE
|
||||
// - all declarations are detached from module 'fmt'
|
||||
// - the module behaves like a traditional static library, too
|
||||
// - all library symbols are mangled traditionally
|
||||
// - you can mix TUs with either importing or #including the {fmt} API
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_ATTACH_TO_GLOBAL_MODULE
|
||||
extern "C++" {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_OS
|
||||
# define FMT_OS 1
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// All library-provided declarations and definitions must be in the module
|
||||
// purview to be exported.
|
||||
#include "fmt/args.h"
|
||||
#include "fmt/chrono.h"
|
||||
#include "fmt/color.h"
|
||||
#include "fmt/compile.h"
|
||||
#include "fmt/format.h"
|
||||
#if FMT_OS
|
||||
# include "fmt/os.h"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#include "fmt/ostream.h"
|
||||
#include "fmt/printf.h"
|
||||
#include "fmt/ranges.h"
|
||||
#include "fmt/std.h"
|
||||
#include "fmt/xchar.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_ATTACH_TO_GLOBAL_MODULE
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// gcc doesn't yet implement private module fragments
|
||||
#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION
|
||||
module :private;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_ATTACH_TO_GLOBAL_MODULE
|
||||
extern "C++" {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("format.cc")
|
||||
# include "format.cc"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#if FMT_OS && FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("os.cc")
|
||||
# include "os.cc"
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_ATTACH_TO_GLOBAL_MODULE
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
46
extlib/libfmt/src/format.cc
vendored
Normal file
46
extlib/libfmt/src/format.cc
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - 2016, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
#include "fmt/format-inl.h"
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template FMT_API auto dragonbox::to_decimal(float x) noexcept
|
||||
-> dragonbox::decimal_fp<float>;
|
||||
template FMT_API auto dragonbox::to_decimal(double x) noexcept
|
||||
-> dragonbox::decimal_fp<double>;
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_LOCALE
|
||||
// DEPRECATED! locale_ref in the detail namespace
|
||||
template FMT_API locale_ref::locale_ref(const std::locale& loc);
|
||||
template FMT_API auto locale_ref::get<std::locale>() const -> std::locale;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Explicit instantiations for char.
|
||||
|
||||
template FMT_API auto thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref)
|
||||
-> thousands_sep_result<char>;
|
||||
template FMT_API auto decimal_point_impl(locale_ref) -> char;
|
||||
|
||||
// DEPRECATED!
|
||||
template FMT_API void buffer<char>::append(const char*, const char*);
|
||||
|
||||
// DEPRECATED!
|
||||
template FMT_API void vformat_to(buffer<char>&, string_view,
|
||||
typename vformat_args<>::type, locale_ref);
|
||||
|
||||
// Explicit instantiations for wchar_t.
|
||||
|
||||
template FMT_API auto thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref)
|
||||
-> thousands_sep_result<wchar_t>;
|
||||
template FMT_API auto decimal_point_impl(locale_ref) -> wchar_t;
|
||||
|
||||
template FMT_API void buffer<wchar_t>::append(const wchar_t*, const wchar_t*);
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
398
extlib/libfmt/src/os.cc
vendored
Normal file
398
extlib/libfmt/src/os.cc
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,398 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - optional OS-specific functionality
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - 2016, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
|
||||
// Disable bogus MSVC warnings.
|
||||
#if !defined(_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS) && defined(_MSC_VER)
|
||||
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "fmt/os.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_MODULE
|
||||
# include <climits>
|
||||
|
||||
# if FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
# include <sys/stat.h>
|
||||
# include <sys/types.h>
|
||||
|
||||
# ifdef _WRS_KERNEL // VxWorks7 kernel
|
||||
# include <ioLib.h> // getpagesize
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
|
||||
# ifndef _WIN32
|
||||
# include <unistd.h>
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# ifndef WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
|
||||
# define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# include <io.h>
|
||||
# endif // _WIN32
|
||||
# endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
# include <windows.h>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
# ifndef S_IRUSR
|
||||
# define S_IRUSR _S_IREAD
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# ifndef S_IWUSR
|
||||
# define S_IWUSR _S_IWRITE
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# ifndef S_IRGRP
|
||||
# define S_IRGRP 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# ifndef S_IWGRP
|
||||
# define S_IWGRP 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# ifndef S_IROTH
|
||||
# define S_IROTH 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# ifndef S_IWOTH
|
||||
# define S_IWOTH 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
// Return type of read and write functions.
|
||||
using rwresult = int;
|
||||
|
||||
// On Windows the count argument to read and write is unsigned, so convert
|
||||
// it from size_t preventing integer overflow.
|
||||
inline unsigned convert_rwcount(std::size_t count) {
|
||||
return count <= UINT_MAX ? static_cast<unsigned>(count) : UINT_MAX;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#elif FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
// Return type of read and write functions.
|
||||
using rwresult = ssize_t;
|
||||
|
||||
inline std::size_t convert_rwcount(std::size_t count) { return count; }
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
class system_message {
|
||||
system_message(const system_message&) = delete;
|
||||
void operator=(const system_message&) = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned long result_;
|
||||
wchar_t* message_;
|
||||
|
||||
static bool is_whitespace(wchar_t c) noexcept {
|
||||
return c == L' ' || c == L'\n' || c == L'\r' || c == L'\t' || c == L'\0';
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit system_message(unsigned long error_code)
|
||||
: result_(0), message_(nullptr) {
|
||||
result_ = FormatMessageW(
|
||||
FORMAT_MESSAGE_ALLOCATE_BUFFER | FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM |
|
||||
FORMAT_MESSAGE_IGNORE_INSERTS,
|
||||
nullptr, error_code, MAKELANGID(LANG_NEUTRAL, SUBLANG_DEFAULT),
|
||||
reinterpret_cast<wchar_t*>(&message_), 0, nullptr);
|
||||
if (result_ != 0) {
|
||||
while (result_ != 0 && is_whitespace(message_[result_ - 1])) {
|
||||
--result_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
~system_message() { LocalFree(message_); }
|
||||
explicit operator bool() const noexcept { return result_ != 0; }
|
||||
operator basic_string_view<wchar_t>() const noexcept {
|
||||
return basic_string_view<wchar_t>(message_, result_);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class utf8_system_category final : public std::error_category {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
const char* name() const noexcept override { return "system"; }
|
||||
std::string message(int error_code) const override {
|
||||
auto&& msg = system_message(error_code);
|
||||
if (msg) {
|
||||
auto utf8_message = to_utf8<wchar_t>();
|
||||
if (utf8_message.convert(msg)) {
|
||||
return utf8_message.str();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "unknown error";
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_API const std::error_category& system_category() noexcept {
|
||||
static const detail::utf8_system_category category;
|
||||
return category;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::system_error vwindows_error(int err_code, string_view format_str,
|
||||
format_args args) {
|
||||
auto ec = std::error_code(err_code, system_category());
|
||||
return std::system_error(ec, vformat(format_str, args));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void detail::format_windows_error(detail::buffer<char>& out, int error_code,
|
||||
const char* message) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_TRY {
|
||||
auto&& msg = system_message(error_code);
|
||||
if (msg) {
|
||||
auto utf8_message = to_utf8<wchar_t>();
|
||||
if (utf8_message.convert(msg)) {
|
||||
fmt::format_to(appender(out), FMT_STRING("{}: {}"), message,
|
||||
string_view(utf8_message));
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CATCH(...) {}
|
||||
format_error_code(out, error_code, message);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void report_windows_error(int error_code, const char* message) noexcept {
|
||||
do_report_error(detail::format_windows_error, error_code, message);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // _WIN32
|
||||
|
||||
buffered_file::~buffered_file() noexcept {
|
||||
if (file_ && FMT_SYSTEM(fclose(file_)) != 0)
|
||||
report_system_error(errno, "cannot close file");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buffered_file::buffered_file(cstring_view filename, cstring_view mode) {
|
||||
FMT_RETRY_VAL(file_, FMT_SYSTEM(fopen(filename.c_str(), mode.c_str())),
|
||||
nullptr);
|
||||
if (!file_)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot open file {}"),
|
||||
filename.c_str()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void buffered_file::close() {
|
||||
if (!file_) return;
|
||||
int result = FMT_SYSTEM(fclose(file_));
|
||||
file_ = nullptr;
|
||||
if (result != 0)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot close file")));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int buffered_file::descriptor() const {
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_HAS_SYSTEM
|
||||
// fileno is a macro on OpenBSD.
|
||||
# ifdef fileno
|
||||
# undef fileno
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
int fd = FMT_POSIX_CALL(fileno(file_));
|
||||
#elif defined(_WIN32)
|
||||
int fd = _fileno(file_);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
int fd = fileno(file_);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
if (fd == -1)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot get file descriptor")));
|
||||
return fd;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
using mode_t = int;
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr mode_t default_open_mode =
|
||||
S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH;
|
||||
|
||||
file::file(cstring_view path, int oflag) {
|
||||
# if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__)
|
||||
fd_ = -1;
|
||||
auto converted = detail::utf8_to_utf16(string_view(path.c_str()));
|
||||
*this = file::open_windows_file(converted.c_str(), oflag);
|
||||
# else
|
||||
FMT_RETRY(fd_, FMT_POSIX_CALL(open(path.c_str(), oflag, default_open_mode)));
|
||||
if (fd_ == -1)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(
|
||||
system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot open file {}"), path.c_str()));
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
file::~file() noexcept {
|
||||
// Don't retry close in case of EINTR!
|
||||
// See http://linux.derkeiler.com/Mailing-Lists/Kernel/2005-09/3000.html
|
||||
if (fd_ != -1 && FMT_POSIX_CALL(close(fd_)) != 0)
|
||||
report_system_error(errno, "cannot close file");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void file::close() {
|
||||
if (fd_ == -1) return;
|
||||
// Don't retry close in case of EINTR!
|
||||
// See http://linux.derkeiler.com/Mailing-Lists/Kernel/2005-09/3000.html
|
||||
int result = FMT_POSIX_CALL(close(fd_));
|
||||
fd_ = -1;
|
||||
if (result != 0)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot close file")));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
long long file::size() const {
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
// Use GetFileSize instead of GetFileSizeEx for the case when _WIN32_WINNT
|
||||
// is less than 0x0500 as is the case with some default MinGW builds.
|
||||
// Both functions support large file sizes.
|
||||
DWORD size_upper = 0;
|
||||
HANDLE handle = reinterpret_cast<HANDLE>(_get_osfhandle(fd_));
|
||||
DWORD size_lower = FMT_SYSTEM(GetFileSize(handle, &size_upper));
|
||||
if (size_lower == INVALID_FILE_SIZE) {
|
||||
DWORD error = GetLastError();
|
||||
if (error != NO_ERROR)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(windows_error(GetLastError(), "cannot get file size"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
unsigned long long long_size = size_upper;
|
||||
return (long_size << sizeof(DWORD) * CHAR_BIT) | size_lower;
|
||||
# else
|
||||
using Stat = struct stat;
|
||||
Stat file_stat = Stat();
|
||||
if (FMT_POSIX_CALL(fstat(fd_, &file_stat)) == -1)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot get file attributes")));
|
||||
static_assert(sizeof(long long) >= sizeof(file_stat.st_size),
|
||||
"return type of file::size is not large enough");
|
||||
return file_stat.st_size;
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::size_t file::read(void* buffer, std::size_t count) {
|
||||
rwresult result = 0;
|
||||
FMT_RETRY(result, FMT_POSIX_CALL(read(fd_, buffer, convert_rwcount(count))));
|
||||
if (result < 0)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot read from file")));
|
||||
return detail::to_unsigned(result);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::size_t file::write(const void* buffer, std::size_t count) {
|
||||
rwresult result = 0;
|
||||
FMT_RETRY(result, FMT_POSIX_CALL(write(fd_, buffer, convert_rwcount(count))));
|
||||
if (result < 0)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot write to file")));
|
||||
return detail::to_unsigned(result);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
file file::dup(int fd) {
|
||||
// Don't retry as dup doesn't return EINTR.
|
||||
// http://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/009695399/functions/dup.html
|
||||
int new_fd = FMT_POSIX_CALL(dup(fd));
|
||||
if (new_fd == -1)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(
|
||||
errno, FMT_STRING("cannot duplicate file descriptor {}"), fd));
|
||||
return file(new_fd);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void file::dup2(int fd) {
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
FMT_RETRY(result, FMT_POSIX_CALL(dup2(fd_, fd)));
|
||||
if (result == -1) {
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(
|
||||
errno, FMT_STRING("cannot duplicate file descriptor {} to {}"), fd_,
|
||||
fd));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void file::dup2(int fd, std::error_code& ec) noexcept {
|
||||
int result = 0;
|
||||
FMT_RETRY(result, FMT_POSIX_CALL(dup2(fd_, fd)));
|
||||
if (result == -1) ec = std::error_code(errno, std::generic_category());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buffered_file file::fdopen(const char* mode) {
|
||||
// Don't retry as fdopen doesn't return EINTR.
|
||||
# if defined(__MINGW32__) && defined(_POSIX_)
|
||||
FILE* f = ::fdopen(fd_, mode);
|
||||
# else
|
||||
FILE* f = FMT_POSIX_CALL(fdopen(fd_, mode));
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
if (!f) {
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(
|
||||
errno, FMT_STRING("cannot associate stream with file descriptor")));
|
||||
}
|
||||
buffered_file bf(f);
|
||||
fd_ = -1;
|
||||
return bf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__)
|
||||
file file::open_windows_file(wcstring_view path, int oflag) {
|
||||
int fd = -1;
|
||||
auto err = _wsopen_s(&fd, path.c_str(), oflag, _SH_DENYNO, default_open_mode);
|
||||
if (fd == -1) {
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(err, FMT_STRING("cannot open file {}"),
|
||||
detail::to_utf8<wchar_t>(path.c_str()).c_str()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
return file(fd);
|
||||
}
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
|
||||
pipe::pipe() {
|
||||
int fds[2] = {};
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
// Make the default pipe capacity same as on Linux 2.6.11+.
|
||||
enum { DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 65536 };
|
||||
int result = FMT_POSIX_CALL(pipe(fds, DEFAULT_CAPACITY, _O_BINARY));
|
||||
# else
|
||||
// Don't retry as the pipe function doesn't return EINTR.
|
||||
// http://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/009696799/functions/pipe.html
|
||||
int result = FMT_POSIX_CALL(pipe(fds));
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
if (result != 0)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot create pipe")));
|
||||
// The following assignments don't throw.
|
||||
read_end = file(fds[0]);
|
||||
write_end = file(fds[1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# if !defined(__MSDOS__)
|
||||
long getpagesize() {
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
SYSTEM_INFO si;
|
||||
GetSystemInfo(&si);
|
||||
return si.dwPageSize;
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# ifdef _WRS_KERNEL
|
||||
long size = FMT_POSIX_CALL(getpagesize());
|
||||
# else
|
||||
long size = FMT_POSIX_CALL(sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE));
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
|
||||
if (size < 0)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot get memory page size")));
|
||||
return size;
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
|
||||
void ostream::grow(buffer<char>& buf, size_t) {
|
||||
if (buf.size() == buf.capacity()) static_cast<ostream&>(buf).flush();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ostream::ostream(cstring_view path, const detail::ostream_params& params)
|
||||
: buffer<char>(grow), file_(path, params.oflag) {
|
||||
set(new char[params.buffer_size], params.buffer_size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ostream::ostream(ostream&& other) noexcept
|
||||
: buffer<char>(grow, other.data(), other.size(), other.capacity()),
|
||||
file_(std::move(other.file_)) {
|
||||
other.clear();
|
||||
other.set(nullptr, 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ostream::~ostream() {
|
||||
flush();
|
||||
delete[] data();
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
15
extlib/libfmt/support/Android.mk
vendored
Normal file
15
extlib/libfmt/support/Android.mk
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
|
||||
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
|
||||
|
||||
LOCAL_MODULE := fmt_static
|
||||
LOCAL_MODULE_FILENAME := libfmt
|
||||
|
||||
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := ../src/format.cc
|
||||
|
||||
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES := $(LOCAL_PATH)
|
||||
LOCAL_EXPORT_C_INCLUDES := $(LOCAL_PATH)
|
||||
|
||||
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -std=c++11 -fexceptions
|
||||
|
||||
include $(BUILD_STATIC_LIBRARY)
|
||||
|
||||
1
extlib/libfmt/support/AndroidManifest.xml
vendored
Normal file
1
extlib/libfmt/support/AndroidManifest.xml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
<manifest package="dev.fmt" />
|
||||
2061
extlib/libfmt/support/C++.sublime-syntax
vendored
Normal file
2061
extlib/libfmt/support/C++.sublime-syntax
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
4
extlib/libfmt/support/README
vendored
Normal file
4
extlib/libfmt/support/README
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
This directory contains build support files such as
|
||||
|
||||
* CMake modules
|
||||
* Build scripts
|
||||
19
extlib/libfmt/support/Vagrantfile
vendored
Normal file
19
extlib/libfmt/support/Vagrantfile
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
|
||||
# vi: set ft=ruby :
|
||||
|
||||
# A vagrant config for testing against gcc-4.8.
|
||||
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
|
||||
config.vm.box = "bento/ubuntu-22.04-arm64"
|
||||
|
||||
config.vm.provider "vmware_desktop" do |vb|
|
||||
vb.memory = "4096"
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
|
||||
apt-get update
|
||||
apt-get install -y g++ make wget git
|
||||
wget -q https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.26.0/cmake-3.26.0-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz
|
||||
tar xzf cmake-3.26.0-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz
|
||||
ln -s `pwd`/cmake-3.26.0-Linux-x86_64/bin/cmake /usr/local/bin
|
||||
SHELL
|
||||
end
|
||||
1
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/.bazelversion
vendored
Normal file
1
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/.bazelversion
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
7.1.2
|
||||
20
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/BUILD.bazel
vendored
Normal file
20
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/BUILD.bazel
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
cc_library(
|
||||
name = "fmt",
|
||||
srcs = [
|
||||
#"src/fmt.cc", # No C++ module support, yet in Bazel (https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazel/pull/19940)
|
||||
"src/format.cc",
|
||||
"src/os.cc",
|
||||
],
|
||||
hdrs = glob([
|
||||
"include/fmt/*.h",
|
||||
]),
|
||||
copts = select({
|
||||
"@platforms//os:windows": ["-utf-8"],
|
||||
"//conditions:default": [],
|
||||
}),
|
||||
includes = [
|
||||
"include",
|
||||
],
|
||||
strip_include_prefix = "include",
|
||||
visibility = ["//visibility:public"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
6
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/MODULE.bazel
vendored
Normal file
6
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/MODULE.bazel
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
module(
|
||||
name = "fmt",
|
||||
compatibility_level = 10,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
bazel_dep(name = "platforms", version = "0.0.10")
|
||||
28
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/README.md
vendored
Normal file
28
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/README.md
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
# Bazel support
|
||||
|
||||
To get [Bazel](https://bazel.build/) working with {fmt} you can copy the files `BUILD.bazel`,
|
||||
`MODULE.bazel`, `WORKSPACE.bazel`, and `.bazelversion` from this folder (`support/bazel`) to the root folder of this project.
|
||||
This way {fmt} gets bazelized and can be used with Bazel (e.g. doing a `bazel build //...` on {fmt}).
|
||||
|
||||
## Using {fmt} as a dependency
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Bzlmod
|
||||
|
||||
The [Bazel Central Registry](https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazel-central-registry/tree/main/modules/fmt) provides support for {fmt}.
|
||||
|
||||
For instance, to use {fmt} add to your `MODULE.bazel` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
bazel_dep(name = "fmt", version = "10.2.1")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Live at head
|
||||
|
||||
For a live-at-head approach, you can copy the contents of this repository and move the Bazel-related build files to the root folder of this project as described above and make use of `local_path_override`, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
local_path_override(
|
||||
module_name = "fmt",
|
||||
path = "../third_party/fmt",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
2
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/WORKSPACE.bazel
vendored
Normal file
2
extlib/libfmt/support/bazel/WORKSPACE.bazel
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
# WORKSPACE marker file needed by Bazel
|
||||
|
||||
132
extlib/libfmt/support/build.gradle
vendored
Normal file
132
extlib/libfmt/support/build.gradle
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
import java.nio.file.Paths
|
||||
|
||||
// General gradle arguments for root project
|
||||
buildscript {
|
||||
repositories {
|
||||
google()
|
||||
jcenter()
|
||||
}
|
||||
dependencies {
|
||||
//
|
||||
// https://developer.android.com/studio/releases/gradle-plugin#updating-gradle
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Notice that 4.0.0 here is the version of [Android Gradle Plugin]
|
||||
// According to URL above you will need Gradle 6.1 or higher
|
||||
//
|
||||
classpath "com.android.tools.build:gradle:4.1.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
repositories {
|
||||
google()
|
||||
jcenter()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Project's root where CMakeLists.txt exists: rootDir/support/.cxx -> rootDir
|
||||
def rootDir = Paths.get(project.buildDir.getParent()).getParent()
|
||||
println("rootDir: ${rootDir}")
|
||||
|
||||
// Output: Shared library (.so) for Android
|
||||
apply plugin: "com.android.library"
|
||||
android {
|
||||
compileSdkVersion 25 // Android 7.0
|
||||
|
||||
// Target ABI
|
||||
// - This option controls target platform of module
|
||||
// - The platform might be limited by compiler's support
|
||||
// some can work with Clang(default), but some can work only with GCC...
|
||||
// if bad, both toolchains might not support it
|
||||
splits {
|
||||
abi {
|
||||
enable true
|
||||
// Specify platforms for Application
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
include "arm64-v8a", "armeabi-v7a", "x86_64"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
ndkVersion "21.3.6528147" // ANDROID_NDK_HOME is deprecated. Be explicit
|
||||
|
||||
defaultConfig {
|
||||
minSdkVersion 21 // Android 5.0+
|
||||
targetSdkVersion 25 // Follow Compile SDK
|
||||
versionCode 34 // Follow release count
|
||||
versionName "7.1.2" // Follow Official version
|
||||
|
||||
externalNativeBuild {
|
||||
cmake {
|
||||
arguments "-DANDROID_STL=c++_shared" // Specify Android STL
|
||||
arguments "-DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=true" // Build shared object
|
||||
arguments "-DFMT_TEST=false" // Skip test
|
||||
arguments "-DFMT_DOC=false" // Skip document
|
||||
cppFlags "-std=c++17"
|
||||
targets "fmt"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
println(externalNativeBuild.cmake.cppFlags)
|
||||
println(externalNativeBuild.cmake.arguments)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// External Native build
|
||||
// - Use existing CMakeList.txt
|
||||
// - Give path to CMake. This gradle file should be
|
||||
// neighbor of the top level cmake
|
||||
externalNativeBuild {
|
||||
cmake {
|
||||
version "3.10.0+"
|
||||
path "${rootDir}/CMakeLists.txt"
|
||||
// buildStagingDirectory "./build" // Custom path for cmake output
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sourceSets{
|
||||
// Android Manifest for Gradle
|
||||
main {
|
||||
manifest.srcFile "AndroidManifest.xml"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// https://developer.android.com/studio/build/native-dependencies#build_system_configuration
|
||||
buildFeatures {
|
||||
prefab true
|
||||
prefabPublishing true
|
||||
}
|
||||
prefab {
|
||||
fmt {
|
||||
headers "${rootDir}/include"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
assemble.doLast
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Instead of `ninja install`, Gradle will deploy the files.
|
||||
// We are doing this since FMT is dependent to the ANDROID_STL after build
|
||||
copy {
|
||||
from "build/intermediates/cmake"
|
||||
into "${rootDir}/libs"
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Copy debug binaries
|
||||
copy {
|
||||
from "${rootDir}/libs/debug/obj"
|
||||
into "${rootDir}/libs/debug"
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Copy Release binaries
|
||||
copy {
|
||||
from "${rootDir}/libs/release/obj"
|
||||
into "${rootDir}/libs/release"
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Remove empty directory
|
||||
delete "${rootDir}/libs/debug/obj"
|
||||
delete "${rootDir}/libs/release/obj"
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy AAR files. Notice that the aar is named after the folder of this script.
|
||||
copy {
|
||||
from "build/outputs/aar/support-release.aar"
|
||||
into "${rootDir}/libs"
|
||||
rename "support-release.aar", "fmt-release.aar"
|
||||
}
|
||||
copy {
|
||||
from "build/outputs/aar/support-debug.aar"
|
||||
into "${rootDir}/libs"
|
||||
rename "support-debug.aar", "fmt-debug.aar"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
43
extlib/libfmt/support/check-commits
vendored
Executable file
43
extlib/libfmt/support/check-commits
vendored
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
||||
|
||||
"""Compile source on a range of commits
|
||||
|
||||
Usage:
|
||||
check-commits <start> <source>
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import docopt, os, sys, tempfile
|
||||
from subprocess import check_call, check_output, run
|
||||
|
||||
args = docopt.docopt(__doc__)
|
||||
start = args.get('<start>')
|
||||
source = args.get('<source>')
|
||||
|
||||
cwd = os.getcwd()
|
||||
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as work_dir:
|
||||
check_call(['git', 'clone', 'https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt.git'],
|
||||
cwd=work_dir)
|
||||
repo_dir = os.path.join(work_dir, 'fmt')
|
||||
commits = check_output(
|
||||
['git', 'rev-list', f'{start}..HEAD', '--abbrev-commit',
|
||||
'--', 'include', 'src'],
|
||||
text=True, cwd=repo_dir).rstrip().split('\n')
|
||||
commits.reverse()
|
||||
print('Time\tCommit')
|
||||
for commit in commits:
|
||||
check_call(['git', '-c', 'advice.detachedHead=false', 'checkout', commit],
|
||||
cwd=repo_dir)
|
||||
returncode = run(
|
||||
['c++', '-std=c++11', '-O3', '-DNDEBUG', '-I', 'include',
|
||||
'src/format.cc', os.path.join(cwd, source)], cwd=repo_dir).returncode
|
||||
if returncode != 0:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
times = []
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
output = check_output([os.path.join(repo_dir, 'a.out')], text=True)
|
||||
times.append(float(output))
|
||||
message = check_output(['git', 'log', '-1', '--pretty=format:%s', commit],
|
||||
cwd=repo_dir, text=True)
|
||||
print(f'{min(times)}\t{commit} {message[:40]}')
|
||||
sys.stdout.flush()
|
||||
7
extlib/libfmt/support/cmake/FindSetEnv.cmake
vendored
Normal file
7
extlib/libfmt/support/cmake/FindSetEnv.cmake
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# A CMake script to find SetEnv.cmd.
|
||||
|
||||
find_program(WINSDK_SETENV NAMES SetEnv.cmd
|
||||
PATHS "[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Microsoft SDKs\\Windows;CurrentInstallFolder]/bin")
|
||||
if (WINSDK_SETENV AND PRINT_PATH)
|
||||
execute_process(COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E echo "${WINSDK_SETENV}")
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
26
extlib/libfmt/support/cmake/JoinPaths.cmake
vendored
Normal file
26
extlib/libfmt/support/cmake/JoinPaths.cmake
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
# This module provides function for joining paths
|
||||
# known from from most languages
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Original license:
|
||||
# SPDX-License-Identifier: (MIT OR CC0-1.0)
|
||||
# Explicit permission given to distribute this module under
|
||||
# the terms of the project as described in /LICENSE.rst.
|
||||
# Copyright 2020 Jan Tojnar
|
||||
# https://github.com/jtojnar/cmake-snips
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Modelled after Python’s os.path.join
|
||||
# https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/os.path.html#os.path.join
|
||||
# Windows not supported
|
||||
function(join_paths joined_path first_path_segment)
|
||||
set(temp_path "${first_path_segment}")
|
||||
foreach(current_segment IN LISTS ARGN)
|
||||
if(NOT ("${current_segment}" STREQUAL ""))
|
||||
if(IS_ABSOLUTE "${current_segment}")
|
||||
set(temp_path "${current_segment}")
|
||||
else()
|
||||
set(temp_path "${temp_path}/${current_segment}")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endforeach()
|
||||
set(${joined_path} "${temp_path}" PARENT_SCOPE)
|
||||
endfunction()
|
||||
7
extlib/libfmt/support/cmake/fmt-config.cmake.in
vendored
Normal file
7
extlib/libfmt/support/cmake/fmt-config.cmake.in
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
@PACKAGE_INIT@
|
||||
|
||||
if (NOT TARGET fmt::fmt)
|
||||
include(${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/@targets_export_name@.cmake)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
check_required_components(fmt)
|
||||
11
extlib/libfmt/support/cmake/fmt.pc.in
vendored
Normal file
11
extlib/libfmt/support/cmake/fmt.pc.in
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
prefix=@CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX@
|
||||
exec_prefix=@CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX@
|
||||
libdir=@libdir_for_pc_file@
|
||||
includedir=@includedir_for_pc_file@
|
||||
|
||||
Name: fmt
|
||||
Description: A modern formatting library
|
||||
Version: @FMT_VERSION@
|
||||
Libs: -L${libdir} -l@FMT_LIB_NAME@
|
||||
Cflags: -I${includedir}
|
||||
|
||||
581
extlib/libfmt/support/docopt.py
vendored
Normal file
581
extlib/libfmt/support/docopt.py
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,581 @@
|
||||
"""Pythonic command-line interface parser that will make you smile.
|
||||
|
||||
* http://docopt.org
|
||||
* Repository and issue-tracker: https://github.com/docopt/docopt
|
||||
* Licensed under terms of MIT license (see LICENSE-MIT)
|
||||
* Copyright (c) 2013 Vladimir Keleshev, vladimir@keleshev.com
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ['docopt']
|
||||
__version__ = '0.6.1'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DocoptLanguageError(Exception):
|
||||
|
||||
"""Error in construction of usage-message by developer."""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DocoptExit(SystemExit):
|
||||
|
||||
"""Exit in case user invoked program with incorrect arguments."""
|
||||
|
||||
usage = ''
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, message=''):
|
||||
SystemExit.__init__(self, (message + '\n' + self.usage).strip())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Pattern(object):
|
||||
|
||||
def __eq__(self, other):
|
||||
return repr(self) == repr(other)
|
||||
|
||||
def __hash__(self):
|
||||
return hash(repr(self))
|
||||
|
||||
def fix(self):
|
||||
self.fix_identities()
|
||||
self.fix_repeating_arguments()
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def fix_identities(self, uniq=None):
|
||||
"""Make pattern-tree tips point to same object if they are equal."""
|
||||
if not hasattr(self, 'children'):
|
||||
return self
|
||||
uniq = list(set(self.flat())) if uniq is None else uniq
|
||||
for i, child in enumerate(self.children):
|
||||
if not hasattr(child, 'children'):
|
||||
assert child in uniq
|
||||
self.children[i] = uniq[uniq.index(child)]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
child.fix_identities(uniq)
|
||||
|
||||
def fix_repeating_arguments(self):
|
||||
"""Fix elements that should accumulate/increment values."""
|
||||
either = [list(child.children) for child in transform(self).children]
|
||||
for case in either:
|
||||
for e in [child for child in case if case.count(child) > 1]:
|
||||
if type(e) is Argument or type(e) is Option and e.argcount:
|
||||
if e.value is None:
|
||||
e.value = []
|
||||
elif type(e.value) is not list:
|
||||
e.value = e.value.split()
|
||||
if type(e) is Command or type(e) is Option and e.argcount == 0:
|
||||
e.value = 0
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def transform(pattern):
|
||||
"""Expand pattern into an (almost) equivalent one, but with single Either.
|
||||
|
||||
Example: ((-a | -b) (-c | -d)) => (-a -c | -a -d | -b -c | -b -d)
|
||||
Quirks: [-a] => (-a), (-a...) => (-a -a)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
groups = [[pattern]]
|
||||
while groups:
|
||||
children = groups.pop(0)
|
||||
parents = [Required, Optional, OptionsShortcut, Either, OneOrMore]
|
||||
if any(t in map(type, children) for t in parents):
|
||||
child = [c for c in children if type(c) in parents][0]
|
||||
children.remove(child)
|
||||
if type(child) is Either:
|
||||
for c in child.children:
|
||||
groups.append([c] + children)
|
||||
elif type(child) is OneOrMore:
|
||||
groups.append(child.children * 2 + children)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
groups.append(child.children + children)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
result.append(children)
|
||||
return Either(*[Required(*e) for e in result])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LeafPattern(Pattern):
|
||||
|
||||
"""Leaf/terminal node of a pattern tree."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, value=None):
|
||||
self.name, self.value = name, value
|
||||
|
||||
def __repr__(self):
|
||||
return '%s(%r, %r)' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.name, self.value)
|
||||
|
||||
def flat(self, *types):
|
||||
return [self] if not types or type(self) in types else []
|
||||
|
||||
def match(self, left, collected=None):
|
||||
collected = [] if collected is None else collected
|
||||
pos, match = self.single_match(left)
|
||||
if match is None:
|
||||
return False, left, collected
|
||||
left_ = left[:pos] + left[pos + 1:]
|
||||
same_name = [a for a in collected if a.name == self.name]
|
||||
if type(self.value) in (int, list):
|
||||
if type(self.value) is int:
|
||||
increment = 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
increment = ([match.value] if type(match.value) is str
|
||||
else match.value)
|
||||
if not same_name:
|
||||
match.value = increment
|
||||
return True, left_, collected + [match]
|
||||
same_name[0].value += increment
|
||||
return True, left_, collected
|
||||
return True, left_, collected + [match]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BranchPattern(Pattern):
|
||||
|
||||
"""Branch/inner node of a pattern tree."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *children):
|
||||
self.children = list(children)
|
||||
|
||||
def __repr__(self):
|
||||
return '%s(%s)' % (self.__class__.__name__,
|
||||
', '.join(repr(a) for a in self.children))
|
||||
|
||||
def flat(self, *types):
|
||||
if type(self) in types:
|
||||
return [self]
|
||||
return sum([child.flat(*types) for child in self.children], [])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Argument(LeafPattern):
|
||||
|
||||
def single_match(self, left):
|
||||
for n, pattern in enumerate(left):
|
||||
if type(pattern) is Argument:
|
||||
return n, Argument(self.name, pattern.value)
|
||||
return None, None
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def parse(class_, source):
|
||||
name = re.findall('(<\S*?>)', source)[0]
|
||||
value = re.findall('\[default: (.*)\]', source, flags=re.I)
|
||||
return class_(name, value[0] if value else None)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Command(Argument):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, name, value=False):
|
||||
self.name, self.value = name, value
|
||||
|
||||
def single_match(self, left):
|
||||
for n, pattern in enumerate(left):
|
||||
if type(pattern) is Argument:
|
||||
if pattern.value == self.name:
|
||||
return n, Command(self.name, True)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
break
|
||||
return None, None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Option(LeafPattern):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, short=None, long=None, argcount=0, value=False):
|
||||
assert argcount in (0, 1)
|
||||
self.short, self.long, self.argcount = short, long, argcount
|
||||
self.value = None if value is False and argcount else value
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def parse(class_, option_description):
|
||||
short, long, argcount, value = None, None, 0, False
|
||||
options, _, description = option_description.strip().partition(' ')
|
||||
options = options.replace(',', ' ').replace('=', ' ')
|
||||
for s in options.split():
|
||||
if s.startswith('--'):
|
||||
long = s
|
||||
elif s.startswith('-'):
|
||||
short = s
|
||||
else:
|
||||
argcount = 1
|
||||
if argcount:
|
||||
matched = re.findall('\[default: (.*)\]', description, flags=re.I)
|
||||
value = matched[0] if matched else None
|
||||
return class_(short, long, argcount, value)
|
||||
|
||||
def single_match(self, left):
|
||||
for n, pattern in enumerate(left):
|
||||
if self.name == pattern.name:
|
||||
return n, pattern
|
||||
return None, None
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def name(self):
|
||||
return self.long or self.short
|
||||
|
||||
def __repr__(self):
|
||||
return 'Option(%r, %r, %r, %r)' % (self.short, self.long,
|
||||
self.argcount, self.value)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Required(BranchPattern):
|
||||
|
||||
def match(self, left, collected=None):
|
||||
collected = [] if collected is None else collected
|
||||
l = left
|
||||
c = collected
|
||||
for pattern in self.children:
|
||||
matched, l, c = pattern.match(l, c)
|
||||
if not matched:
|
||||
return False, left, collected
|
||||
return True, l, c
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Optional(BranchPattern):
|
||||
|
||||
def match(self, left, collected=None):
|
||||
collected = [] if collected is None else collected
|
||||
for pattern in self.children:
|
||||
m, left, collected = pattern.match(left, collected)
|
||||
return True, left, collected
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class OptionsShortcut(Optional):
|
||||
|
||||
"""Marker/placeholder for [options] shortcut."""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class OneOrMore(BranchPattern):
|
||||
|
||||
def match(self, left, collected=None):
|
||||
assert len(self.children) == 1
|
||||
collected = [] if collected is None else collected
|
||||
l = left
|
||||
c = collected
|
||||
l_ = None
|
||||
matched = True
|
||||
times = 0
|
||||
while matched:
|
||||
# could it be that something didn't match but changed l or c?
|
||||
matched, l, c = self.children[0].match(l, c)
|
||||
times += 1 if matched else 0
|
||||
if l_ == l:
|
||||
break
|
||||
l_ = l
|
||||
if times >= 1:
|
||||
return True, l, c
|
||||
return False, left, collected
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Either(BranchPattern):
|
||||
|
||||
def match(self, left, collected=None):
|
||||
collected = [] if collected is None else collected
|
||||
outcomes = []
|
||||
for pattern in self.children:
|
||||
matched, _, _ = outcome = pattern.match(left, collected)
|
||||
if matched:
|
||||
outcomes.append(outcome)
|
||||
if outcomes:
|
||||
return min(outcomes, key=lambda outcome: len(outcome[1]))
|
||||
return False, left, collected
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Tokens(list):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, source, error=DocoptExit):
|
||||
self += source.split() if hasattr(source, 'split') else source
|
||||
self.error = error
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def from_pattern(source):
|
||||
source = re.sub(r'([\[\]\(\)\|]|\.\.\.)', r' \1 ', source)
|
||||
source = [s for s in re.split('\s+|(\S*<.*?>)', source) if s]
|
||||
return Tokens(source, error=DocoptLanguageError)
|
||||
|
||||
def move(self):
|
||||
return self.pop(0) if len(self) else None
|
||||
|
||||
def current(self):
|
||||
return self[0] if len(self) else None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_long(tokens, options):
|
||||
"""long ::= '--' chars [ ( ' ' | '=' ) chars ] ;"""
|
||||
long, eq, value = tokens.move().partition('=')
|
||||
assert long.startswith('--')
|
||||
value = None if eq == value == '' else value
|
||||
similar = [o for o in options if o.long == long]
|
||||
if tokens.error is DocoptExit and similar == []: # if no exact match
|
||||
similar = [o for o in options if o.long and o.long.startswith(long)]
|
||||
if len(similar) > 1: # might be simply specified ambiguously 2+ times?
|
||||
raise tokens.error('%s is not a unique prefix: %s?' %
|
||||
(long, ', '.join(o.long for o in similar)))
|
||||
elif len(similar) < 1:
|
||||
argcount = 1 if eq == '=' else 0
|
||||
o = Option(None, long, argcount)
|
||||
options.append(o)
|
||||
if tokens.error is DocoptExit:
|
||||
o = Option(None, long, argcount, value if argcount else True)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
o = Option(similar[0].short, similar[0].long,
|
||||
similar[0].argcount, similar[0].value)
|
||||
if o.argcount == 0:
|
||||
if value is not None:
|
||||
raise tokens.error('%s must not have an argument' % o.long)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if value is None:
|
||||
if tokens.current() in [None, '--']:
|
||||
raise tokens.error('%s requires argument' % o.long)
|
||||
value = tokens.move()
|
||||
if tokens.error is DocoptExit:
|
||||
o.value = value if value is not None else True
|
||||
return [o]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_shorts(tokens, options):
|
||||
"""shorts ::= '-' ( chars )* [ [ ' ' ] chars ] ;"""
|
||||
token = tokens.move()
|
||||
assert token.startswith('-') and not token.startswith('--')
|
||||
left = token.lstrip('-')
|
||||
parsed = []
|
||||
while left != '':
|
||||
short, left = '-' + left[0], left[1:]
|
||||
similar = [o for o in options if o.short == short]
|
||||
if len(similar) > 1:
|
||||
raise tokens.error('%s is specified ambiguously %d times' %
|
||||
(short, len(similar)))
|
||||
elif len(similar) < 1:
|
||||
o = Option(short, None, 0)
|
||||
options.append(o)
|
||||
if tokens.error is DocoptExit:
|
||||
o = Option(short, None, 0, True)
|
||||
else: # why copying is necessary here?
|
||||
o = Option(short, similar[0].long,
|
||||
similar[0].argcount, similar[0].value)
|
||||
value = None
|
||||
if o.argcount != 0:
|
||||
if left == '':
|
||||
if tokens.current() in [None, '--']:
|
||||
raise tokens.error('%s requires argument' % short)
|
||||
value = tokens.move()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
value = left
|
||||
left = ''
|
||||
if tokens.error is DocoptExit:
|
||||
o.value = value if value is not None else True
|
||||
parsed.append(o)
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_pattern(source, options):
|
||||
tokens = Tokens.from_pattern(source)
|
||||
result = parse_expr(tokens, options)
|
||||
if tokens.current() is not None:
|
||||
raise tokens.error('unexpected ending: %r' % ' '.join(tokens))
|
||||
return Required(*result)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_expr(tokens, options):
|
||||
"""expr ::= seq ( '|' seq )* ;"""
|
||||
seq = parse_seq(tokens, options)
|
||||
if tokens.current() != '|':
|
||||
return seq
|
||||
result = [Required(*seq)] if len(seq) > 1 else seq
|
||||
while tokens.current() == '|':
|
||||
tokens.move()
|
||||
seq = parse_seq(tokens, options)
|
||||
result += [Required(*seq)] if len(seq) > 1 else seq
|
||||
return [Either(*result)] if len(result) > 1 else result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_seq(tokens, options):
|
||||
"""seq ::= ( atom [ '...' ] )* ;"""
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
while tokens.current() not in [None, ']', ')', '|']:
|
||||
atom = parse_atom(tokens, options)
|
||||
if tokens.current() == '...':
|
||||
atom = [OneOrMore(*atom)]
|
||||
tokens.move()
|
||||
result += atom
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_atom(tokens, options):
|
||||
"""atom ::= '(' expr ')' | '[' expr ']' | 'options'
|
||||
| long | shorts | argument | command ;
|
||||
"""
|
||||
token = tokens.current()
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
if token in '([':
|
||||
tokens.move()
|
||||
matching, pattern = {'(': [')', Required], '[': [']', Optional]}[token]
|
||||
result = pattern(*parse_expr(tokens, options))
|
||||
if tokens.move() != matching:
|
||||
raise tokens.error("unmatched '%s'" % token)
|
||||
return [result]
|
||||
elif token == 'options':
|
||||
tokens.move()
|
||||
return [OptionsShortcut()]
|
||||
elif token.startswith('--') and token != '--':
|
||||
return parse_long(tokens, options)
|
||||
elif token.startswith('-') and token not in ('-', '--'):
|
||||
return parse_shorts(tokens, options)
|
||||
elif token.startswith('<') and token.endswith('>') or token.isupper():
|
||||
return [Argument(tokens.move())]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return [Command(tokens.move())]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_argv(tokens, options, options_first=False):
|
||||
"""Parse command-line argument vector.
|
||||
|
||||
If options_first:
|
||||
argv ::= [ long | shorts ]* [ argument ]* [ '--' [ argument ]* ] ;
|
||||
else:
|
||||
argv ::= [ long | shorts | argument ]* [ '--' [ argument ]* ] ;
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
parsed = []
|
||||
while tokens.current() is not None:
|
||||
if tokens.current() == '--':
|
||||
return parsed + [Argument(None, v) for v in tokens]
|
||||
elif tokens.current().startswith('--'):
|
||||
parsed += parse_long(tokens, options)
|
||||
elif tokens.current().startswith('-') and tokens.current() != '-':
|
||||
parsed += parse_shorts(tokens, options)
|
||||
elif options_first:
|
||||
return parsed + [Argument(None, v) for v in tokens]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
parsed.append(Argument(None, tokens.move()))
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_defaults(doc):
|
||||
defaults = []
|
||||
for s in parse_section('options:', doc):
|
||||
# FIXME corner case "bla: options: --foo"
|
||||
_, _, s = s.partition(':') # get rid of "options:"
|
||||
split = re.split('\n[ \t]*(-\S+?)', '\n' + s)[1:]
|
||||
split = [s1 + s2 for s1, s2 in zip(split[::2], split[1::2])]
|
||||
options = [Option.parse(s) for s in split if s.startswith('-')]
|
||||
defaults += options
|
||||
return defaults
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_section(name, source):
|
||||
pattern = re.compile('^([^\n]*' + name + '[^\n]*\n?(?:[ \t].*?(?:\n|$))*)',
|
||||
re.IGNORECASE | re.MULTILINE)
|
||||
return [s.strip() for s in pattern.findall(source)]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def formal_usage(section):
|
||||
_, _, section = section.partition(':') # drop "usage:"
|
||||
pu = section.split()
|
||||
return '( ' + ' '.join(') | (' if s == pu[0] else s for s in pu[1:]) + ' )'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def extras(help, version, options, doc):
|
||||
if help and any((o.name in ('-h', '--help')) and o.value for o in options):
|
||||
print(doc.strip("\n"))
|
||||
sys.exit()
|
||||
if version and any(o.name == '--version' and o.value for o in options):
|
||||
print(version)
|
||||
sys.exit()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Dict(dict):
|
||||
def __repr__(self):
|
||||
return '{%s}' % ',\n '.join('%r: %r' % i for i in sorted(self.items()))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def docopt(doc, argv=None, help=True, version=None, options_first=False):
|
||||
"""Parse `argv` based on command-line interface described in `doc`.
|
||||
|
||||
`docopt` creates your command-line interface based on its
|
||||
description that you pass as `doc`. Such description can contain
|
||||
--options, <positional-argument>, commands, which could be
|
||||
[optional], (required), (mutually | exclusive) or repeated...
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters
|
||||
----------
|
||||
doc : str
|
||||
Description of your command-line interface.
|
||||
argv : list of str, optional
|
||||
Argument vector to be parsed. sys.argv[1:] is used if not
|
||||
provided.
|
||||
help : bool (default: True)
|
||||
Set to False to disable automatic help on -h or --help
|
||||
options.
|
||||
version : any object
|
||||
If passed, the object will be printed if --version is in
|
||||
`argv`.
|
||||
options_first : bool (default: False)
|
||||
Set to True to require options precede positional arguments,
|
||||
i.e. to forbid options and positional arguments intermix.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns
|
||||
-------
|
||||
args : dict
|
||||
A dictionary, where keys are names of command-line elements
|
||||
such as e.g. "--verbose" and "<path>", and values are the
|
||||
parsed values of those elements.
|
||||
|
||||
Example
|
||||
-------
|
||||
>>> from docopt import docopt
|
||||
>>> doc = '''
|
||||
... Usage:
|
||||
... my_program tcp <host> <port> [--timeout=<seconds>]
|
||||
... my_program serial <port> [--baud=<n>] [--timeout=<seconds>]
|
||||
... my_program (-h | --help | --version)
|
||||
...
|
||||
... Options:
|
||||
... -h, --help Show this screen and exit.
|
||||
... --baud=<n> Baudrate [default: 9600]
|
||||
... '''
|
||||
>>> argv = ['tcp', '127.0.0.1', '80', '--timeout', '30']
|
||||
>>> docopt(doc, argv)
|
||||
{'--baud': '9600',
|
||||
'--help': False,
|
||||
'--timeout': '30',
|
||||
'--version': False,
|
||||
'<host>': '127.0.0.1',
|
||||
'<port>': '80',
|
||||
'serial': False,
|
||||
'tcp': True}
|
||||
|
||||
See also
|
||||
--------
|
||||
* For video introduction see http://docopt.org
|
||||
* Full documentation is available in README.rst as well as online
|
||||
at https://github.com/docopt/docopt#readme
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
argv = sys.argv[1:] if argv is None else argv
|
||||
|
||||
usage_sections = parse_section('usage:', doc)
|
||||
if len(usage_sections) == 0:
|
||||
raise DocoptLanguageError('"usage:" (case-insensitive) not found.')
|
||||
if len(usage_sections) > 1:
|
||||
raise DocoptLanguageError('More than one "usage:" (case-insensitive).')
|
||||
DocoptExit.usage = usage_sections[0]
|
||||
|
||||
options = parse_defaults(doc)
|
||||
pattern = parse_pattern(formal_usage(DocoptExit.usage), options)
|
||||
# [default] syntax for argument is disabled
|
||||
#for a in pattern.flat(Argument):
|
||||
# same_name = [d for d in arguments if d.name == a.name]
|
||||
# if same_name:
|
||||
# a.value = same_name[0].value
|
||||
argv = parse_argv(Tokens(argv), list(options), options_first)
|
||||
pattern_options = set(pattern.flat(Option))
|
||||
for options_shortcut in pattern.flat(OptionsShortcut):
|
||||
doc_options = parse_defaults(doc)
|
||||
options_shortcut.children = list(set(doc_options) - pattern_options)
|
||||
#if any_options:
|
||||
# options_shortcut.children += [Option(o.short, o.long, o.argcount)
|
||||
# for o in argv if type(o) is Option]
|
||||
extras(help, version, argv, doc)
|
||||
matched, left, collected = pattern.fix().match(argv)
|
||||
if matched and left == []: # better error message if left?
|
||||
return Dict((a.name, a.value) for a in (pattern.flat() + collected))
|
||||
raise DocoptExit()
|
||||
76
extlib/libfmt/support/mkdocs
vendored
Executable file
76
extlib/libfmt/support/mkdocs
vendored
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
||||
# A script to invoke mkdocs with the correct environment.
|
||||
# Additionally supports deploying via mike:
|
||||
# ./mkdocs deploy [mike-deploy-options]
|
||||
|
||||
import errno, os, shutil, sys
|
||||
from subprocess import call
|
||||
|
||||
support_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.normpath(__file__))
|
||||
build_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(support_dir), 'build')
|
||||
|
||||
# Set PYTHONPATH for the mkdocstrings handler.
|
||||
env = os.environ.copy()
|
||||
path = env.get('PYTHONPATH')
|
||||
env['PYTHONPATH'] = \
|
||||
(path + ':' if path else '') + os.path.join(support_dir, 'python')
|
||||
|
||||
redirect_page = \
|
||||
'''<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html>
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8">
|
||||
<title>Redirecting</title>
|
||||
<noscript>
|
||||
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="1; url=11.0/" />
|
||||
</noscript>
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
window.location.replace(
|
||||
"api/" + window.location.search + window.location.hash
|
||||
);
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
Redirecting to <a href="api/">api</a>...
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
'''
|
||||
|
||||
config_path = os.path.join(support_dir, 'mkdocs.yml')
|
||||
args = sys.argv[1:]
|
||||
if len(args) > 0:
|
||||
command = args[0]
|
||||
if command == 'deploy':
|
||||
git_url = 'https://github.com/' if 'CI' in os.environ else 'git@github.com:'
|
||||
site_repo = git_url + 'fmtlib/fmt.dev.git'
|
||||
|
||||
site_dir = os.path.join(build_dir, 'fmt.dev')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
shutil.rmtree(site_dir)
|
||||
except OSError as e:
|
||||
if e.errno == errno.ENOENT:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
ret = call(['git', 'clone', '--depth=1', site_repo, site_dir])
|
||||
if ret != 0:
|
||||
sys.exit(ret)
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy the config to the build dir because the site is built relative to it.
|
||||
config_build_path = os.path.join(build_dir, 'mkdocs.yml')
|
||||
shutil.copyfile(config_path, config_build_path)
|
||||
|
||||
version = args[1]
|
||||
ret = call(['mike'] + args + ['--config-file', config_build_path,
|
||||
'--branch', 'master'], cwd=site_dir, env=env)
|
||||
if ret != 0 or version == 'dev':
|
||||
sys.exit(ret)
|
||||
redirect_page_path = os.path.join(site_dir, version, 'api.html')
|
||||
with open(redirect_page_path, "w") as file:
|
||||
file.write(redirect_page)
|
||||
ret = call(['git', 'add', redirect_page_path], cwd=site_dir)
|
||||
if ret != 0:
|
||||
sys.exit(ret)
|
||||
ret = call(['git', 'commit', '--amend', '--no-edit'], cwd=site_dir)
|
||||
sys.exit(ret)
|
||||
elif not command.startswith('-'):
|
||||
args += ['-f', config_path]
|
||||
sys.exit(call(['mkdocs'] + args, env=env))
|
||||
48
extlib/libfmt/support/mkdocs.yml
vendored
Normal file
48
extlib/libfmt/support/mkdocs.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
site_name: '{fmt}'
|
||||
|
||||
docs_dir: ../doc
|
||||
|
||||
repo_url: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt
|
||||
|
||||
theme:
|
||||
name: material
|
||||
features:
|
||||
- navigation.tabs
|
||||
- navigation.top
|
||||
- toc.integrate
|
||||
|
||||
extra_javascript:
|
||||
- https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/highlight.js/10.7.2/highlight.min.js
|
||||
- fmt.js
|
||||
|
||||
extra_css:
|
||||
- https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/highlight.js/10.7.2/styles/default.min.css
|
||||
- fmt.css
|
||||
|
||||
markdown_extensions:
|
||||
- pymdownx.highlight:
|
||||
# Use JavaScript syntax highlighter instead of Pygments because it
|
||||
# automatically applies to code blocks extracted through Doxygen.
|
||||
use_pygments: false
|
||||
anchor_linenums: true
|
||||
line_spans: __span
|
||||
pygments_lang_class: true
|
||||
- pymdownx.inlinehilite
|
||||
- pymdownx.snippets
|
||||
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- search
|
||||
- mkdocstrings:
|
||||
default_handler: cxx
|
||||
nav:
|
||||
- Home: index.md
|
||||
- Get Started: get-started.md
|
||||
- API: api.md
|
||||
- Syntax: syntax.md
|
||||
|
||||
exclude_docs: ChangeLog-old.md
|
||||
|
||||
extra:
|
||||
version:
|
||||
provider: mike
|
||||
generator: false
|
||||
201
extlib/libfmt/support/printable.py
vendored
Executable file
201
extlib/libfmt/support/printable.py
vendored
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
||||
|
||||
# This script is based on
|
||||
# https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/master/library/core/src/unicode/printable.py
|
||||
# distributed under https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/master/LICENSE-MIT.
|
||||
|
||||
# This script uses the following Unicode tables:
|
||||
# - UnicodeData.txt
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from collections import namedtuple
|
||||
import csv
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
|
||||
NUM_CODEPOINTS=0x110000
|
||||
|
||||
def to_ranges(iter):
|
||||
current = None
|
||||
for i in iter:
|
||||
if current is None or i != current[1] or i in (0x10000, 0x20000):
|
||||
if current is not None:
|
||||
yield tuple(current)
|
||||
current = [i, i + 1]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
current[1] += 1
|
||||
if current is not None:
|
||||
yield tuple(current)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_escaped(codepoints):
|
||||
for c in codepoints:
|
||||
if (c.class_ or "Cn") in "Cc Cf Cs Co Cn Zl Zp Zs".split() and c.value != ord(' '):
|
||||
yield c.value
|
||||
|
||||
def get_file(f):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return open(os.path.basename(f))
|
||||
except FileNotFoundError:
|
||||
subprocess.run(["curl", "-O", f], check=True)
|
||||
return open(os.path.basename(f))
|
||||
|
||||
Codepoint = namedtuple('Codepoint', 'value class_')
|
||||
|
||||
def get_codepoints(f):
|
||||
r = csv.reader(f, delimiter=";")
|
||||
prev_codepoint = 0
|
||||
class_first = None
|
||||
for row in r:
|
||||
codepoint = int(row[0], 16)
|
||||
name = row[1]
|
||||
class_ = row[2]
|
||||
|
||||
if class_first is not None:
|
||||
if not name.endswith("Last>"):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Missing Last after First")
|
||||
|
||||
for c in range(prev_codepoint + 1, codepoint):
|
||||
yield Codepoint(c, class_first)
|
||||
|
||||
class_first = None
|
||||
if name.endswith("First>"):
|
||||
class_first = class_
|
||||
|
||||
yield Codepoint(codepoint, class_)
|
||||
prev_codepoint = codepoint
|
||||
|
||||
if class_first is not None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Missing Last after First")
|
||||
|
||||
for c in range(prev_codepoint + 1, NUM_CODEPOINTS):
|
||||
yield Codepoint(c, None)
|
||||
|
||||
def compress_singletons(singletons):
|
||||
uppers = [] # (upper, # items in lowers)
|
||||
lowers = []
|
||||
|
||||
for i in singletons:
|
||||
upper = i >> 8
|
||||
lower = i & 0xff
|
||||
if len(uppers) == 0 or uppers[-1][0] != upper:
|
||||
uppers.append((upper, 1))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
upper, count = uppers[-1]
|
||||
uppers[-1] = upper, count + 1
|
||||
lowers.append(lower)
|
||||
|
||||
return uppers, lowers
|
||||
|
||||
def compress_normal(normal):
|
||||
# lengths 0x00..0x7f are encoded as 00, 01, ..., 7e, 7f
|
||||
# lengths 0x80..0x7fff are encoded as 80 80, 80 81, ..., ff fe, ff ff
|
||||
compressed = [] # [truelen, (truelenaux), falselen, (falselenaux)]
|
||||
|
||||
prev_start = 0
|
||||
for start, count in normal:
|
||||
truelen = start - prev_start
|
||||
falselen = count
|
||||
prev_start = start + count
|
||||
|
||||
assert truelen < 0x8000 and falselen < 0x8000
|
||||
entry = []
|
||||
if truelen > 0x7f:
|
||||
entry.append(0x80 | (truelen >> 8))
|
||||
entry.append(truelen & 0xff)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
entry.append(truelen & 0x7f)
|
||||
if falselen > 0x7f:
|
||||
entry.append(0x80 | (falselen >> 8))
|
||||
entry.append(falselen & 0xff)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
entry.append(falselen & 0x7f)
|
||||
|
||||
compressed.append(entry)
|
||||
|
||||
return compressed
|
||||
|
||||
def print_singletons(uppers, lowers, uppersname, lowersname):
|
||||
print(" static constexpr singleton {}[] = {{".format(uppersname))
|
||||
for u, c in uppers:
|
||||
print(" {{{:#04x}, {}}},".format(u, c))
|
||||
print(" };")
|
||||
print(" static constexpr unsigned char {}[] = {{".format(lowersname))
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(lowers), 8):
|
||||
print(" {}".format(" ".join("{:#04x},".format(l) for l in lowers[i:i+8])))
|
||||
print(" };")
|
||||
|
||||
def print_normal(normal, normalname):
|
||||
print(" static constexpr unsigned char {}[] = {{".format(normalname))
|
||||
for v in normal:
|
||||
print(" {}".format(" ".join("{:#04x},".format(i) for i in v)))
|
||||
print(" };")
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
file = get_file("https://www.unicode.org/Public/UNIDATA/UnicodeData.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
codepoints = get_codepoints(file)
|
||||
|
||||
CUTOFF=0x10000
|
||||
singletons0 = []
|
||||
singletons1 = []
|
||||
normal0 = []
|
||||
normal1 = []
|
||||
extra = []
|
||||
|
||||
for a, b in to_ranges(get_escaped(codepoints)):
|
||||
if a > 2 * CUTOFF:
|
||||
extra.append((a, b - a))
|
||||
elif a == b - 1:
|
||||
if a & CUTOFF:
|
||||
singletons1.append(a & ~CUTOFF)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
singletons0.append(a)
|
||||
elif a == b - 2:
|
||||
if a & CUTOFF:
|
||||
singletons1.append(a & ~CUTOFF)
|
||||
singletons1.append((a + 1) & ~CUTOFF)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
singletons0.append(a)
|
||||
singletons0.append(a + 1)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if a >= 2 * CUTOFF:
|
||||
extra.append((a, b - a))
|
||||
elif a & CUTOFF:
|
||||
normal1.append((a & ~CUTOFF, b - a))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
normal0.append((a, b - a))
|
||||
|
||||
singletons0u, singletons0l = compress_singletons(singletons0)
|
||||
singletons1u, singletons1l = compress_singletons(singletons1)
|
||||
normal0 = compress_normal(normal0)
|
||||
normal1 = compress_normal(normal1)
|
||||
|
||||
print("""\
|
||||
FMT_FUNC auto is_printable(uint32_t cp) -> bool {\
|
||||
""")
|
||||
print_singletons(singletons0u, singletons0l, 'singletons0', 'singletons0_lower')
|
||||
print_singletons(singletons1u, singletons1l, 'singletons1', 'singletons1_lower')
|
||||
print_normal(normal0, 'normal0')
|
||||
print_normal(normal1, 'normal1')
|
||||
print("""\
|
||||
auto lower = static_cast<uint16_t>(cp);
|
||||
if (cp < 0x10000) {
|
||||
return is_printable(lower, singletons0,
|
||||
sizeof(singletons0) / sizeof(*singletons0),
|
||||
singletons0_lower, normal0, sizeof(normal0));
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (cp < 0x20000) {
|
||||
return is_printable(lower, singletons1,
|
||||
sizeof(singletons1) / sizeof(*singletons1),
|
||||
singletons1_lower, normal1, sizeof(normal1));
|
||||
}\
|
||||
""")
|
||||
for a, b in extra:
|
||||
print(" if (0x{:x} <= cp && cp < 0x{:x}) return false;".format(a, a + b))
|
||||
print("""\
|
||||
return cp < 0x{:x};
|
||||
}}\
|
||||
""".format(NUM_CODEPOINTS))
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main()
|
||||
338
extlib/libfmt/support/python/mkdocstrings_handlers/cxx/__init__.py
vendored
Normal file
338
extlib/libfmt/support/python/mkdocstrings_handlers/cxx/__init__.py
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,338 @@
|
||||
# A basic mkdocstrings handler for {fmt}.
|
||||
# Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
# https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ElementTree
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from subprocess import PIPE, STDOUT, CalledProcessError, Popen
|
||||
from typing import Any, List, Mapping, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from mkdocstrings.handlers.base import BaseHandler
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Definition:
|
||||
"""A definition extracted by Doxygen."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, name: str, kind: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
node: Optional[ElementTree.Element] = None,
|
||||
is_member: bool = False):
|
||||
self.name = name
|
||||
self.kind = kind if kind is not None else node.get('kind')
|
||||
self.desc = None
|
||||
self.id = name if not is_member else None
|
||||
self.members = None
|
||||
self.params = None
|
||||
self.template_params = None
|
||||
self.trailing_return_type = None
|
||||
self.type = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# A map from Doxygen to HTML tags.
|
||||
tag_map = {
|
||||
'bold': 'b',
|
||||
'emphasis': 'em',
|
||||
'computeroutput': 'code',
|
||||
'para': 'p',
|
||||
'programlisting': 'pre',
|
||||
'verbatim': 'pre'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# A map from Doxygen tags to text.
|
||||
tag_text_map = {
|
||||
'codeline': '',
|
||||
'highlight': '',
|
||||
'sp': ' '
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def escape_html(s: str) -> str:
|
||||
return s.replace("<", "<")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def doxyxml2html(nodes: List[ElementTree.Element]):
|
||||
out = ''
|
||||
for n in nodes:
|
||||
tag = tag_map.get(n.tag)
|
||||
if not tag:
|
||||
out += tag_text_map[n.tag]
|
||||
out += '<' + tag + '>' if tag else ''
|
||||
out += '<code class="language-cpp">' if tag == 'pre' else ''
|
||||
if n.text:
|
||||
out += escape_html(n.text)
|
||||
out += doxyxml2html(list(n))
|
||||
out += '</code>' if tag == 'pre' else ''
|
||||
out += '</' + tag + '>' if tag else ''
|
||||
if n.tail:
|
||||
out += n.tail
|
||||
return out
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def convert_template_params(node: ElementTree.Element) -> Optional[List[Definition]]:
|
||||
template_param_list = node.find('templateparamlist')
|
||||
if template_param_list is None:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
params = []
|
||||
for param_node in template_param_list.findall('param'):
|
||||
name = param_node.find('declname')
|
||||
param = Definition(name.text if name is not None else '', 'param')
|
||||
param.type = param_node.find('type').text
|
||||
params.append(param)
|
||||
return params
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_description(node: ElementTree.Element) -> List[ElementTree.Element]:
|
||||
return node.findall('briefdescription/para') + \
|
||||
node.findall('detaileddescription/para')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def normalize_type(type_: str) -> str:
|
||||
type_ = type_.replace('< ', '<').replace(' >', '>')
|
||||
return type_.replace(' &', '&').replace(' *', '*')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def convert_type(type_: ElementTree.Element) -> Optional[str]:
|
||||
if type_ is None:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
result = type_.text if type_.text else ''
|
||||
for ref in type_:
|
||||
result += ref.text
|
||||
if ref.tail:
|
||||
result += ref.tail
|
||||
result += type_.tail.strip()
|
||||
return normalize_type(result)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def convert_params(func: ElementTree.Element) -> List[Definition]:
|
||||
params = []
|
||||
for p in func.findall('param'):
|
||||
d = Definition(p.find('declname').text, 'param')
|
||||
d.type = convert_type(p.find('type'))
|
||||
params.append(d)
|
||||
return params
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def convert_return_type(d: Definition, node: ElementTree.Element) -> None:
|
||||
d.trailing_return_type = None
|
||||
if d.type == 'auto' or d.type == 'constexpr auto':
|
||||
parts = node.find('argsstring').text.split(' -> ')
|
||||
if len(parts) > 1:
|
||||
d.trailing_return_type = normalize_type(parts[1])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def render_param(param: Definition) -> str:
|
||||
return param.type + (f' {param.name}' if len(param.name) > 0 else '')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def render_decl(d: Definition) -> str:
|
||||
text = ''
|
||||
if d.id is not None:
|
||||
text += f'<a id="{d.id}">\n'
|
||||
text += '<pre><code class="language-cpp decl">'
|
||||
|
||||
text += '<div>'
|
||||
if d.template_params is not None:
|
||||
text += 'template <'
|
||||
text += ', '.join([render_param(p) for p in d.template_params])
|
||||
text += '>\n'
|
||||
text += '</div>'
|
||||
|
||||
text += '<div>'
|
||||
end = ';'
|
||||
if d.kind == 'function' or d.kind == 'variable':
|
||||
text += d.type + ' ' if len(d.type) > 0 else ''
|
||||
elif d.kind == 'typedef':
|
||||
text += 'using '
|
||||
elif d.kind == 'define':
|
||||
end = ''
|
||||
else:
|
||||
text += d.kind + ' '
|
||||
text += d.name
|
||||
|
||||
if d.params is not None:
|
||||
params = ', '.join([
|
||||
(p.type + ' ' if p.type else '') + p.name for p in d.params])
|
||||
text += '(' + escape_html(params) + ')'
|
||||
if d.trailing_return_type:
|
||||
text += ' -⁠> ' + escape_html(d.trailing_return_type)
|
||||
elif d.kind == 'typedef':
|
||||
text += ' = ' + escape_html(d.type)
|
||||
|
||||
text += end
|
||||
text += '</div>'
|
||||
text += '</code></pre>\n'
|
||||
if d.id is not None:
|
||||
text += f'</a>\n'
|
||||
return text
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CxxHandler(BaseHandler):
|
||||
def __init__(self, **kwargs: Any) -> None:
|
||||
super().__init__(handler='cxx', **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
headers = [
|
||||
'args.h', 'base.h', 'chrono.h', 'color.h', 'compile.h', 'format.h',
|
||||
'os.h', 'ostream.h', 'printf.h', 'ranges.h', 'std.h', 'xchar.h'
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# Run doxygen.
|
||||
cmd = ['doxygen', '-']
|
||||
support_dir = Path(__file__).parents[3]
|
||||
top_dir = os.path.dirname(support_dir)
|
||||
include_dir = os.path.join(top_dir, 'include', 'fmt')
|
||||
self._ns2doxyxml = {}
|
||||
build_dir = os.path.join(top_dir, 'build')
|
||||
os.makedirs(build_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
self._doxyxml_dir = os.path.join(build_dir, 'doxyxml')
|
||||
p = Popen(cmd, stdin=PIPE, stdout=PIPE, stderr=STDOUT)
|
||||
_, _ = p.communicate(input=r'''
|
||||
PROJECT_NAME = fmt
|
||||
GENERATE_XML = YES
|
||||
GENERATE_LATEX = NO
|
||||
GENERATE_HTML = NO
|
||||
INPUT = {0}
|
||||
XML_OUTPUT = {1}
|
||||
QUIET = YES
|
||||
AUTOLINK_SUPPORT = NO
|
||||
MACRO_EXPANSION = YES
|
||||
PREDEFINED = _WIN32=1 \
|
||||
__linux__=1 \
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(...)= \
|
||||
FMT_USE_USER_LITERALS=1 \
|
||||
FMT_USE_ALIAS_TEMPLATES=1 \
|
||||
FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS=1 \
|
||||
FMT_API= \
|
||||
"FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE=namespace fmt {{" \
|
||||
"FMT_END_NAMESPACE=}}" \
|
||||
"FMT_DOC=1"
|
||||
'''.format(
|
||||
' '.join([os.path.join(include_dir, h) for h in headers]),
|
||||
self._doxyxml_dir).encode('utf-8'))
|
||||
if p.returncode != 0:
|
||||
raise CalledProcessError(p.returncode, cmd)
|
||||
|
||||
# Merge all file-level XMLs into one to simplify search.
|
||||
self._file_doxyxml = None
|
||||
for h in headers:
|
||||
filename = h.replace(".h", "_8h.xml")
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(self._doxyxml_dir, filename)) as f:
|
||||
doxyxml = ElementTree.parse(f)
|
||||
if self._file_doxyxml is None:
|
||||
self._file_doxyxml = doxyxml
|
||||
continue
|
||||
root = self._file_doxyxml.getroot()
|
||||
for node in doxyxml.getroot():
|
||||
root.append(node)
|
||||
|
||||
def collect_compound(self, identifier: str,
|
||||
cls: List[ElementTree.Element]) -> Definition:
|
||||
"""Collect a compound definition such as a struct."""
|
||||
path = os.path.join(self._doxyxml_dir, cls[0].get('refid') + '.xml')
|
||||
with open(path) as f:
|
||||
xml = ElementTree.parse(f)
|
||||
node = xml.find('compounddef')
|
||||
d = Definition(identifier, node=node)
|
||||
d.template_params = convert_template_params(node)
|
||||
d.desc = get_description(node)
|
||||
d.members = []
|
||||
for m in \
|
||||
node.findall('sectiondef[@kind="public-attrib"]/memberdef') + \
|
||||
node.findall('sectiondef[@kind="public-func"]/memberdef'):
|
||||
name = m.find('name').text
|
||||
# Doxygen incorrectly classifies members of private unnamed unions as
|
||||
# public members of the containing class.
|
||||
if name.endswith('_'):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
desc = get_description(m)
|
||||
if len(desc) == 0:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
kind = m.get('kind')
|
||||
member = Definition(name if name else '', kind=kind, is_member=True)
|
||||
type_text = m.find('type').text
|
||||
member.type = type_text if type_text else ''
|
||||
if kind == 'function':
|
||||
member.params = convert_params(m)
|
||||
convert_return_type(member, m)
|
||||
member.template_params = None
|
||||
member.desc = desc
|
||||
d.members.append(member)
|
||||
return d
|
||||
|
||||
def collect(self, identifier: str, _config: Mapping[str, Any]) -> Definition:
|
||||
qual_name = 'fmt::' + identifier
|
||||
|
||||
param_str = None
|
||||
paren = qual_name.find('(')
|
||||
if paren > 0:
|
||||
qual_name, param_str = qual_name[:paren], qual_name[paren + 1:-1]
|
||||
|
||||
colons = qual_name.rfind('::')
|
||||
namespace, name = qual_name[:colons], qual_name[colons + 2:]
|
||||
|
||||
# Load XML.
|
||||
doxyxml = self._ns2doxyxml.get(namespace)
|
||||
if doxyxml is None:
|
||||
path = f'namespace{namespace.replace("::", "_1_1")}.xml'
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(self._doxyxml_dir, path)) as f:
|
||||
doxyxml = ElementTree.parse(f)
|
||||
self._ns2doxyxml[namespace] = doxyxml
|
||||
|
||||
nodes = doxyxml.findall(
|
||||
f"compounddef/sectiondef/memberdef/name[.='{name}']/..")
|
||||
if len(nodes) == 0:
|
||||
nodes = self._file_doxyxml.findall(
|
||||
f"compounddef/sectiondef/memberdef/name[.='{name}']/..")
|
||||
candidates = []
|
||||
for node in nodes:
|
||||
# Process a function or a typedef.
|
||||
params = None
|
||||
d = Definition(name, node=node)
|
||||
if d.kind == 'function':
|
||||
params = convert_params(node)
|
||||
node_param_str = ', '.join([p.type for p in params])
|
||||
if param_str and param_str != node_param_str:
|
||||
candidates.append(f'{name}({node_param_str})')
|
||||
continue
|
||||
elif d.kind == 'define':
|
||||
params = []
|
||||
for p in node.findall('param'):
|
||||
param = Definition(p.find('defname').text, kind='param')
|
||||
param.type = None
|
||||
params.append(param)
|
||||
d.type = convert_type(node.find('type'))
|
||||
d.template_params = convert_template_params(node)
|
||||
d.params = params
|
||||
convert_return_type(d, node)
|
||||
d.desc = get_description(node)
|
||||
return d
|
||||
|
||||
cls = doxyxml.findall(f"compounddef/innerclass[.='{qual_name}']")
|
||||
if not cls:
|
||||
raise Exception(f'Cannot find {identifier}. Candidates: {candidates}')
|
||||
return self.collect_compound(identifier, cls)
|
||||
|
||||
def render(self, d: Definition, config: dict) -> str:
|
||||
if d.id is not None:
|
||||
self.do_heading('', 0, id=d.id)
|
||||
text = '<div class="docblock">\n'
|
||||
text += render_decl(d)
|
||||
text += '<div class="docblock-desc">\n'
|
||||
text += doxyxml2html(d.desc)
|
||||
if d.members is not None:
|
||||
for m in d.members:
|
||||
text += self.render(m, config)
|
||||
text += '</div>\n'
|
||||
text += '</div>\n'
|
||||
return text
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_handler(theme: str, custom_templates: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
**_config: Any) -> CxxHandler:
|
||||
"""Return an instance of `CxxHandler`.
|
||||
|
||||
Arguments:
|
||||
theme: The theme to use when rendering contents.
|
||||
custom_templates: Directory containing custom templates.
|
||||
**_config: Configuration passed to the handler.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return CxxHandler(theme=theme, custom_templates=custom_templates)
|
||||
1
extlib/libfmt/support/python/mkdocstrings_handlers/cxx/templates/README
vendored
Normal file
1
extlib/libfmt/support/python/mkdocstrings_handlers/cxx/templates/README
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
mkdocsstrings requires a handler to have a templates directory.
|
||||
188
extlib/libfmt/support/release.py
vendored
Executable file
188
extlib/libfmt/support/release.py
vendored
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
||||
|
||||
"""Make a release.
|
||||
|
||||
Usage:
|
||||
release.py [<branch>]
|
||||
|
||||
For the release command $FMT_TOKEN should contain a GitHub personal access token
|
||||
obtained from https://github.com/settings/tokens.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import datetime, docopt, errno, fileinput, json, os
|
||||
import re, shutil, sys
|
||||
from subprocess import check_call
|
||||
import urllib.request
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Git:
|
||||
def __init__(self, dir):
|
||||
self.dir = dir
|
||||
|
||||
def call(self, method, args, **kwargs):
|
||||
return check_call(['git', method] + list(args), **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def add(self, *args):
|
||||
return self.call('add', args, cwd=self.dir)
|
||||
|
||||
def checkout(self, *args):
|
||||
return self.call('checkout', args, cwd=self.dir)
|
||||
|
||||
def clean(self, *args):
|
||||
return self.call('clean', args, cwd=self.dir)
|
||||
|
||||
def clone(self, *args):
|
||||
return self.call('clone', list(args) + [self.dir])
|
||||
|
||||
def commit(self, *args):
|
||||
return self.call('commit', args, cwd=self.dir)
|
||||
|
||||
def pull(self, *args):
|
||||
return self.call('pull', args, cwd=self.dir)
|
||||
|
||||
def push(self, *args):
|
||||
return self.call('push', args, cwd=self.dir)
|
||||
|
||||
def reset(self, *args):
|
||||
return self.call('reset', args, cwd=self.dir)
|
||||
|
||||
def update(self, *args):
|
||||
clone = not os.path.exists(self.dir)
|
||||
if clone:
|
||||
self.clone(*args)
|
||||
return clone
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def clean_checkout(repo, branch):
|
||||
repo.clean('-f', '-d')
|
||||
repo.reset('--hard')
|
||||
repo.checkout(branch)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Runner:
|
||||
def __init__(self, cwd):
|
||||
self.cwd = cwd
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
kwargs['cwd'] = kwargs.get('cwd', self.cwd)
|
||||
check_call(args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_build_env():
|
||||
"""Create a build environment."""
|
||||
class Env:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
env = Env()
|
||||
env.fmt_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
|
||||
env.build_dir = 'build'
|
||||
env.fmt_repo = Git(os.path.join(env.build_dir, 'fmt'))
|
||||
return env
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
args = docopt.docopt(__doc__)
|
||||
env = create_build_env()
|
||||
fmt_repo = env.fmt_repo
|
||||
|
||||
branch = args.get('<branch>')
|
||||
if branch is None:
|
||||
branch = 'master'
|
||||
if not fmt_repo.update('-b', branch, 'git@github.com:fmtlib/fmt'):
|
||||
clean_checkout(fmt_repo, branch)
|
||||
|
||||
# Update the date in the changelog and extract the version and the first
|
||||
# section content.
|
||||
changelog = 'ChangeLog.md'
|
||||
changelog_path = os.path.join(fmt_repo.dir, changelog)
|
||||
is_first_section = True
|
||||
first_section = []
|
||||
for i, line in enumerate(fileinput.input(changelog_path, inplace=True)):
|
||||
if i == 0:
|
||||
version = re.match(r'# (.*) - TBD', line).group(1)
|
||||
line = '# {} - {}\n'.format(
|
||||
version, datetime.date.today().isoformat())
|
||||
elif not is_first_section:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
elif line.startswith('#'):
|
||||
is_first_section = False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
first_section.append(line)
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(line)
|
||||
if first_section[0] == '\n':
|
||||
first_section.pop(0)
|
||||
|
||||
ns_version = None
|
||||
base_h_path = os.path.join(fmt_repo.dir, 'include', 'fmt', 'base.h')
|
||||
for line in fileinput.input(base_h_path):
|
||||
m = re.match(r'\s*inline namespace v(.*) .*', line)
|
||||
if m:
|
||||
ns_version = m.group(1)
|
||||
break
|
||||
major_version = version.split('.')[0]
|
||||
if not ns_version or ns_version != major_version:
|
||||
raise Exception(f'Version mismatch {ns_version} != {major_version}')
|
||||
|
||||
# Workaround GitHub-flavored Markdown treating newlines as <br>.
|
||||
changes = ''
|
||||
code_block = False
|
||||
stripped = False
|
||||
for line in first_section:
|
||||
if re.match(r'^\s*```', line):
|
||||
code_block = not code_block
|
||||
changes += line
|
||||
stripped = False
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if code_block:
|
||||
changes += line
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if line == '\n' or re.match(r'^\s*\|.*', line):
|
||||
if stripped:
|
||||
changes += '\n'
|
||||
stripped = False
|
||||
changes += line
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if stripped:
|
||||
line = ' ' + line.lstrip()
|
||||
changes += line.rstrip()
|
||||
stripped = True
|
||||
|
||||
fmt_repo.checkout('-B', 'release')
|
||||
fmt_repo.add(changelog)
|
||||
fmt_repo.commit('-m', 'Update version')
|
||||
|
||||
# Build the docs and package.
|
||||
run = Runner(fmt_repo.dir)
|
||||
run('cmake', '.')
|
||||
run('make', 'doc', 'package_source')
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a release on GitHub.
|
||||
fmt_repo.push('origin', 'release')
|
||||
auth_headers = {'Authorization': 'token ' + os.getenv('FMT_TOKEN')}
|
||||
req = urllib.request.Request(
|
||||
'https://api.github.com/repos/fmtlib/fmt/releases',
|
||||
data=json.dumps({'tag_name': version,
|
||||
'target_commitish': 'release',
|
||||
'body': changes, 'draft': True}).encode('utf-8'),
|
||||
headers=auth_headers, method='POST')
|
||||
with urllib.request.urlopen(req) as response:
|
||||
if response.status != 201:
|
||||
raise Exception(f'Failed to create a release ' +
|
||||
'{response.status} {response.reason}')
|
||||
response_data = json.loads(response.read().decode('utf-8'))
|
||||
id = response_data['id']
|
||||
|
||||
# Upload the package.
|
||||
uploads_url = 'https://uploads.github.com/repos/fmtlib/fmt/releases'
|
||||
package = 'fmt-{}.zip'.format(version)
|
||||
req = urllib.request.Request(
|
||||
f'{uploads_url}/{id}/assets?name={package}',
|
||||
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/zip'} | auth_headers,
|
||||
data=open('build/fmt/' + package, 'rb').read(), method='POST')
|
||||
with urllib.request.urlopen(req) as response:
|
||||
if response.status != 201:
|
||||
raise Exception(f'Failed to upload an asset '
|
||||
'{response.status} {response.reason}')
|
||||
|
||||
short_version = '.'.join(version.split('.')[:-1])
|
||||
check_call(['./mkdocs', 'deploy', short_version])
|
||||
@ -37,6 +37,9 @@ using std::vector;
|
||||
|
||||
// libfmt
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
# include <fmt/xchar.h>
|
||||
#endif /* !_WIN32 */
|
||||
#define FSTR FMT_STRING
|
||||
|
||||
// tchar
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
// libfmt
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
# include <fmt/xchar.h>
|
||||
#endif /* !_WIN32 */
|
||||
#define FSTR FMT_STRING
|
||||
|
||||
#else /* !__cplusplus */
|
||||
|
||||
@ -44,6 +44,9 @@ using std::string;
|
||||
|
||||
// libfmt
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
# include <fmt/xchar.h>
|
||||
#endif /* !_WIN32 */
|
||||
#define FSTR FMT_STRING
|
||||
|
||||
// Uninitialized vector class
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user